Abstract
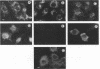
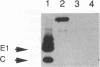
Vaux et al. (D. J. T. Vaux, A. Helenius, and I. Mellman, Nature (London) 336:36-42, 1988) recently reported the production of network antibodies that were suggested to have reconstructed a specific interaction between the nucleocapsid of Semliki Forest virus and the cytoplasmic tail of the viral E2 spike protein. The F13 anti-idiotype antibody, which was raised against anti-E2 tail antibodies, was claimed to recognize the virus nucleocapsid. In this report, we have used recombinant SFV viruses to demonstrate that the F13 antibody is not nucleocapsid specific but instead most likely recognizes some component of the viral replication machinery.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton D. J., Sawicki S. G., Sawicki D. L. Solubilization and immunoprecipitation of alphavirus replication complexes. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1496–1506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1496-1506.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Alphavirus RNA replicase is located on the cytoplasmic surface of endosomes and lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2075–2086. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Frischauf A. M., Simons K., Lehrach H., Delius H. Nucleotide sequence of cdna coding for Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):236–241. doi: 10.1038/288236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiser-Wilke I., Moenning V., Kaaden O. R., Figueiredo L. T. Most alphaviruses share a conserved epitopic region on their nucleocapsid protein. J Gen Virol. 1989 Mar;70(Pt 3):743–748. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-3-743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondor-Koch C., Burke B., Garoff H. Expression of Semliki Forest virus proteins from cloned complementary DNA. I. The fusion activity of the spike glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):644–651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Garoff H. A new generation of animal cell expression vectors based on the Semliki Forest virus replicon. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Dec;9(12):1356–1361. doi: 10.1038/nbt1291-1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Lusa S., Huylebroeck D., Garoff H. In vitro mutagenesis of a full-length cDNA clone of Semliki Forest virus: the small 6,000-molecular-weight membrane protein modulates virus release. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4107–4113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4107-4113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peränen J., Käriäinen L. Biogenesis of type I cytopathic vacuoles in Semliki Forest virus-infected BHK cells. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1623–1627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1623-1627.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peränen J., Takkinen K., Kalkkinen N., Käriäinen L. Semliki Forest virus-specific non-structural protein nsP3 is a phosphoprotein. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2165–2178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Garoff H. The budding mechanisms of enveloped animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G. Mutants of Sindbis virus. III. Host polypeptides present in purified HR and ts103 virus particles. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):466–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.466-474.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M., Garoff H., Baron M. D. The E2 signal sequence of rubella virus remains part of the capsid protein and confers membrane association in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5500–5509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5500-5509.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Spike protein-nucleocapsid interactions drive the budding of alphaviruses. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4737–4747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4737-4747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. J., Helenius A., Mellman I. Spike--nucleocapsid interaction in Semliki Forest virus reconstructed using network antibodies. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):36–42. doi: 10.1038/336036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg J. M., Boere W. A., Garoff H. The heterodimeric association between the membrane proteins of Semliki Forest virus changes its sensitivity to low pH during virus maturation. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):4991–4997. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.4991-4997.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]