Abstract
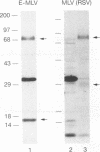
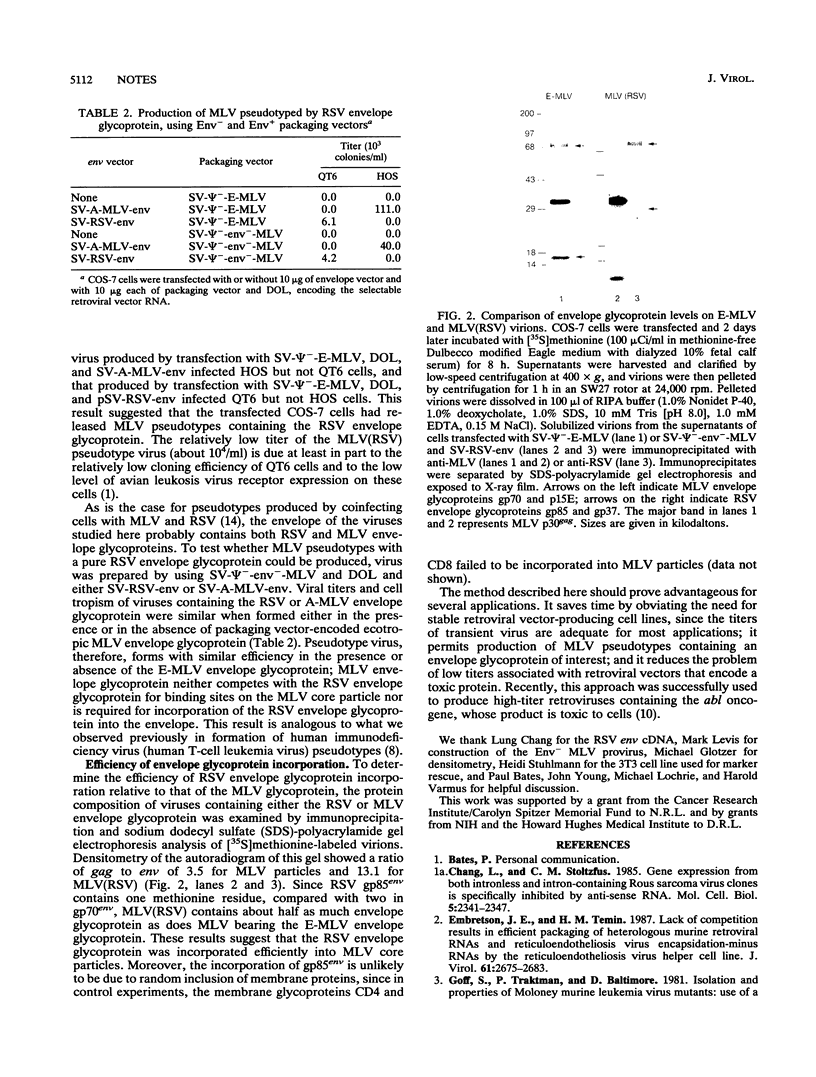
A method for rapidly producing helper-free murine leukemia virus (MLV) without using packaging cell lines is described. Viruses bearing ecotropic or amphotropic MLV or Rous sarcoma virus envelope glycoprotein and containing various retroviral vector genomes have been prepared with titers 30 to 40-fold higher than those produced by transient transfection of standard packaging cells. This system can be used to alter the cellular tropism of MLV by incorporating other envelope glycoproteins and to prepare retroviral vector stocks without establishing stable producer cell lines. This method will be particularly useful for preparing viruses that encode toxic proteins and for the rapid analysis of panels of mutant envelope glycoproteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang L. J., Stoltzfus C. M. Gene expression from both intronless and intron-containing Rous sarcoma virus clones is specifically inhibited by anti-sense RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2341–2348. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embretson J. E., Temin H. M. Lack of competition results in efficient packaging of heterologous murine retroviral RNAs and reticuloendotheliosis virus encapsidation-minus RNAs by the reticuloendotheliosis virus helper cell line. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2675–2683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2675-2683.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild B. C., Finer M. H., Housman D. E., Mulligan R. C. Development of retrovirus vectors useful for expressing genes in cultured murine embryonal cells and hematopoietic cells in vivo. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3795–3801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3795-3801.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Naturally occurring murine leukemia viruses in wild mice: characterization of a new "amphotropic" class. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.19-25.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschmeier P. T., Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Perkins A. S., Weinstein I. B. Construction and characterization of a retroviral vector demonstrating efficient expression of cloned cDNA sequences. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):219–225. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Frantz J. D., Strominger J. L., Mulligan R. C. Expression of human class II major histocompatibility complex antigens using retrovirus vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2150–2154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Page K. A., Littman D. R. Pseudotyping with human T-cell leukemia virus type I broadens the human immunodeficiency virus host range. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):162–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.162-169.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A. J., Young J. C., Pendergast A. M., Pondel M., Landau N. R., Littman D. R., Witte O. N. BCR first exon sequences specifically activate the BCR/ABL tyrosine kinase oncogene of Philadelphia chromosome-positive human leukemias. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1785–1792. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scadden D. T., Fuller B., Cunningham J. M. Human cells infected with retrovirus vectors acquire an endogenous murine provirus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):424–427. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.424-427.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuve L. L., Brown-Shimer S., Pachl C., Najarian R., Dina D., Burke R. L. Structure and expression of the herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein gB gene. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):326–335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.326-335.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. M., Brodsky M. H., Irving B. A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Littman D. R. Interaction of the unique N-terminal region of tyrosine kinase p56lck with cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 is mediated by cysteine motifs. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]