Abstract
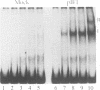
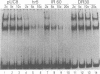
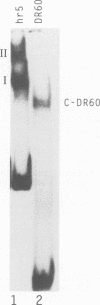
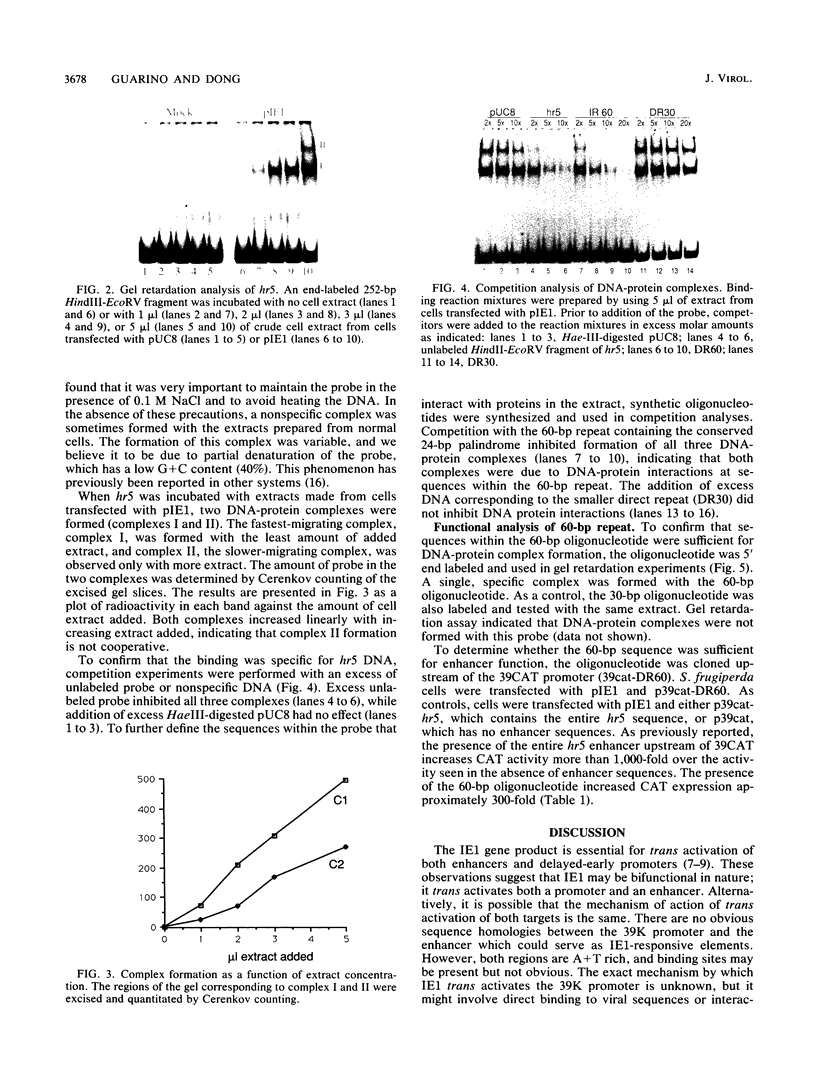
The baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus contains an element known as homologous region 5 (hr5) which is an enhancer of delayed-early viral gene expression. To begin to identify proteins that interact with hr5, DNA-protein interactions were analyzed by using extracts from Spodoptera frugiperda cells and a fragment of DNA containing the left half of the hr5 enhancer. This 252-bp DNA fragment contains two copies of a 30-bp direct repeat (DR30) and two copies of a 24-bp imperfect palindrome contained within a 60-bp direct repeat (DR60). Extracts prepared from normal S. frugiperda cells and cells transfected with pUC8 lacked enhancer-binding proteins. However, when gel shift assays were performed with extracts from cells transfected with a plasmid containing the viral trans-activator IE1 gene, two DNA-protein complexes were formed. Both DNA-protein complexes were specifically inhibited by competition with a 60-bp oligonucleotide corresponding to DR60 but not by competition with a different oligonucleotide corresponding to DR30. Formation of the two complexes did not appear to involve cooperative interactions between binding proteins. When DR60 was used as a probe, a single complex was formed. To measure the enhancer activity of DR60, a reporter plasmid was constructed that contained DR60 cloned upstream of the reporter chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene under the control of the delayed-early 39K promoter. Transient expression analysis indicated that the oligonucleotide increased expression of this gene 300-fold over the level obtained in the absence of any enhancer sequences.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus diversity and molecular biology. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:127–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M. A., Faulkner P. Location of Homologous DNA Sequences Interspersed at Five Regions in the Baculovirus AcMNPV Genome. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):961–970. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.961-970.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Gonzalez M. A., Summers M. D. Complete Sequence and Enhancer Function of the Homologous DNA Regions of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):224–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.224-229.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Interspersed Homologous DNA of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Enhances Delayed-Early Gene Expression. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):215–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.215-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Nucleotide sequence and temporal expression of a baculovirus regulatory gene. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2091–2099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2091-2099.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A., Anderson E. S. A simple method for the preparation of large quantities of pure plasmid DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 2;383(4):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen M. S., Friesen P. D. Molecular analysis of the transcriptional regulatory region of an early baculovirus gene. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):493–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.493-503.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Inagami S., Lovegren E., Chalkley R. DNA denatures upon drying after ethanol precipitation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8739–8754. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Wu C. Induction of sequence-specific binding of Drosophila heat shock activator protein without protein synthesis. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):727–730. doi: 10.1038/327727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]