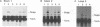Abstract
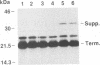
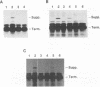
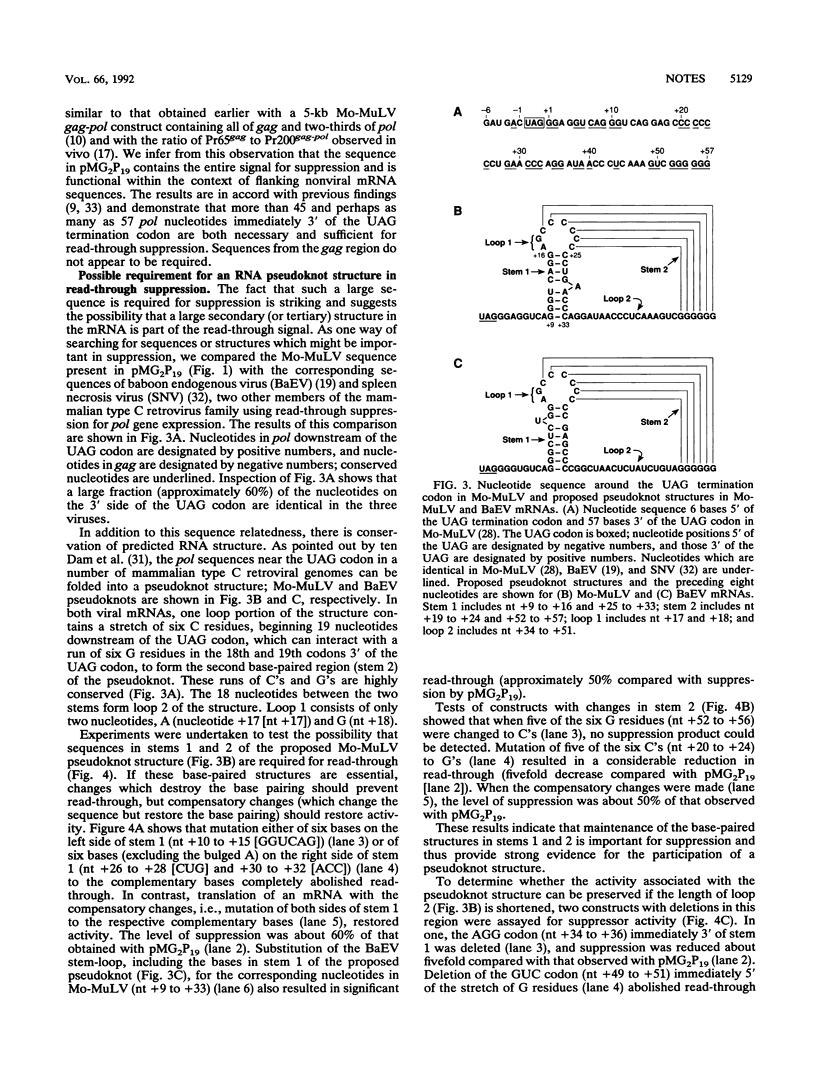
The pol gene of murine leukemia virus and other mammalian type C retroviruses is expressed by read-through suppression of an in-frame UAG codon which separates the gag and pol coding regions. In this study, we have analyzed the sequence requirements for read-through suppression by placing different portions of wild-type and mutant viral sequences from the gag-pol junction between reporter genes and testing transcripts of these constructs for suppression in reticulocyte lysates. We find that the read-through signal is contained within the first 57 nucleotides on the 3' side of the UAG codon. Our results indicate that the identities of six conserved bases in the eight-nucleotide, purine-rich sequence immediately downstream of the UAG codon are critical for suppression, as is the existence of a pseudoknot structure spanning the next 49 nucleotides. Thus, read-through suppression depends on a complex, bipartite signal in the mRNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beier H., Barciszewska M., Krupp G., Mitnacht R., Gross H. J. UAG readthrough during TMV RNA translation: isolation and sequence of two tRNAs with suppressor activity from tobacco plants. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):351–356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Banu L., Chen Y. Y., Mandel S. J., Kieffer J. D., Harney J. W., Larsen P. R. Recognition of UGA as a selenocysteine codon in type I deiodinase requires sequences in the 3' untranslated region. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):273–276. doi: 10.1038/353273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Rolley N. J., Jenner A. J., Inglis S. C. Mutational analysis of the RNA pseudoknot component of a coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 20;220(4):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90361-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro M., Parkin N., Varmus H. E. An RNA pseudoknot and an optimal heptameric shift site are required for highly efficient ribosomal frameshifting on a retroviral messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):713–717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinman J. D., Icho T., Wickner R. B. A -1 ribosomal frameshift in a double-stranded RNA virus of yeast forms a gag-pol fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):174–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etzerodt M., Mikkelsen T., Pedersen F. S., Kjeldgaard N. O., Jørgensen P. The nucleotide sequence of the Akv murine leukemia virus genome. Virology. 1984 Apr 15;134(1):196–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. X., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Rein A., Levin J. G. Identification of amino acids inserted during suppression of UAA and UGA termination codons at the gag-pol junction of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8860–8863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. X., Hatfield D. L., Rein A., Levin J. G. Translational readthrough of the murine leukemia virus gag gene amber codon does not require virus-induced alteration of tRNA. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2405–2410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2405-2410.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. X., Levin J. G., Hatfield D. L., Schaefer T. S., Gorelick R. J., Rein A. Suppression of UAA and UGA termination codons in mutant murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2870–2873. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2870-2873.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D. L., Levin J. G., Rein A., Oroszlan S. Translational suppression in retroviral gene expression. Adv Virus Res. 1992;41:193–239. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60037-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigman A., Wolf D., Yaish S., Falk H., Panet A. cis Acting RNA sequences control the gag-pol translation readthrough in murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90144-Z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. C., Court D. L., Zweig M., Levin J. G. Murine leukemia virus pol gene products: analysis with antisera generated against reverse transcriptase and endonuclease fusion proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):267–274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.267-274.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Madhani H. D., Masiarz F. R., Varmus H. E. Signals for ribosomal frameshifting in the Rous sarcoma virus gag-pol region. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90031-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamjoom G. A., Naso R. B., Arlinghaus R. B. Further characterization of intracellular precursor polyproteins of Rauscher leukemia virus. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):11–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. S., Nemoto F., Kuchino Y., Masuda M., Yoshikura H., Nishimura S. The effect of specific mutations at and around the gag-pol gene junction of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):5933–5945. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.5933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Verma I. M. Two base changes restore infectivity to a noninfectious molecular clone of Moloney murine leukemia virus (pMLV-1). J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):214–222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.214-222.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. C., Jr, Wills N., Arlinghaus R. B. Suppression of murine retrovirus polypeptide termination: effect of amber suppressor tRNA on the cell-free translation of Rauscher murine leukemia virus, Moloney murine leukemia virus, and Moloney murine sarcoma virus 124 RNA. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):464–473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.464-473.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T. Retroviral gag gene amber codon suppression is caused by an intrinsic cis-acting component of the viral mRNA. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3574–3580. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3574-3580.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Andersson P., Olshevsky U., Weinberg R., Baltimore D., Gesteland R. Translation of MuLV and MSV RNAs in nuclease-treated reticulocyte extracts: enhancement of the gag-pol polypeptide with yeast suppressor tRNA. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W. Pseudoknots: a new motif in the RNA game. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Apr;15(4):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90214-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Rietveld K., Bosch L. A new principle of RNA folding based on pseudoknotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1717–1731. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P. RNA pseudoknots that interact with components of the translation apparatus. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90395-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuzeski J. M., Nichols L. M., Gesteland R. F., Atkins J. F. The signal for a leaky UAG stop codon in several plant viruses includes the two downstream codons. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90718-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Biosynthesis and function of selenocysteine-containing enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16257–16260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. A., Talbot K. J., Panganiban A. T. Spleen necrosis virus gag polyprotein is necessary for particle assembly and release but not for proteolytic processing. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2642–2652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2642-2652.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills N. M., Gesteland R. F., Atkins J. F. Evidence that a downstream pseudoknot is required for translational read-through of the Moloney murine leukemia virus gag stop codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6991–6995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Katoh I., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus protease is encoded by the gag-pol gene and is synthesized through suppression of an amber termination codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1618–1622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dam E. B., Pleij C. W., Bosch L. RNA pseudoknots: translational frameshifting and readthrough on viral RNAs. Virus Genes. 1990 Jul;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00678404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]