Abstract
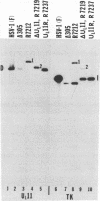
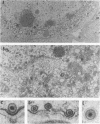
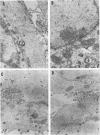
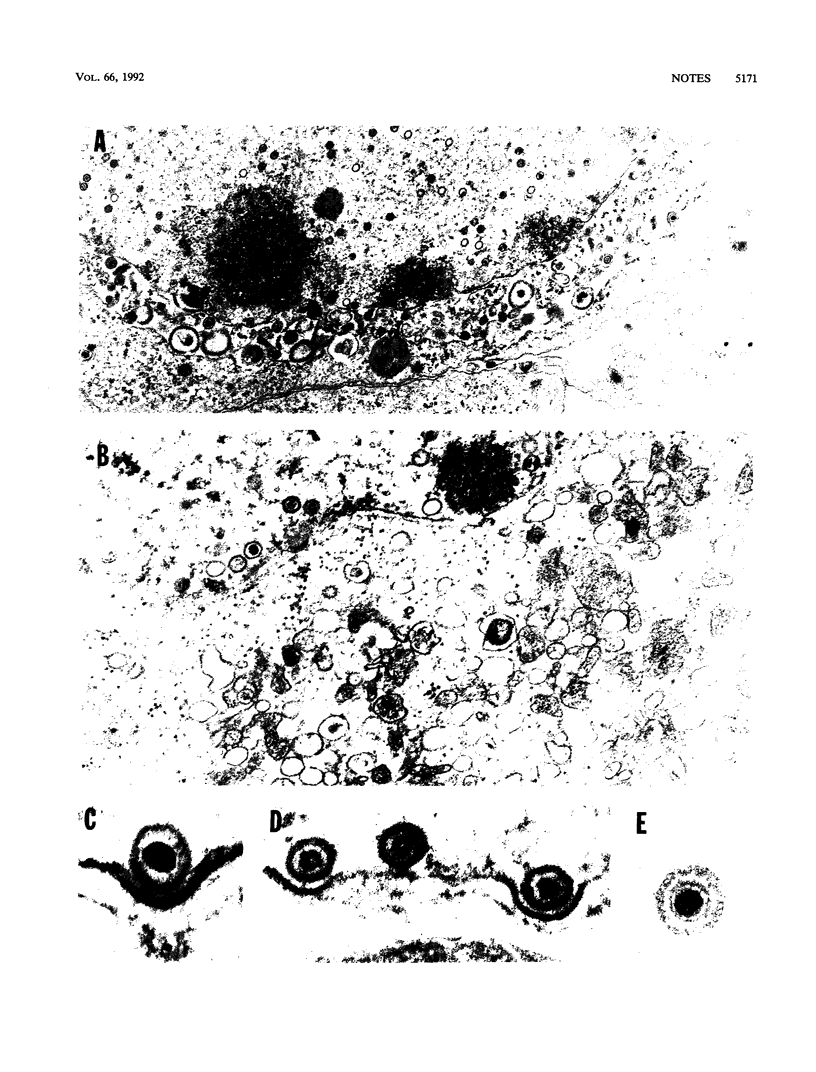
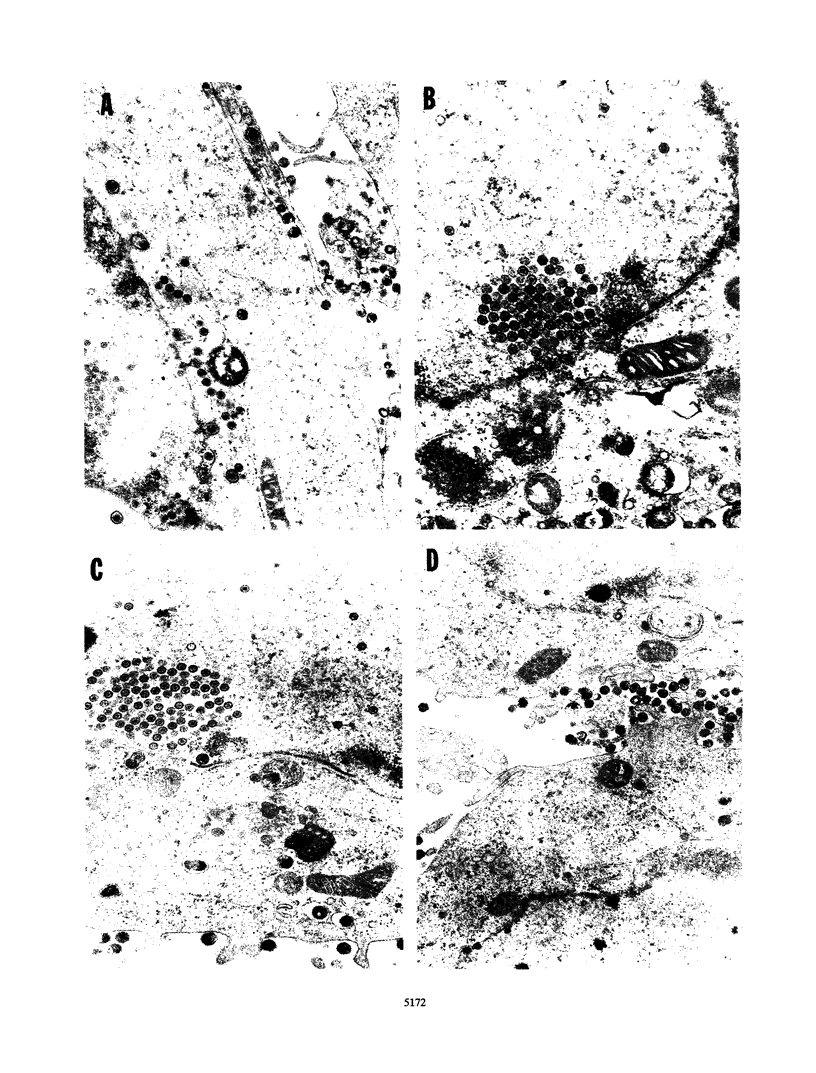
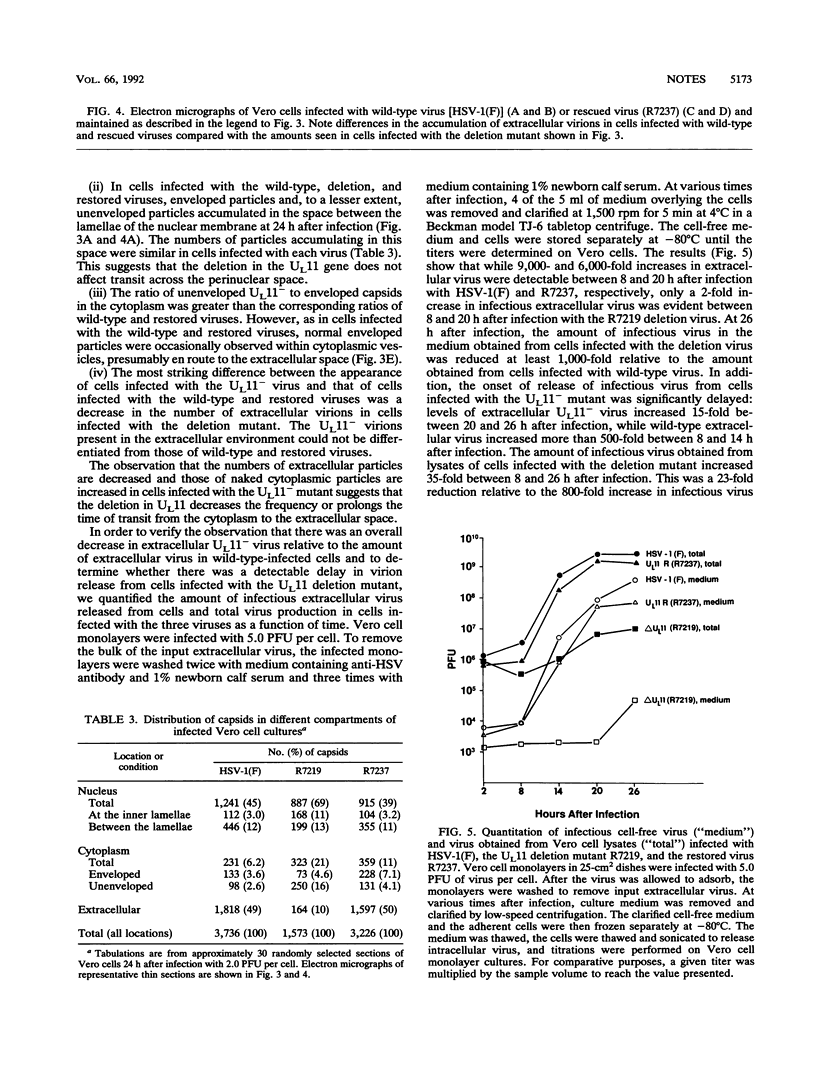
The UL11 gene of herpes simplex virus 1 was reported to encode a myristylated protein (C. A. MacLean, B. Clark, and D. J. McGeoch, J. Gen. Virol. 70:3147-3157, 1989). To determine the function of the gene product, a recombinant virus (R7219) lacking 61% of the codons (176 bp of the 288-bp coding domain) was genetically engineered. The deletion mutant replicated in all cell lines tested, albeit to titers 30- to 250-fold lower than those obtained from cells infected with wild-type virus. Electron microscopic analyses indicated that both full and empty capsids accumulated in the nuclei, juxtaposed with the inner lamellae of the nuclear membranes, and that increased numbers of naked particles were present in the cytoplasm of cells infected with the mutant virus. There was a greater than 1,000-fold decrease in the amount of infectious extracellular virus released from Vero cells infected with the deletion mutant compared with that from cells infected with wild-type virus. Furthermore, the onset of release of infectious virus from cells infected with the UL11- mutant was significantly delayed: levels of extracellular UL11- virus increased 15-fold between 20 and 26 h after infection, while levels of wild-type extracellular virus increased 500-fold between 8 and 14 h after infection. A virus in which the UL11 gene was restored produced wild-type levels of total and extracellular virus and was indistinguishable from wild-type virus upon analysis by electron microscopy. Taken together, the data indicate that the absence of the UL11 gene causes a reduced capacity to envelope and transport virions into the extracellular space.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baines J. D., Roizman B. The open reading frames UL3, UL4, UL10, and UL16 are dispensable for the replication of herpes simplex virus 1 in cell culture. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):938–944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.938-944.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines J. D., Ward P. L., Campadelli-Fiume G., Roizman B. The UL20 gene of herpes simplex virus 1 encodes a function necessary for viral egress. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6414–6424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6414-6424.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. E., Roizman B. The unique sequence of the herpes simplex virus 1 L component contains an additional translated open reading frame designated UL49.5. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):562–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.562-566.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Farabegoli F., Di Gaeta S., Roizman B. Origin of unenveloped capsids in the cytoplasm of cells infected with herpes simplex virus 1. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1589–1595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1589-1595.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 gene for ICP34.5, which maps in inverted repeats, is conserved in several limited-passage isolates but not in strain 17syn+. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1014-1020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai P. J., Schaffer P. A., Minson A. C. Excretion of non-infectious virus particles lacking glycoprotein H by a temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1: evidence that gH is essential for virion infectivity. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1147–1156. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Roizman B. The promoter, transcriptional unit, and coding sequence of herpes simplex virus 1 family 35 proteins are contained within and in frame with the UL26 open reading frame. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):206–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.206-212.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean C. A., Clark B., McGeoch D. J. Gene UL11 of herpes simplex virus type 1 encodes a virion protein which is myristylated. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3147–3157. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscufo N., Simons J., Chow M. Myristoylation is important at multiple stages in poliovirus assembly. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2372–2380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2372-2380.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Roizman B. A generalized technique for deletion of specific genes in large genomes: alpha gene 22 of herpes simplex virus 1 is not essential for growth. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prange R., Clemen A., Streeck R. E. Myristylation is involved in intracellular retention of hepatitis B virus envelope proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3919–3923. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3919-3923.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Rein A. Unmyristylated Moloney murine leukemia virus Pr65gag is excluded from virus assembly and maturation events. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2370–2373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2370-2373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick P., Berthelot N. Inverted repetitions in the chromosome of herpes simplex virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):667–678. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S., Jacob R. J., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. II. Size, composition, and arrangement of inverted terminal repetitions. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1487–1497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1487-1497.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]