Abstract
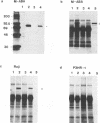
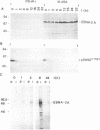
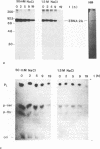
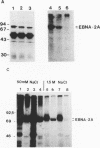
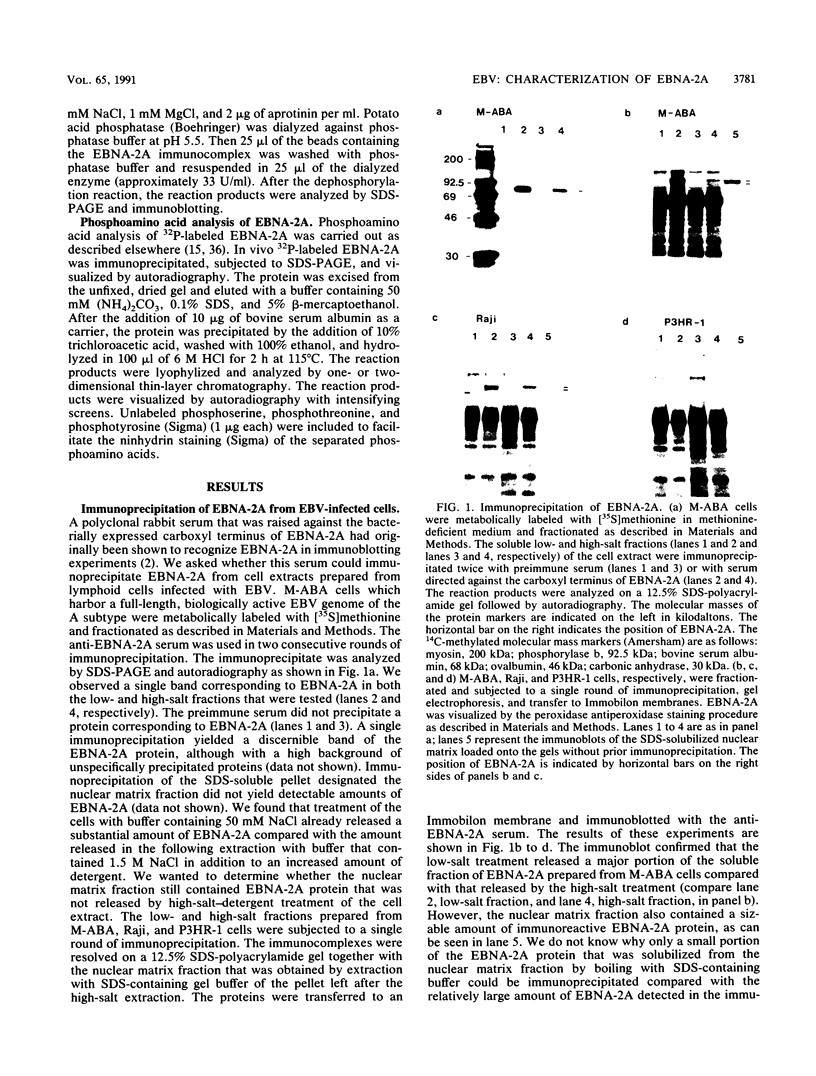
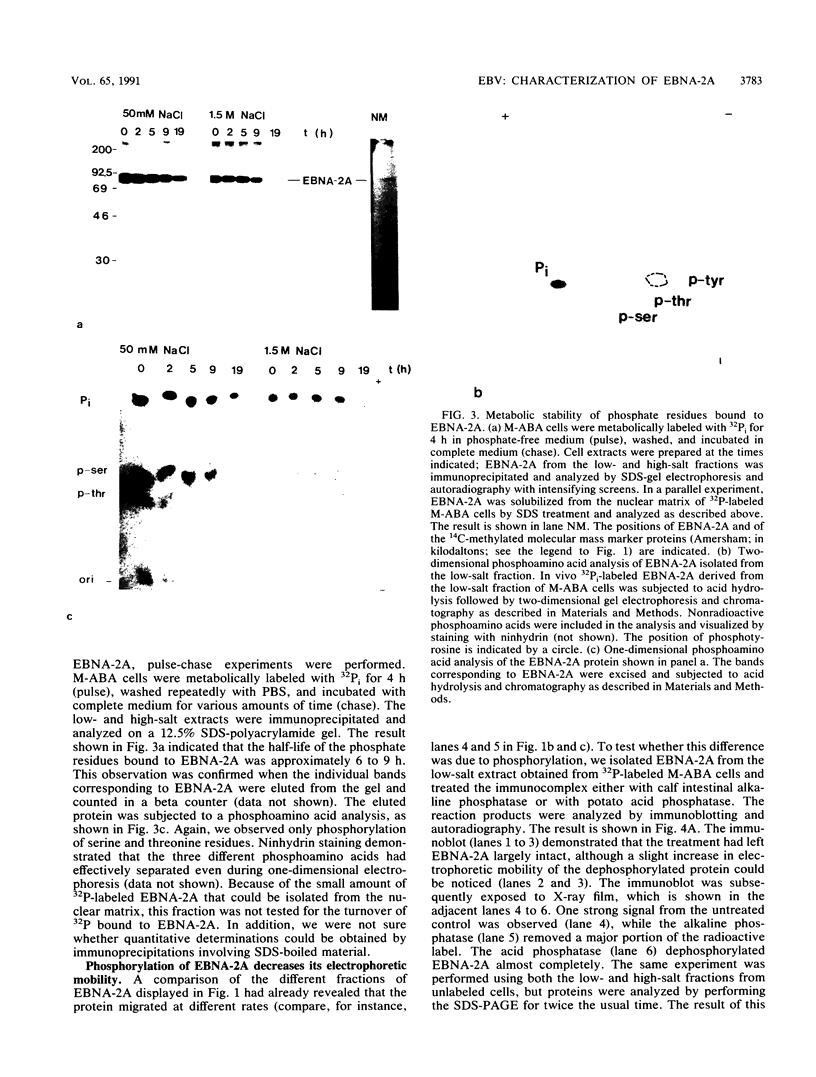
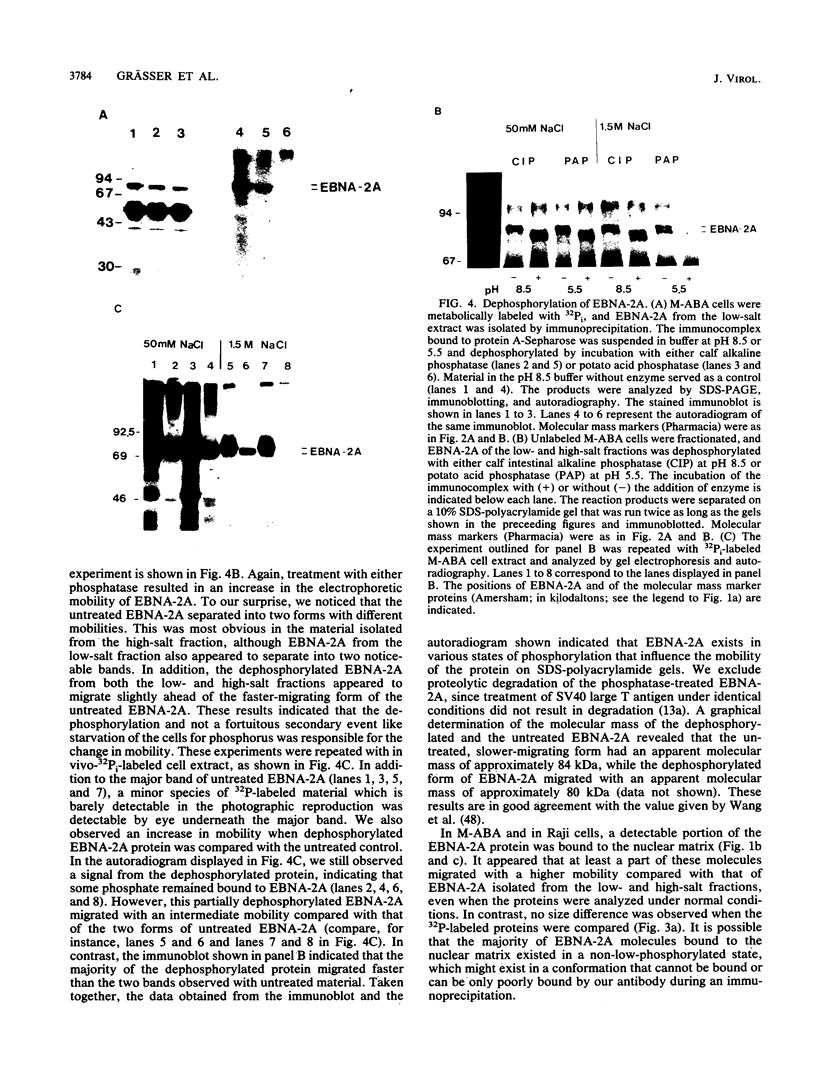
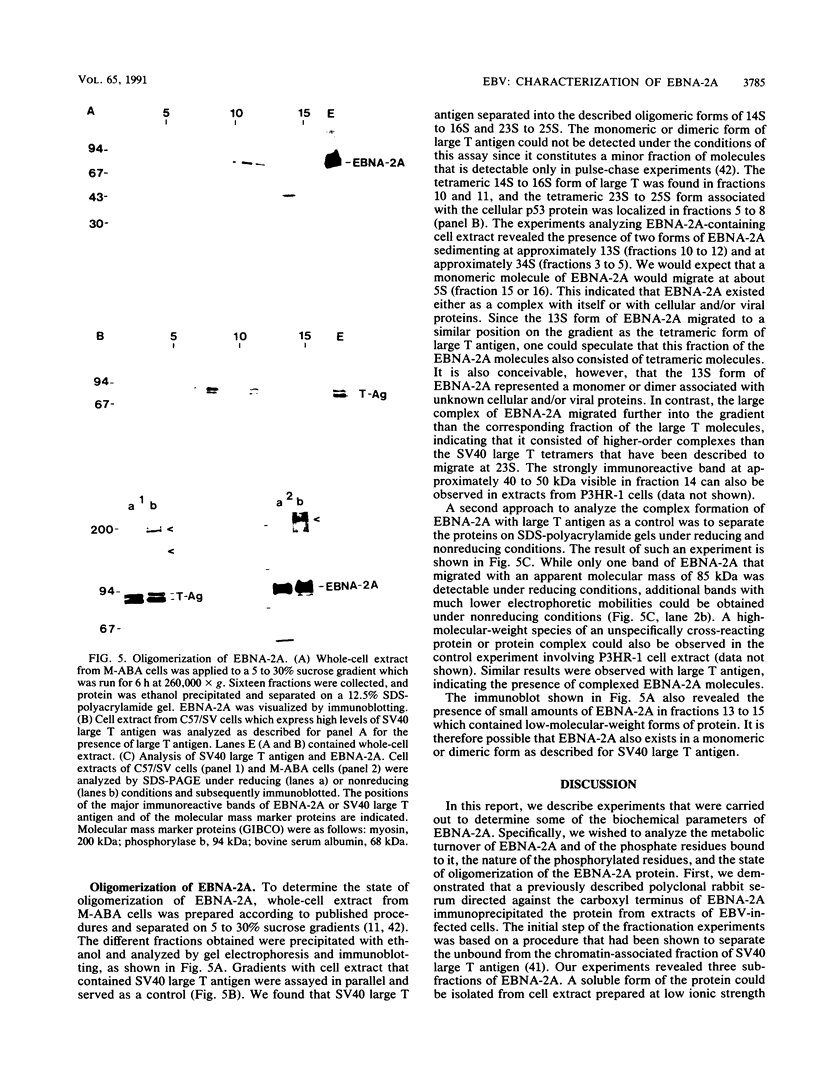
The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2A (EBNA-2A) was immunoprecipitated from latently Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphocytes with a polyclonal serum raised against the EBNA-2A C terminus. The nucleus contained three subfractions of EBNA-2A which could be distinguished by their resistance to salt extraction: (i) a nucleoplasmatic fraction that was solubilized at 50 mM NaCl, (ii) a chromatin-associated fraction extractable at 1.5 M NaCl, and (iii) a nuclear matrix-associated fraction solubilized only by boiling with buffer containing 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate. The three subfractions were phosphorylated; it was demonstrated that the nucleoplasmatic and the chromatin-associated fractions were phosphorylated at serine and threonine residues. The half-life of the EBNA-2A protein was determined by cycloheximide treatment and by pulse-chase experiments and was found to be at least 24 h. The turnover of the phosphate residues bound to the two salt-soluble subfractions was determined to be approximately 6 to 9 h, suggesting a possible role of the phosphorylation in the regulation of the biological activity of EBNA-2A. Dephosphorylation of EBNA-2A resulted in an increased mobility of the protein during sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and indicated the presence of differentially phosphorylated subclasses of the protein. Analysis of EBNA-2A by sucrose gradient centrifugation revealed the existence of two subclasses of complexed molecules which exhibited sedimentation coefficients of approximately 13S and 34S.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aman P., Rowe M., Kai C., Finke J., Rymo L., Klein E., Klein G. Effect of the EBNA-2 gene on the surface antigen phenotype of transfected EBV-negative B-lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jan 15;45(1):77–82. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billaud M., Busson P., Huang D., Mueller-Lantzch N., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Wakasugi H., Seigneurin J. M., Tursz T., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-containing nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells express the B-cell activation antigen blast2/CD23 and low levels of the EBV receptor CR2. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4121–4128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4121-4128.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Hudewentz J., Freese U. K., Zimber U. Deletion of the nontransforming Epstein-Barr virus strain P3HR-1 causes fusion of the large internal repeat to the DSL region. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):952–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.952-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Zimber U., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Banchereau J., Tursz T., Bornkamm G., Lenoir G. M. Stable transfection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 in lymphoma cells containing the EBV P3HR1 genome induces expression of B-cell activation molecules CD21 and CD23. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1002-1013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Epstein M. A., Bornkamm G. W., Achong B. G., Finerty S., Thompson J. L. Biological and biochemical observations on isolates of EB virus from the malignant epithelial cells of two nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1979 Sep 15;24(3):294–302. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Bornkamm G. W. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus. III. Comparison of a transforming and a nontransforming virus by partial denaturation mapping of their DNAs. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.81-89.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Wendel-Hansen V., Kjellström G., Kallin B., Rosén A. Purification and characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 using monoclonal antipeptide antibodies. Int J Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;42(5):721–727. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Nowak B., Burger C. Detection and characterization of multiple forms of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):92–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.92-102.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald S., van Santen V., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.411-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech B., Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Pavlish O., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus terminal protein 1 (TP1) in extracts of four lymphoid cell lines, expression in insect cells, and detection of antibodies in human sera. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2759–2767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2759-2767.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Mann K., Walter G. Removal of serine phosphates from simian virus 40 large T antigen increases its ability to stimulate DNA replication in vitro but has no effect on ATPase and DNA binding. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3373–3380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3373-3380.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Scheidtmann K. H., Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A., Walter G. In vitro phosphorylation of SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90653-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst H., Niedobitek G., Kneba M., Hummel M., Finn T., Anagnostopoulos I., Bergholz M., Krieger G., Stein H. High incidence of Epstein-Barr virus genomes in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jul;137(1):13–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Konn M., Yamaguchi J., Wudarski D. J., Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Grace J. T., Jr Immunofluorescence and herpes-type virus particles in the P3HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.1045-1051.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. H., Hayward S. D., Rawlins D. R. Interaction of the lymphocyte-derived Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA-1 with its DNA-binding sites. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):101–110. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.101-110.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Viral latency and transformation: the strategy of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C. The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2530–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2530-2536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir G. M., Vuillaume M., Bonnardel C. The use of lymphomatous and lymphoblastoid cell lines in the study of Burkitt's lymphoma. IARC Sci Publ. 1985;(60):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. c-myc and c-myb protein degradation: effect of metabolic inhibitors and heat shock. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2504–2512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Staunton D., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.710-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Lantzsch N., Lenoir G. M., Sauter M., Takaki K., Béchet J. M., Kuklik-Roos C., Wunderlich D., Bornkamm G. W. Identification of the coding region for a second Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA 2) by transfection of cloned DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1805–1811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Sample C., Kieff E. Subnuclear localization and phosphorylation of Epstein-Barr virus latent infection nuclear proteins. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):563–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90027-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polack A., Hartl G., Zimber U., Freese U. K., Laux G., Takaki K., Hohn B., Gissmann L., Bornkamm G. W. A complete set of overlapping cosmid clones of M-ABA virus derived from nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its similarity to other Epstein-Barr virus isolates. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. The replication functions of SV40 T antigen are regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90179-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Pritchett R., Kieff E. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus. III. Identification of restriction enzyme fragments that contain DNA sequences which differ among strains of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):388–398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.388-398.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeckel D., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Biochemical characterization of two Epstein-Barr virus early antigen-associated phosphopolypeptides. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.933-937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauter M., Boos H., Hirsch F., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Characterization of a latent protein encoded by the large internal repeats and the BamHI Y fragment of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):586–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauter M., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 variant (EBNA 2B) by specific sera. Virus Res. 1987 Aug;8(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Hardung M., Echle B., Walter G. DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 large T antigen correlates with a distinct phosphorylation state. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.1-12.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H. Phosphorylation of simian virus 40 large T antigen: cytoplasmic and nuclear phophorylation sites differ in their metabolic stability. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):85–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schickedanz J., Scheidtmann K. H., Walter G. Kinetics of nuclear transport and oligomerization of simian virus 40 large T antigen. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90402-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffel A., Weist S., Ball R. K., Scheidtmann K. H., Braun D. G., Brandner G. Synthetic oligopeptides define epitopes at the amino- and carboxy-terminus of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen which are recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B. An intricate route to immortality. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Petti L., Braun D., Seung S., Kieff E. A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):945–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.945-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Tsang S. F., Kurilla M. G., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3407–3416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3407-3416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]