Abstract
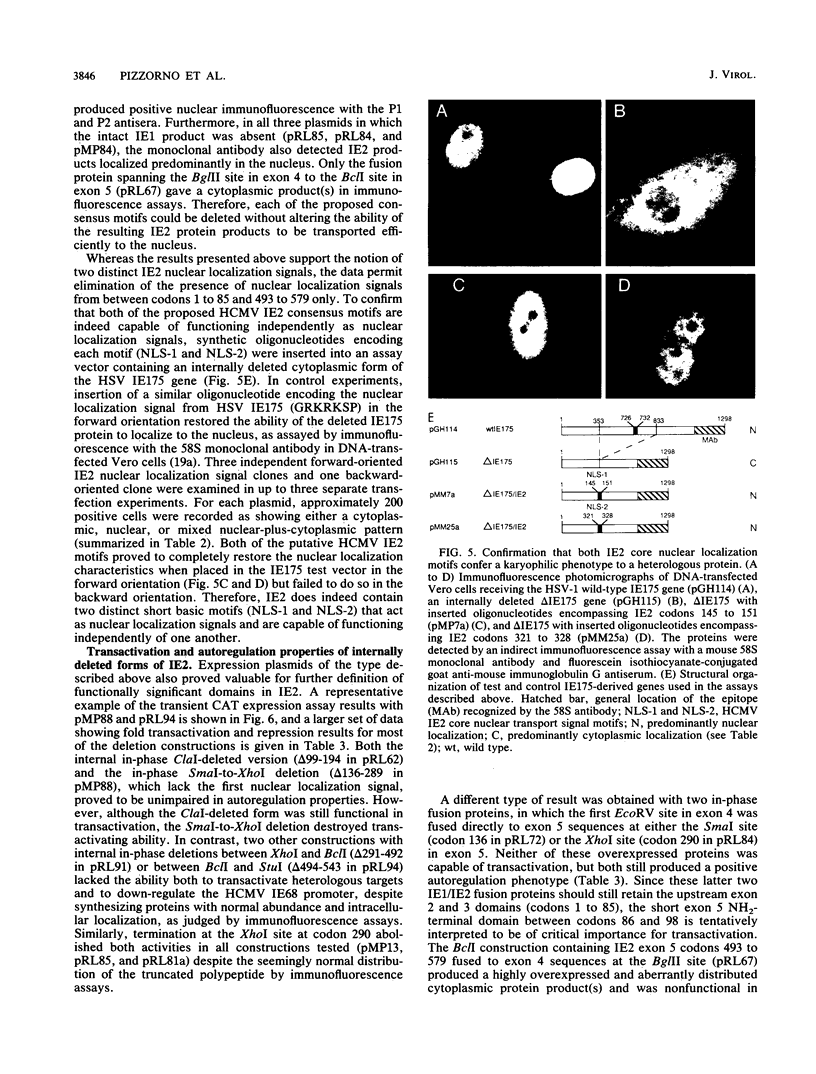
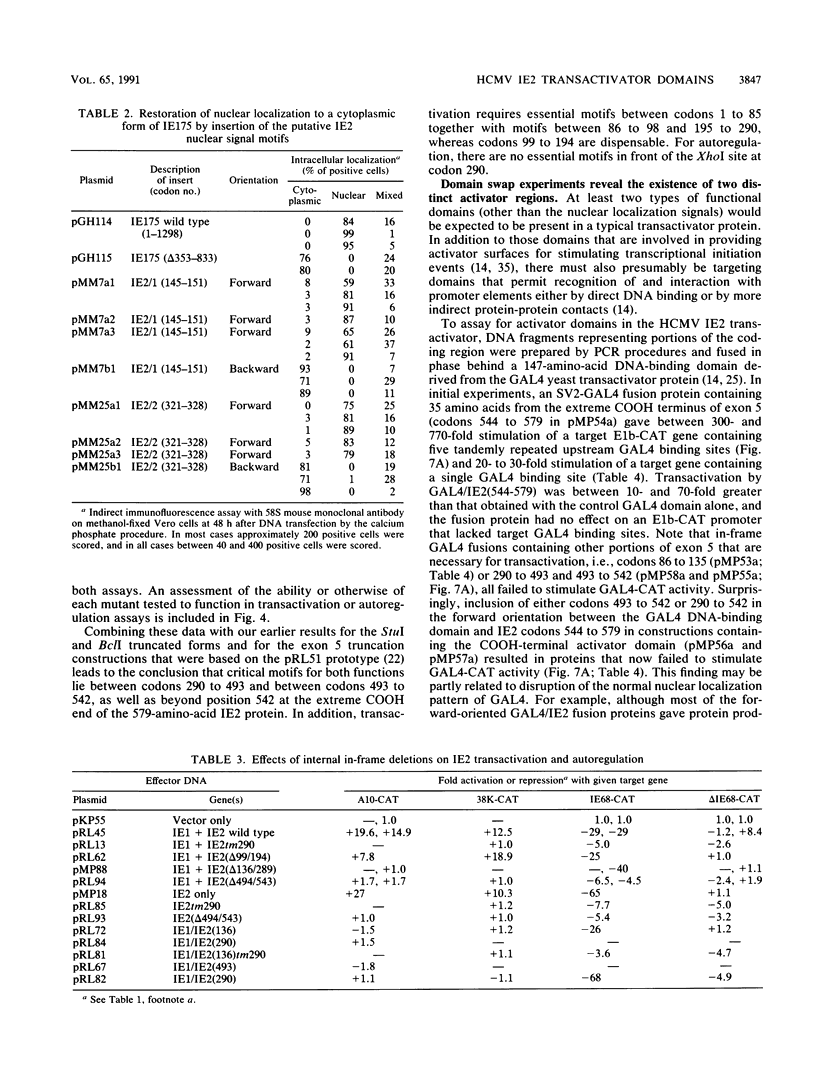
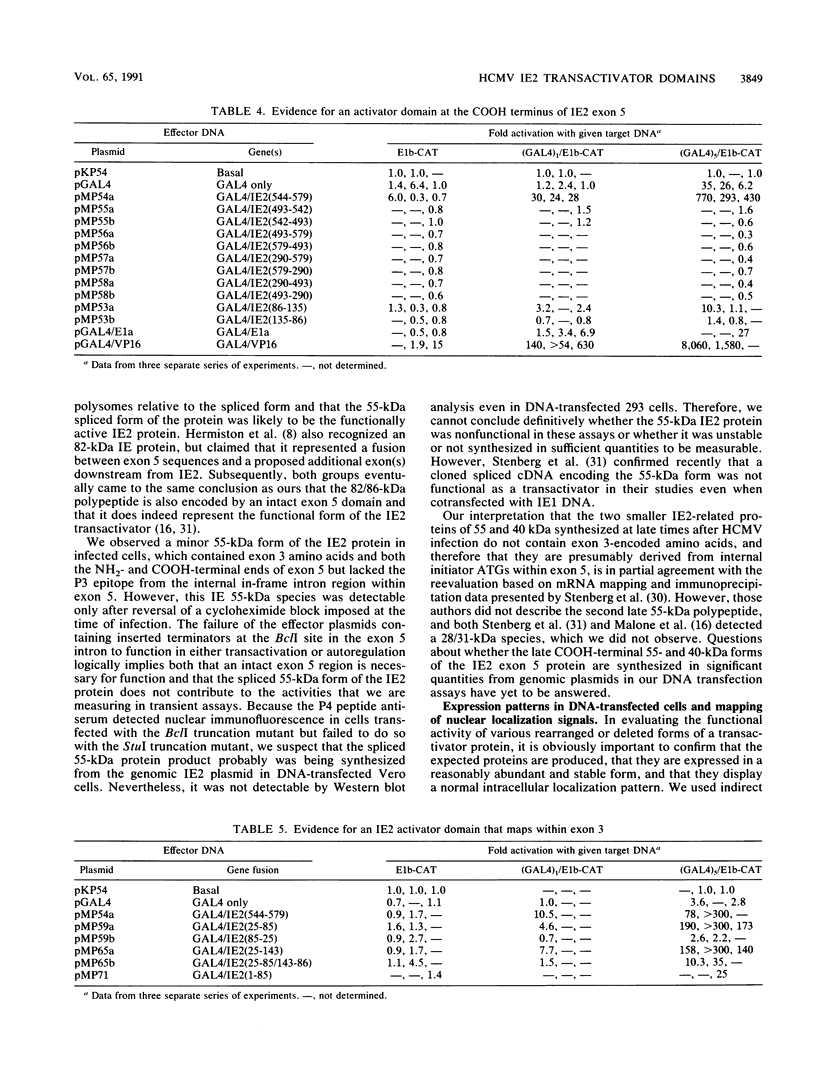
The IE2 region of the human cytomegalovirus (CMV) strain Towne major immediate-early (MIE) gene encodes a transcriptional transactivator that stimulates expression from a variety of heterologous target promoters but specifically down-regulates its own promoter. By immunofluorescence and Western immunoblot analysis with monospecific peptide antisera, we found that human CMV MIE exon 5 encodes four overlapping polypeptides, two present at immediate-early times (80 and 55 kDa) and two others detected only at late times after infection (55 and 40 kDa). However, only the 80-kDa version (579 amino acids), which is derived from the small upstream exons 2 and 3 fused to the intact exon 5 region, was functionally active in both transactivation and autoregulation as assessed by cotransfection experiments. These results confirm the corrected assignment of the coding capacity of the exon 5 region based on amino acid homology with the equivalent IE2 protein from simian CMV (Colburn). In transient DNA transfection assays, IE2 expression plasmids also produced a predominant full-length 80-kDa protein, which was localized in a distinctive reticular pattern in the nucleus. Two short basic nuclear localization signals in IE2 were identified by deletion analysis and by conversion of a test cytoplasmic herpes simplex virus protein into a form that localized in the nucleus after insertion of either of these two human CMV motifs. Functional assays with MIE region plasmids containing deletions or truncations in exon 5 revealed that both transactivation and autoregulation required several distinct domains within the COOH half of the IE2 protein, whereas a region between codons 99 and 194 could be discarded. Three segments at the NH2 end of the protein between codons 1 to 85, 86 to 98, and 195 to 290 were also essential for transactivation but played no role in autoregulation. Finally, in domain swap experiments, GAL4-fusion proteins containing either an NH2-terminal 51-amino-acid domain from exon 3 (codons 25 to 85) or the COOH-terminal 33-amino-acid domain from exon 5 (codons 544 to 579) identified two distinct activator domains from IE2, both of which have acidic characteristics.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang C. P., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. A human cytomegalovirus early gene has three inducible promoters that are regulated differentially at various times after infection. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.281-290.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. A., Leahy J., Hardwick J. M. An enhancer within the divergent promoter of Epstein-Barr virus responds synergistically to the R and Z transactivators. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.313-321.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Kenney S. C., Kamine J., Pagano J. S., Huang E. S. Immediate-early gene region of human cytomegalovirus trans-activates the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8642–8646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depto A. S., Stenberg R. M. Regulated expression of the human cytomegalovirus pp65 gene: octamer sequence in the promoter is required for activation by viral gene products. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1232-1238.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. C., McDougall J., Hackman R., Meyers J. D., Thomas E. D., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to cytomegalovirus: rapid identification of clinical isolates and preliminary use in diagnosis of cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.273-281.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Gibson W. A cycloheximide-enhanced protein in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):362–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Shero J. H., Kelly T. J., Hayward G. S. Multiple tandemly repeated binding sites for cellular nuclear factor 1 that surround the major immediate-early promoters of simian and human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1559–1570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1559-1570.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafemina R. L., Pizzorno M. C., Mosca J. D., Hayward G. S. Expression of the acidic nuclear immediate-early protein (IE1) of human cytomegalovirus in stable cell lines and its preferential association with metaphase chromosomes. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):584–600. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. A transcriptional repressor encoded by BPV-1 shares a common carboxy-terminal domain with the E2 transactivator. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone C. L., Vesole D. H., Stinski M. F. Transactivation of a human cytomegalovirus early promoter by gene products from the immediate-early gene IE2 and augmentation by IE1: mutational analysis of the viral proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1498-1506.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. The carboxy-terminal domain shared by the bovine papillomavirus E2 transactivator and repressor proteins contains a specific DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):533–539. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Bednarik D. P., Raj N. B., Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Activation of human immunodeficiency virus by herpesvirus infection: identification of a region within the long terminal repeat that responds to a trans-acting factor encoded by herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7408–7412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Jeang K. T., Pitha P. M., Hayward G. S. Novel induction by herpes simplex virus of hybrid interferon gene transcripts driven by the strong cytomegalovirus IE94 promoter. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):819–828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.819-828.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Expression of recombinant genes containing herpes simplex virus delayed-early and immediate-early regulatory regions and trans activation by herpesvirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.522-531.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Hayward G. S. The IE2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus specifically down-regulate expression from the major immediate-early promoter through a target sequence located near the cap site. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6154–6165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6154-6165.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihs H. P., Peters R. Nuclear transport kinetics depend on phosphorylation-site-containing sequences flanking the karyophilic signal of the Simian virus 40 T-antigen. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1479–1484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. S., Boundy A., O'Hare P., Pizzorno M. C., Ciufo D. M., Hayward G. S. Direct correlation between a negative autoregulatory response element at the cap site of the herpes simplex virus type 1 IE175 (alpha 4) promoter and a specific binding site for the IE175 (ICP4) protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4307–4320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4307-4320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression: alpha and beta promoters are trans activated by viral functions in permissive human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.135-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., Tevethia M. J. Identification of a human cytomegalovirus virus DNA segment that complements an adenovirus 5 immediate early mutant. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Identification of sequence requirements and trans-acting functions necessary for regulated expression of a human cytomegalovirus early gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3463–3473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3463-3473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Fortney J., Barlow S. W., Magrane B. P., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Promoter-specific trans activation and repression by human cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins involves common and unique protein domains. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1556–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1556-1565.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Spector D. J., Leisure K. M., Stinski M. F. Participation of two human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene regions in transcriptional activation of adenovirus promoters. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







