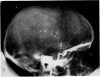
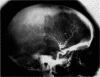
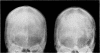
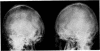
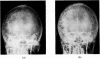
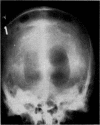
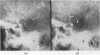
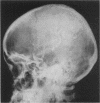
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASK-UPMARK E., INGVAR D. A follow-up examination of 138 cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Med Scand. 1950;138(1):15–31. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1950.tb10092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK S. P., GERMAN W. J. The treatment of internal carotid artery aneurysms by proximal arterial ligation; a follow-up study. J Neurosurg. 1953 Nov;10(6):590–601. doi: 10.3171/jns.1953.10.6.0590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTTERELL E. H., LOUGHEED W. M., SCOTT J. W., VANDEWATER S. L. Hypothermia, and interruption of carotid, or carotid and vertebral circulation, in the surgical management of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1956 Jan;13(1):1–42. doi: 10.3171/jns.1956.13.1.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECKER A., RIEMENSCHNEIDER P. A. Arteriographic demonstration of spasm of the intracranial arteries, with special reference to saccular arterial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1951 Nov;8(6):660–667. doi: 10.3171/jns.1951.8.6.0660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLINGHAM F. J. The management of ruptured intracranial aneurysm. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1958 Aug;23(2):89–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDY W. G., THOMAS L. M., WEBSTER J. E., GURDJIAN E. S. Carotid ligation for intracranial aneurysm; a follow-up study of 54 patients. J Neurosurg. 1958 May;15(3):281–289. doi: 10.3171/jns.1958.15.3.0281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYLAND H. H. Prognosis in spontaneous subarachnoid. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1950 Jan;63(1):61-78, illust. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1950.02310190067005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUGHEED W. M., KAHN D. S. Circumvention of anoxia during arrest of cerebral circulation for intracranial surgery. J Neurosurg. 1955 May;12(3):226–239. doi: 10.3171/jns.1955.12.3.0226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOL J. L., JACOBSON S., FLETCHER T. A. Cerebral vasospasm; clinical and experimental evidence. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Jul 26;167(13):1599–1601. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.02990300025005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAYNOR R. B., ROSS G. Arteriography and vasospasm. The effects of intracarotid contrast media on vasospasm. J Neurosurg. 1960 Nov;17:1055–1061. doi: 10.3171/jns.1960.17.6.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON E. G. Cerebral lesions due to intracranial aneurysms. Brain. 1949 Jun;72(Pt 2):150–185. doi: 10.1093/brain/72.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSOMOFF H. L., HOLADAY D. A. Cerebral blood flow and cerebral oxygen consumption during hypothermia. Am J Physiol. 1954 Oct;179(1):85–88. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.179.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMLINSON B. E. Brain changes in ruptured intracranial aneurysm. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Sep;12:391–399. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.5.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON G., RIGGS H. E., RUPP C. The pathologic anatomy of ruptured cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1954 Mar;11(2):128–134. doi: 10.3171/jns.1954.11.2.0128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]