Abstract
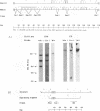
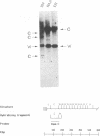
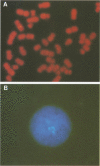
IB4 is a prototype, latently Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected, lymphoblastoid cell line. We show here that IB4 contains only integrated EBV genomes. Episomal EBV DNA is not detected by Gardella gel analysis or in situ hybridization. Restriction enzyme mapping indicates that the EBV genomes first circularized and then integrated into and deleted part of the BamHI C fragment. IB4 is therefore the only lymphoblastoid cell line described to date that lacks episomal EBV and has integrated EBV genomes with joined ends. Thus, the detection of joined EBV termini on Southern blots is not as reliable as the Gardella gel system for detecting episomal EBV DNA, and IB4 is not an ideal prototype cell line for the study of latent infection by EBV.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Griffin B. E. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1755–1764. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aman P., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Klein G. Epstein-Barr virus susceptibility of normal human B lymphocyte populations. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):208–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsma J., Miller G. Nucleic acid spot hybridization: rapid quantitative screening of lymphoid cell lines for Epstein-Barr viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Beisel C., Hummel M., King W., Fennewald S., Cheung A., Heller M., Raab-Traub N., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8) DNA VII: molecular cloning and detailed mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Medveczky P., Sairenji T., Mulder C. Detection of circular and linear herpesvirus DNA molecules in mammalian cells by gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A., Ripley S., Heller M., Kieff E. Chromosome site for Epstein-Barr virus DNA in a Burkitt tumor cell line and in lymphocytes growth-transformed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1987–1991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley E. A., Agger S., McNeil J. A., Lawrence J. B., Calendar A., Lenoir G., Thorley-Lawson D. A. When Epstein-Barr virus persistently infects B-cell lines, it frequently integrates. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1245–1254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1245-1254.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley E. A., Thorley-Lawson D. A. B cell activation and the establishment of Epstein-Barr virus latency. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2059–2075. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Thomas-Powell A. L., Raab-Traub N., Hawke M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA. V. Viral RNA in a restringently infected, growth-transformed cell line. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):506–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.506-518.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., Marselle L. M. Highly localized tracks of specific transcripts within interphase nuclei visualized by in situ hybridization. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Villnave C. A., Singer R. H. Sensitive, high-resolution chromatin and chromosome mapping in situ: presence and orientation of two closely integrated copies of EBV in a lymphoma line. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Heller M., Petti L., O'Shiro E., Kieff E. Persistence of the entire Epstein-Barr virus genome integrated into human lymphocyte DNA. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1322–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.6095452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Kieff E. Transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus genome during latency in growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1667–1674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1667-1674.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Phelps M., Domoradzki J. Epstein-Barr virus DNA is amplified in transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):590–595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.590-595.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Mann K. P. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection provide a model for B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):45–59. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Promoter switching in Epstein-Barr virus during the initial stages of infection of B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]