Abstract
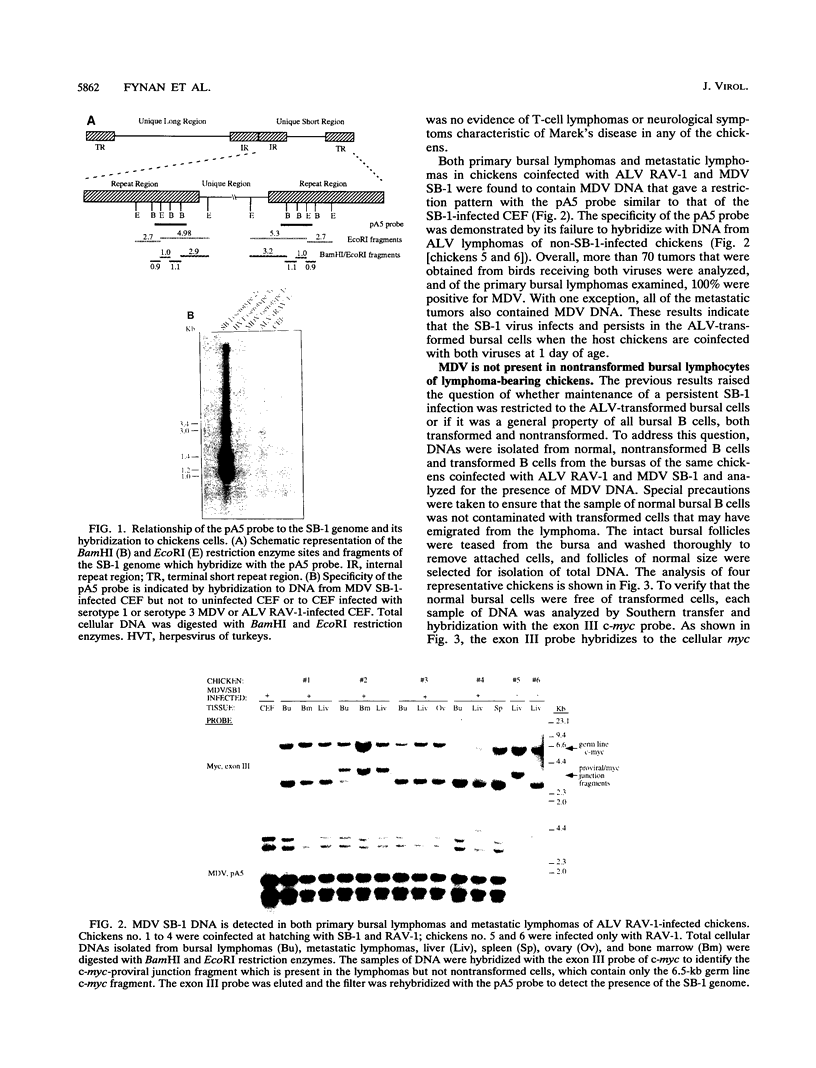
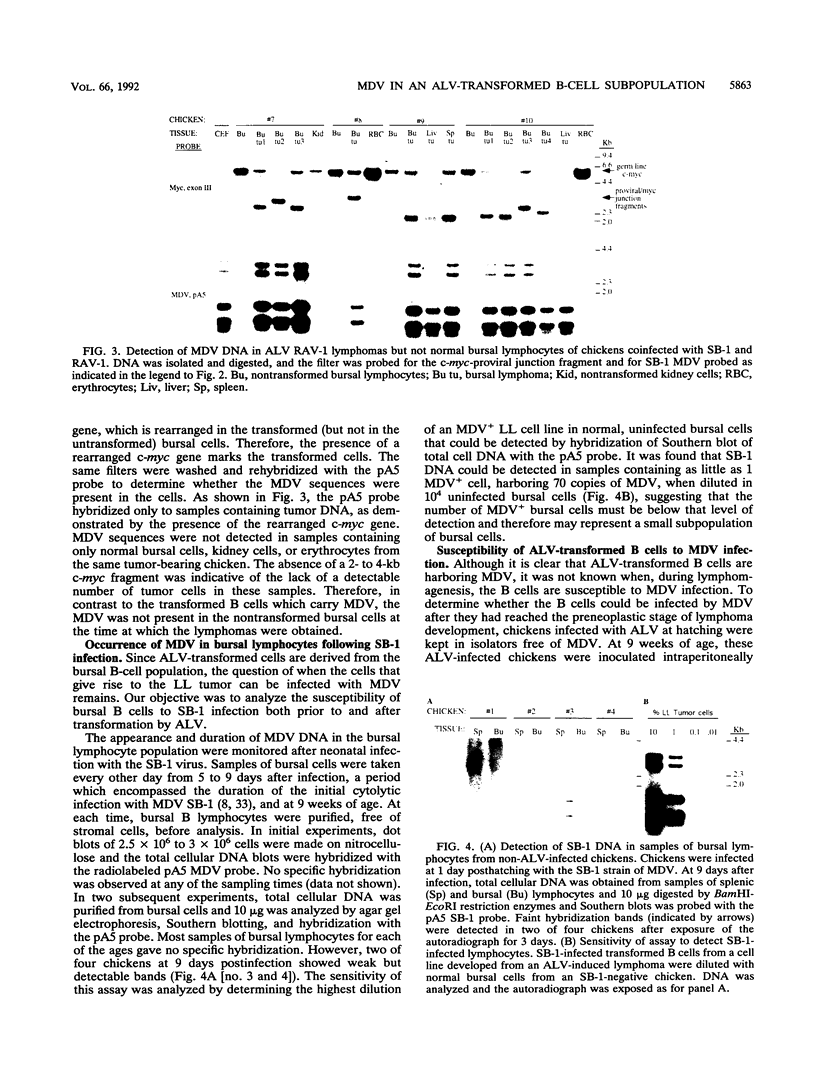
Previous studies have described an augmentation of avian leukosis virus (ALV)-induced lymphoid leukosis in chickens that were coinfected with a serotype 2 Marek's disease virus (MDV) strain, SB-1. As a first step toward understanding the mechanism of this augmentation, we have analyzed the tropism of the MDV for the ALV-transformed B cell. After hatching, chickens were coinfected with ALV and a nonpathogenic strain of MDV, SB-1. Seventy primary and metastatic ALV-induced lymphomas that developed in chickens between 14 and 20 weeks of age were found, with only one exception, to carry SB-1 DNA. The MDV genome was maintained in cell lines derived from the tumors. However, MDV DNA could not be detected in nontransformed bursal B cells from chickens carrying ALV lymphomas. Moreover, during and after the lytic phase of MDV infection, SB-1 DNA was near or below the level of detection in bursal cells, suggesting that MDV most likely infects only a small subpopulation of bursal cells. By contrast, ALV-transformed B cells from MDV-free chickens could be persistently infected with MDV in vitro. These findings indicate that ALV lymphoma cells, unlike nontransformed bursal B cells, are susceptible to persistent MDV infection and can serve as a reservoir of MDV that can potentially influence the physiology of the transformed cell.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURMESTER B. R., FONTES A. K., WALTER W. G. Pathogenicity of a viral strain (RPL 12) causing avian visceral lymphomatosis and related neoplasms. III. Influence of host age and route of inoculation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1960 Jun;24:1423–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T. W., Giroir B. P., Humphries E. H. Cell lines derived from avian lymphomas exhibit two distinct phenotypes. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T. W., Humphries E. H. Formation of a transformed follicle is necessary but not sufficient for development of an avian leukosis virus-induced lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):213–216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon L. D., Witter R. L., Fadly A. M. Augmentation of retrovirus-induced lymphoid leukosis by Marek's disease herpesviruses in White Leghorn chickens. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):504–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.504-512.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Carlisle J. C., Fabricant J., Murthy K. K., Schat K. A. Comparative pathogenesis studies with oncogenic and nononcogenic Marek's disease viruses and turkey herpesvirus. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Apr;40(4):541–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Schat K. A., Ross L. J., Shek W. R., Chen C. L. Further characterization of Marek's disease virus-infected lymphocytes. I. In vivo infection. Int J Cancer. 1984 Mar 15;33(3):389–398. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill A. E., Biggs P. M. Agent of Marek's disease in tissue culture. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):528–530. doi: 10.1038/215528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Purchase H. G., Bockman D. E., Gathings W. E. Studies on the nature of the abnormality of B cell differentiation in avian lymphoid leukosis: production of heterogeneous IgM by tumor cells. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1210–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert D. L., Avdalovic N., Goldstein C. Follicular exclusion of retroviruses in the bursa of Fabricius. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert D. L., Weber W. T. Effect of phorbol myristate acetate on in vitro growth of lymphocytes from the chicken thymus and bursa of Fabricius. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;238:67–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J. W., Farrow W. M., Prickett C. O., Smith M. E., Campbell W. F., Groupè V. Responses of isolator-derived and conventional chickens to Marek's disease herpesvirus and avian leukosis virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 May;52(5):1491–1497. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.5.1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J. W., Groupé V. Interactions between Marek's disease herpesvirus and avian leucosis virus in tissue culture. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 24;234(47):125–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio234125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier J. A. Ultrastructure of lymphoid tissue from chicks infected with Marek's disease virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Mar;52(3):829–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakovleva L. S., Mazurenko N. P. Increased susceptibility of leukemia-infected chickens to Marek's disease. Neoplasma. 1979;26(4):393–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeurissen S. H., Scholten R., Hilgers L. A., Pol J. M., De Boer G. F. In situ detection by monoclonal antibody D-35.1 of cells infected with Marek's disease virus that interact with splenic ellipsoid-associated reticulum cells. Avian Dis. 1989 Oct-Dec;33(4):657–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E., Gehly E. B., Carlson L. M., Cotter R. C., Thompson C. B. Bursal stem cells as targets for myc-induced preneoplastic proliferation and maturation arrest. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;141:67–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74006-0_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P., Wolf C., Enrietto P. J., Cooper G. M. A retroviral myc gene induces preneoplastic transformation of lymphocytes in a bursal transplantation assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):222–226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. P., Kufe D., Schlom J., Frankel J. W., Prickett C. O., Groupé V., Spiegelman S. Biological and biochemical evidence for an interaction between Marek's disease herpesvirus and avian leukosis virus in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3175–3178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Markham P. D., Josephs S. F., Sturzenegger S., Kaplan M., Halligan G., Biberfeld P., Wong-Staal F., Kramarsky B. Isolation of a new virus, HBLV, in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):596–601. doi: 10.1126/science.2876520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shek W. R., Calnek B. W., Schat K. A., Chen C. H. Characterization of Marek's disease virus-infected lymphocytes: discrimination between cytolytically and latently infected cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Mar;70(3):485–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. J., Witter R. L., Nazerian K., Burmester B. R. Studies on the etiology of Marek's disease. I. Propagation of the agent in cell culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):173–177. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieber V. L., Zalinskis L. L., Silva R. F., Finkelstein A., Coussens P. M. Transactivation of the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat promoter by Marek's disease virus. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):719–727. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90139-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen P., Toivanen A. Bursal and postbursal stem cells in chicken. Functional characteristics. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Sep;3(9):585–595. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G., Clifford P., Santesson L. EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/2281056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]