Abstract
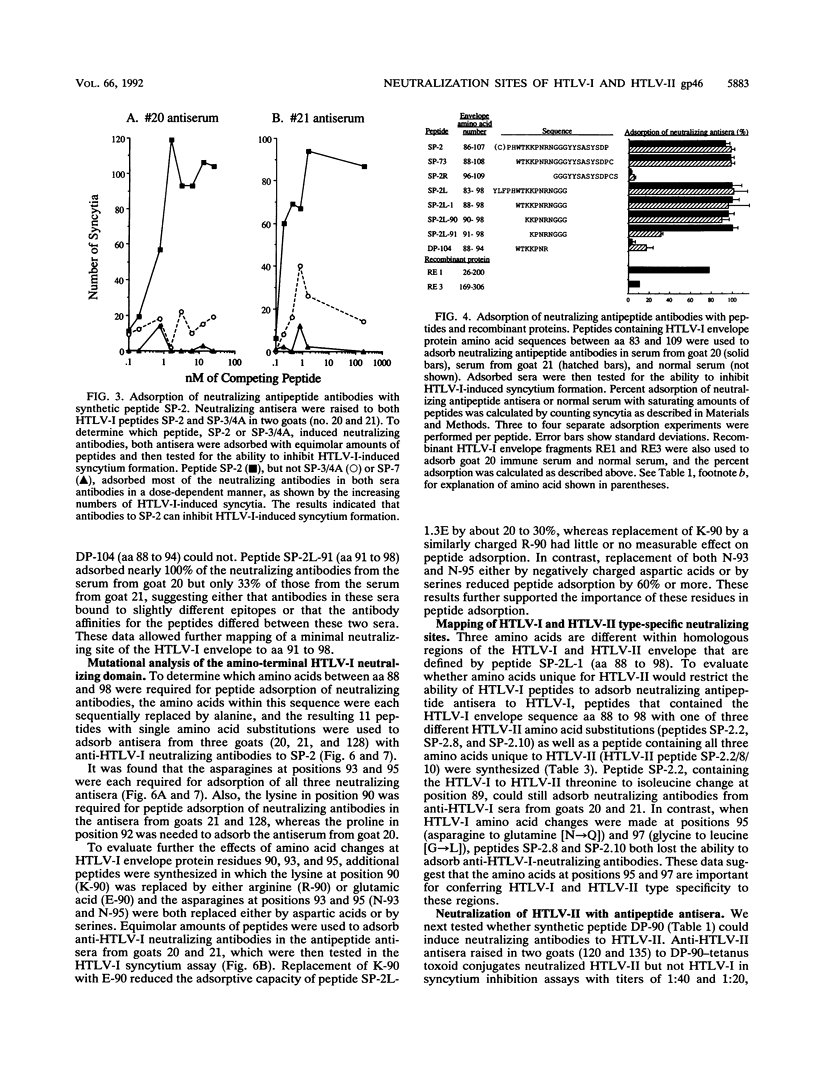
Twelve synthetic peptides containing hydrophilic amino acid sequences of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) envelope glycoprotein were coupled to tetanus toxoid and used to raise epitope-specific antisera in goats and rabbits. Low neutralizing antibody titers (1:10 to 1:20) raised in rabbits to peptides SP-2 (envelope amino acids [aa] 86 to 107), SP-3 (aa 176 to 189), and SP-4A (aa 190 to 209) as well as to combined peptide SP-3/4A (aa 176 to 209) were detected in the vesicular stomatitis virus-HTLV-I pseudotype assay. Higher-titered neutralizing antibody responses to HTLV-I (1:10 to 1:640) were detected with pseudotype and syncytium inhibition assays in four goats immunized with a combined inoculum containing peptides SP-2, SP-3, and SP-4A linked to tetanus toxoid. These neutralizing anti-HTLV-I antibodies were type specific in that they did not inhibit HTLV-II syncytium formation. Neutralizing antibodies in sera from three goats could be absorbed with peptide SP-2 (aa 86 to 107) as well as truncated peptides containing envelope aa 90 to 98, but not with equimolar amounts of peptides lacking envelope aa 90 to 98. To map critical amino acids that contributed to HTLV-I neutralization within aa 88 to 98, peptides in which each amino acid was sequentially replaced by alanine were synthesized. The resulting 11 synthetic peptides with single alanine substitutions were then used to absorb three neutralizing goat antipeptide antisera. Both asparagines at positions 93 and 95 were required for adsorption of neutralizing anti-HTLV-I antibodies from all three sera. Peptide DP-90, containing the homologous region of HTLV-II envelope glycoprotein (aa 82 to 97), elicited antipeptide neutralizing antibodies to HTLV-II in goats that were type specific. In further adsorption experiments, it was determined that amino acid differences between homologous HTLV-I and HTLV-II envelope sequences at HTLV-I aa 95 (N to Q) and 97 (G to L) determined the type specificity of these neutralizing sites. Thus, the amino-terminal regions of HTLV-I and -II gp46 contain homologous, linear, neutralizing determinants that are type specific.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball J. M., Rushlow K. E., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Detailed mapping of the antigenicity of the surface unit glycoprotein of equine infectious anemia virus by using synthetic peptide strategies. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):732–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.732-742.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Gregory T. J., Riddle L., Nakamura G. R., Champe M. A., Porter J. P., Wurm F. M., Hershberg R. D., Cobb E. K., Eichberg J. W. Protection of chimpanzees from infection by HIV-1 after vaccination with recombinant glycoprotein gp120 but not gp160. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):622–625. doi: 10.1038/345622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUICKSHANK E. K. A neuropathic syndrome of uncertain origin; review of 100 cases. West Indian Med J. 1956 Sep;5(3):147–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P., Nagy K., Weiss R. A. Pseudotypes of human T-cell leukemia virus types 1 and 2: neutralization by patients' sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. J., Price-Jones M. J., Stephens P. E., Sutton C., Schulz T. F., Clapham P. R., McKeating J. A., McClure M. O., Thomson S., Marsh M. The V3 loops of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 surface glycoproteins contain proteolytic cleavage sites: a possible function in viral fusion? AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jan;7(1):3–16. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., McClure M. A., Johnson M. S. Retrovirus phylogeny and evolution. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:1–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzolo L., Duc Dodon M. Direct activation of resting T lymphocytes by human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):714–717. doi: 10.1038/326714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessain A., Barin F., Vernant J. C., Gout O., Maurs L., Calender A., de Thé G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985 Aug 24;2(8452):407–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92734-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. K., Ernisse B. J., Jarrett O., Jones F. R. Feline leukemia virus envelope gp70 of subgroups B and C defined by monoclonal antibodies with cytotoxic and neutralizing functions. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3042–3048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. K., Palker T. J., Matthews T. J., Langlois A. J., Lerche N. W., Martin M. E., Scearce R. M., McDanal C., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Synthetic peptides containing T and B cell epitopes from human immunodeficiency virus envelope gp120 induce anti-HIV proliferative responses and high titers of neutralizing antibodies in rhesus monkeys. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2677–2685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Koito A., Takatsuki K., Kido H., Katunuma N. Involvement of tryptase-related cellular protease(s) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Miller S. E., Palker T. J., Moore J. O., Dunn P. H., Bolognesi D. P., Metzgar R. S. Identification of human T cell leukemia virus in a Japanese patient with adult T cell leukemia and cutaneous lymphomatous vasculitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2054–2058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. S., Boyle T. J., Lyerly H. K., Cullen B. R. Identification of the envelope V3 loop as the primary determinant of cell tropism in HIV-1. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1905842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ijichi S., Matsuda T., Maruyama I., Izumihara T., Kojima K., Niimura T., Maruyama Y., Sonoda S., Yoshida A., Osame M. Arthritis in a human T lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) carrier. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Sep;49(9):718–721. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.9.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ina Y., Gojobori T. Molecular evolution of human T-cell leukemia virus. J Mol Evol. 1990 Dec;31(6):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF02102076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Yamato K., Iwahara Y., Eguchi T., Uemura Y., Takehara N., Ohtsuki Y., Taguchi H., Miyoshi I. Isolation of HTLV-I from muscle of a patient with polymyositis. Am J Med. 1991 Feb;90(2):267–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalyanaraman V. S., Sarngadharan M. G., Robert-Guroff M., Miyoshi I., Golde D., Gallo R. C. A new subtype of human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-II) associated with a T-cell variant of hairy cell leukemia. Science. 1982 Nov 5;218(4572):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.6981847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Gritz L., Stallard G., Cranage M. P., Collignon C., Thiriart C., Corcoran T., Silvera P., Stott E. J. Production and of monoclonal antibodies to simian immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins. AIDS. 1991 Jul;5(7):829–836. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199107000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido H., Fukutomi A., Katunuma N. A novel membrane-bound serine esterase in human T4+ lymphocytes immunologically reactive with antibody inhibiting syncytia induced by HIV-1. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21979–21985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima I., Maruyama I., Maruyama Y., Ijichi S., Eiraku N., Mimura Y., Osame M. Polyarthritis in human T lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Oct;32(10):1342–1344. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiser C., Schneider J., Bayer H., Hunsmann G. Immunoprevention of Friend leukaemia virus-induced erythroleukaemia by vaccination with aggregated gp70. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1901–1907. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata A., Palker T. J., Streilein R. D., Scearce R. M., Haynes B. F., Berzofsky J. A. Immunodominant sites of human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 envelope protein for murine helper T cells. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):2024–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGrenade L., Hanchard B., Fletcher V., Cranston B., Blattner W. Infective dermatitis of Jamaican children: a marker for HTLV-I infection. Lancet. 1990 Dec 1;336(8727):1345–1347. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92896-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Davide J. P., Weinhold K., Waterbury J. A., Profy A. T., Lewis J. A., Langlois A. J., Dreesman G. R., Boswell R. N., Shadduck P. Conserved sequence and structural elements in the HIV-1 principal neutralizing determinant. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2392685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal R. B., Rudolph D. L., Kaplan J. E., Hjelle B., Levine P. H., Coligan J. E., Viscidi R. P. Identification of immunodominant epitopes in envelope glycoprotein of human T lymphotropic virus type II. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):274–279. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90081-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., DeSantis P., Mark G., Pfeifer A., Newman M., Gibbs N., Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C., Clark J. HTLV-I--associated B-cell CLL: indirect role for retrovirus in leukemogenesis. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1103–1106. doi: 10.1126/science.2883731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita S., Robert-Guroff M., Trepel J., Cossman J., Mitsuya H., Broder S. Human monoclonal antibody directed against an envelope glycoprotein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2672–2676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan O. S., Rodgers-Johnson P., Mora C., Char G. HTLV-1 and polymyositis in Jamaica. Lancet. 1989 Nov 18;2(8673):1184–1187. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91793-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai K., Tachibana N., Shioiri S., Shishime E., Okayama A., Ishizaki J., Tsuda K., Mueller N. Suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity to PPD and PHA in elderly HTLV-I carriers. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(10):1006–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy K., Clapham P., Cheingsong-Popov R., Weiss R. A. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I: induction of syncytia and inhibition by patients' sera. Int J Cancer. 1983 Sep 15;32(3):321–328. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Hayami M., Ohta Y., Ishikawa K., Tsujimoto H., Kiyokawa T., Yoshida M., Sasagawa A., Honjo S. Protection of cynomolgus monkeys against infection by human T-cell leukemia virus type-I by immunization with viral env gene products produced in Escherichia coli. Int J Cancer. 1987 Sep 15;40(3):403–407. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka K., Maruyama I., Sato K., Kitajima I., Nakajima Y., Osame M. Chronic inflammatory arthropathy associated with HTLV-I. Lancet. 1989 Feb 25;1(8635):441–441. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osame M., Usuku K., Izumo S., Ijichi N., Amitani H., Igata A., Matsumoto M., Tara M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986 May 3;1(8488):1031–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Clark M. E., Langlois A. J., Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Randall R. R., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Type-specific neutralization of the human immunodeficiency virus with antibodies to env-encoded synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Clark M. E., Sarngadharan M. G., Matthews T. J. Purification of envelope glycoproteins of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) by affinity chromatography. J Virol Methods. 1987 Dec;18(4):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Matthews T. J., Langlois A., Tanner M. E., Martin M. E., Scearce R. M., Kim J. E., Berzofsky J. A., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Polyvalent human immunodeficiency virus synthetic immunogen comprised of envelope gp120 T helper cell sites and B cell neutralization epitopes. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3612–3619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Tanner M. E., Scearce R. M., Streilein R. D., Clark M. E., Haynes B. F. Mapping of immunogenic regions of human T cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) gp46 and gp21 envelope glycoproteins with env-encoded synthetic peptides and a monoclonal antibody to gp46. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):971–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Reitz M. S., Kalyanaraman V. S., Gallo R. C. Isolation of a new type C retrovirus (HTLV) in primary uncultured cells of a patient with Sézary T-cell leukaemia. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):268–271. doi: 10.1038/294268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Reitz M. S., Jr, Sarngadharan M. G., Robert-Guroff M., Kalyanaraman V. S., Nakao Y., Miyoshi I., Minowada J., Yoshida M., Ito Y. The virus of Japanese adult T-cell leukaemia is a member of the human T-cell leukaemia virus group. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):63–66. doi: 10.1038/300063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portetelle D., Dandoy C., Burny A., Zavada J., Siakkou H., Gras-Masse H., Drobecq H., Tartar A. Synthetic peptides approach to identification of epitopes on bovine leukemia virus envelope glycoprotein gp51. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):34–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODGERS P. E. THE CLINICAL FEATURES AND AETIOLOGY OF THE NEUROPATHIC SYNDROME IN JAMAICA. West Indian Med J. 1965 Mar;14:36–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston S., Hoeprich P., Akita R. Identification and synthesis of the epitope for a human monoclonal antibody which can neutralize human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16343–16346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Stephens R. M., Couez D., Deschamps J., Kettmann R., Burny A., Gilden R. V. The nucleotide sequence of the env gene and post-env region of bovine leukemia virus. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román G. C., Schoenberg B. S., Madden D. L., Sever J. L., Hugon J., Ludolph A., Spencer P. S. Human T-lymphotropic virus type I antibodies in the serum of patients with tropical spastic paraparesis in the Seychelles. Arch Neurol. 1987 Jun;44(6):605–607. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520180029011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose R. M., O'Hara C. J., Harbison M. A., Pinkston P., Marselle L. M., Deleo M., Hammer S. M. Infiltration of the lower respiratory tract by helper/inducer T lymphocytes in HTLV-1-associated adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Am J Med. 1991 Jan;90(1):118–123. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90514-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. D., Gasson J. C., Glaspy J., Bhuta S., Aboud M., Chen I. S., Golde D. W. Relationship between human T cell leukemia virus-II and atypical hairy cell leukemia: a serologic study of hairy cell leukemia patients. Leukemia. 1987 Apr;1(4):397–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel K. P., Lautenberger J. A., Jorcyk C. L., Josephs S., Wong-Staal F., Papas T. S. Diagnostic potential for human malignancies of bacterially produced HTLV-I envelope protein. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1094–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.6208612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafferman A., Jahrling P. B., Benveniste R. E., Lewis M. G., Phipps T. J., Eden-McCutchan F., Sadoff J., Eddy G. A., Burke D. S. Protection of macaques with a simian immunodeficiency virus envelope peptide vaccine based on conserved human immunodeficiency virus type 1 sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7126–7130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shida H., Tochikura T., Sato T., Konno T., Hirayoshi K., Seki M., Ito Y., Hatanaka M., Hinuma Y., Sugimoto M. Effect of the recombinant vaccinia viruses that express HTLV-I envelope gene on HTLV-I infection. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3379–3384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02660.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Patarca R., Perkins D., Briggs D., Lee T. H., Essex M., Coligan J., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Haseltine W. A. Sequence of the envelope glycoprotein gene of type II human T lymphotropic virus. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):421–424. doi: 10.1126/science.6204380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi H., Miyoshi I. Immune suppression in HTLV-I carriers: a predictive sign of adult T-cell leukemia. Acta Med Okayama. 1989 Dec;43(6):317–321. doi: 10.18926/AMO/30865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Zeng L., Shiraki H., Shida H., Tozawa H. Identification of a neutralization epitope on the envelope gp46 antigen of human T cell leukemia virus type I and induction of neutralizing antibody by peptide immunization. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):354–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. K., Weber J. N., McClure J., Clapham P. R., Singhal M. C., Shriver M. K., Weiss R. A. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the AIDS virus. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):25–29. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Yodoi J., Sagawa K., Takatsuki K., Uchino H. Adult T-cell leukemia: clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):481–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernant J. C., Maurs L., Gessain A., Barin F., Gout O., Delaporte J. M., Sanhadji K., Buisson G., de-Thé G. Endemic tropical spastic paraparesis associated with human T-lymphotropic virus type I: a clinical and seroepidemiological study of 25 cases. Ann Neurol. 1987 Feb;21(2):123–130. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Miyoshi I., Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






