Abstract
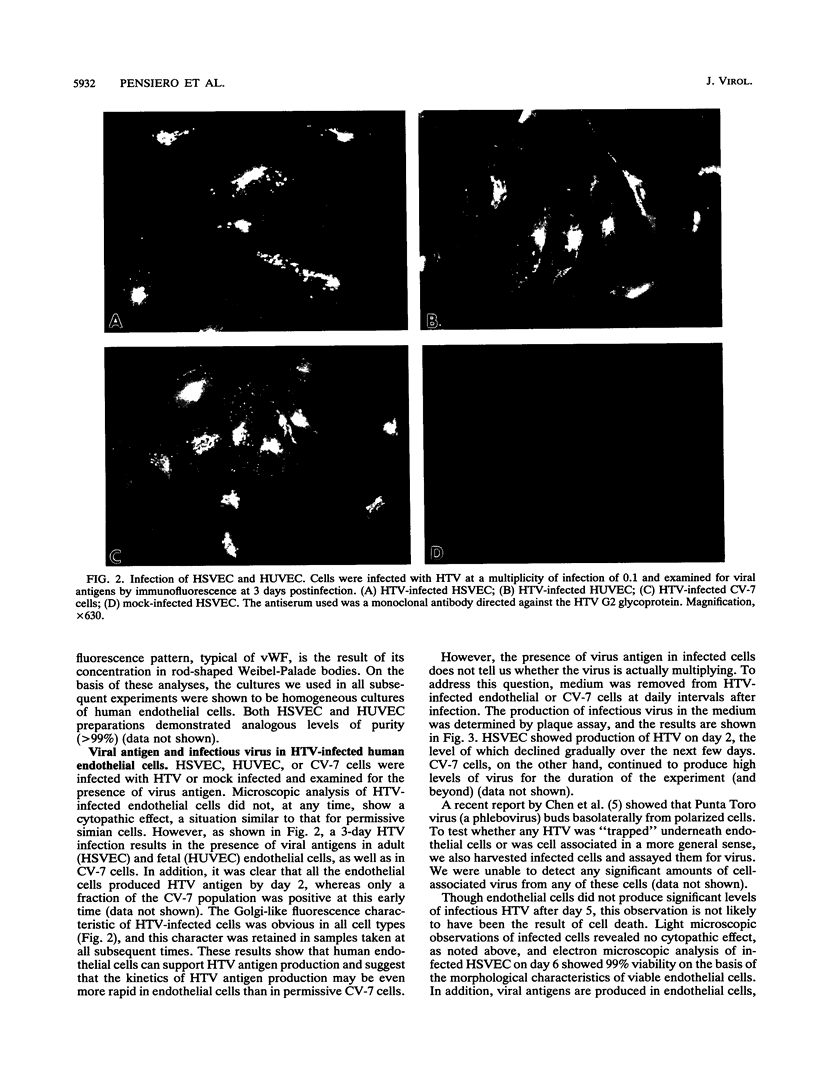
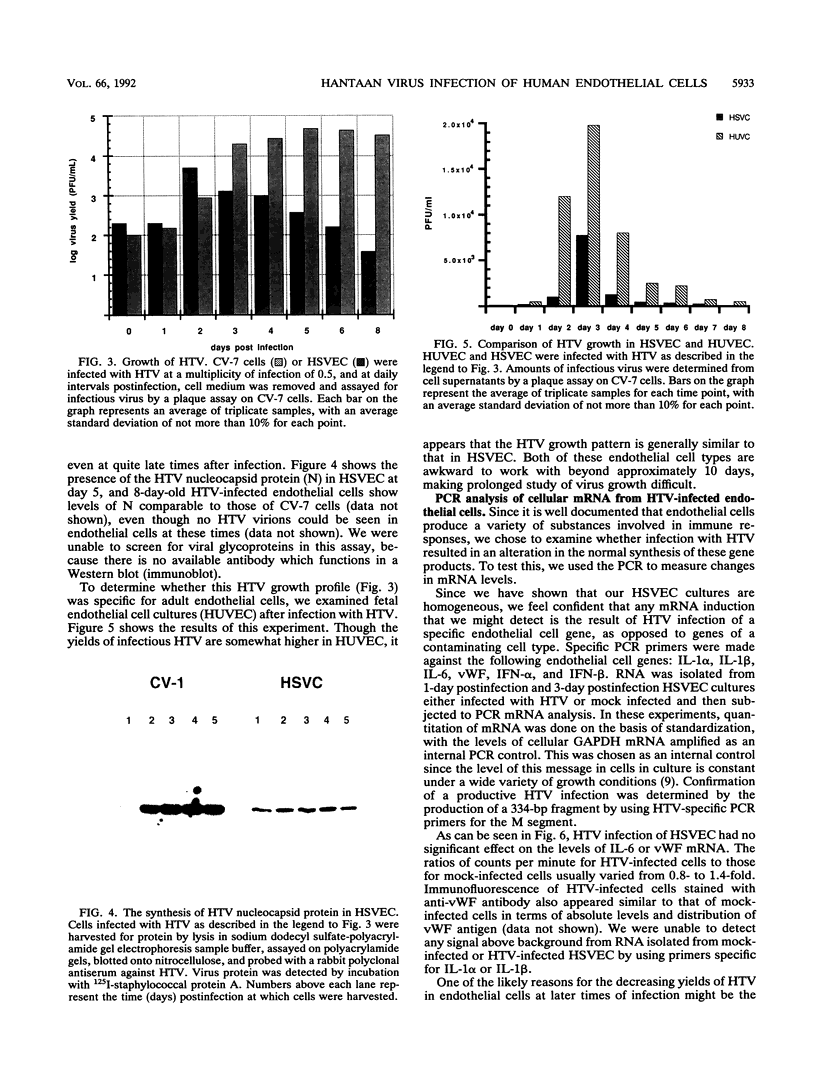
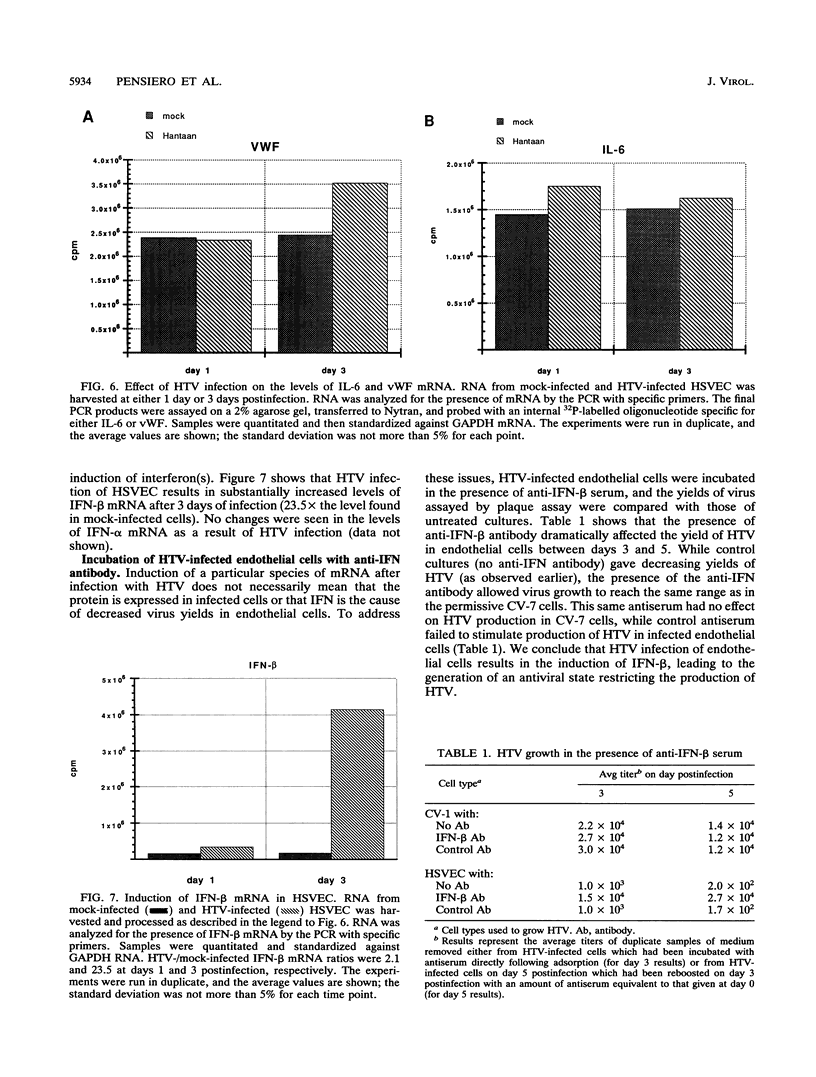
The primary pathophysiologic finding of the viral disease known as Korean hemorrhagic fever, the etiological agent of which is Hantaan virus (HTV), is vascular instability. To investigate whether HTV was able to infect cells derived from human vascular tissue and alter their behavior, we infected in vitro primary adult human endothelial cells from saphenous veins (HSVEC). We were able to detect the presence of viral antigens in infected cells both by immunofluorescence and by Western blot (immunoblot) analysis as early as day 1 postinfection. HSVEC infected with HTV produce infectious virus during the first 3 days of infection but, at later times (days 4 to 8), show decreasing yields of virus. This contrasts with the HTV growth pattern observed for the permissive simian CV-7 cell line, which generates infectious virus up to day 12 after infection. Further investigation showed that the late decrease in viral production in HSVEC is the result of the induction of beta interferon and can be reversed by the addition of anti-beta interferon serum to the culture medium. At no time during the course of infection of HSVEC with HTV was any obvious cytopathic effect observed. When tests for changes in mRNA levels of other cytokines and endothelial cell gene products following HTV infection of HSVEC were done by reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction methods, no significant changes were observed in the levels of interleukin 1, interleukin 6, or von Willebrand factor mRNA. We hypothesize that, while HTV can replicate in human vascular endothelial cells, the mechanism of microvascular damage seen with Korean hemorrhagic fever is not likely to be a direct effect of virus replication but may conceivably be the consequence of an immune-mediated endothelial injury triggered by viral infection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asada H., Tamura M., Kondo K., Dohi Y., Yamanishi K. Cell-mediated immunity to virus causing haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2179–2188. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty B. J., Calisher C. H. Bunyaviridae--natural history. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;169:27–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthron D., Orr E. C., Mitsock L. M., Ginsburg D., Handin R. I., Orkin S. H. Nucleotide sequence of pre-pro-von Willebrand factor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7125–7127. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavender D. E., Edelbaum D., Welkovich L. Effects of inflammatory cytokines and phorbol esters on the adhesion of U937 cells, a human monocyte-like cell line, to endothelial cell monolayers and extracellular matrix proteins. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jun;49(6):566–578. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.6.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Y., Matsuoka Y., Compans R. W. Assembly and polarized release of Punta Toro virus and effects of brefeldin A. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1427–1439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1427-1439.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgriff T. M. Mechanisms of disease in Hantavirus infection: pathophysiology of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):97–107. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino F., Torcia M., Aldinucci D., Ziche M., Almerigogna F., Bani D., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 is an autocrine regulator of human endothelial cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6487–6491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dveksler G. S., Basile A. A., Dieffenbach C. W. Analysis of gene expression: use of oligonucleotide primers for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 May;1(4):283–285. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.4.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo L. F. The complexity of endothelial cells. A review. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Aug;92(2):241–250. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/92.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Friedman R. M., Joe S., Baca L. M., Turpin J. A., Dveksler G., Meltzer M. S., Dieffenbach C. A selective defect of interferon alpha production in human immunodeficiency virus-infected monocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1433–1442. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grcevska L., Polenaković M., Oncevski A., Zografski D., Gligić A. Different pathohistological presentations of acute renal involvement in Hantaan virus infection: report of two cases. Clin Nephrol. 1990 Nov;34(5):197–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen H., Mestan J., Mittnacht S., Dieffenbach C. W. Beta interferon subtype 1 induction by tumor necrosis factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3037–3042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata T., Tsai T. F., Bauer S. P., McCormick J. B. Immunofluorescence studies of disseminated Hantaan virus infection of suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):391–398. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.391-398.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDuc J. W. Epidemiology of hemorrhagic fever viruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11 (Suppl 4):S730–S735. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_4.s730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C., Yanagihara R. Serotypic classification of hantaviruses by indirect immunofluorescent antibody and plaque reduction neutralization tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):940–944. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.940-944.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. M., Lee H. W., See A. F., Parrish D. B., Moon J. S., Kim D. J., Cosgriff T. M. Changes in populations of immune effector cells during the course of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Mar-Apr;85(2):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Worrall N. K., Shelton-Inloes B. B., Sorace J. M., Alevy Y. G., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19514–19527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani A., Dejana E. Cytokines as communication signals between leukocytes and endothelial cells. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):370–375. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani A., Sica A., Colotta F., Dejana E. The role of cytokines as communication signals between leukocytes and endothelial cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;349:343–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensiero M. N., Jennings G. B., Schmaljohn C. S., Hay J. Expression of the Hantaan virus M genome segment by using a vaccinia virus recombinant. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):696–702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.696-702.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. Cytokines and endothelial cell biology. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):427–451. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn C. S., Hasty S. E., Harrison S. A., Dalrymple J. M. Characterization of Hantaan virions, the prototype virus of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1005–1012. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn C. S., Schmaljohn A. L., Dalrymple J. M. Hantaan virus M RNA: coding strategy, nucleotide sequence, and gene order. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharefkin J. B., Fairchild K. D., Albus R. A., Cruess D. F., Rich N. M. The cytotoxic effect of surgical glove powder particles on adult human vascular endothelial cell cultures: implications for clinical uses of tissue culture techniques. J Surg Res. 1986 Nov;41(5):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(86)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Asada H., Kondo K., Takahashi M., Yamanishi K. Effects of human and murine interferons against hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) virus (Hantaan virus). Antiviral Res. 1987 Nov;8(4):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum S. H., Gralnick H. R. Gamma-interferon modulates von Willebrand factor release by cultured human endothelial cells. Blood. 1990 Jun 1;75(11):2177–2184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Samuel J. E., Perera L. P., Sharefkin J. B., O'Brien A. D. Evaluation of the role of Shiga and Shiga-like toxins in mediating direct damage to human vascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):344–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao S. Y., Yanagihara R., Godec M. S., Eldadah Z. A., Johnson B. K., Gajdusek D. C., Asher D. M. Detection of hantavirus RNA in tissues of experimentally infected mice using reverse transcriptase-directed polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1991 Apr;33(4):277–282. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890330413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara R., Silverman D. J. Experimental infection of human vascular endothelial cells by pathogenic and nonpathogenic hantaviruses. Arch Virol. 1990;111(3-4):281–286. doi: 10.1007/BF01311063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. T., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Interferon alpha inhibits vesicular stomatitis virus primary transcript accumulation in P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase-deficient human fibroblast cells. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1987 Oct-Dec;1(4):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]