Abstract
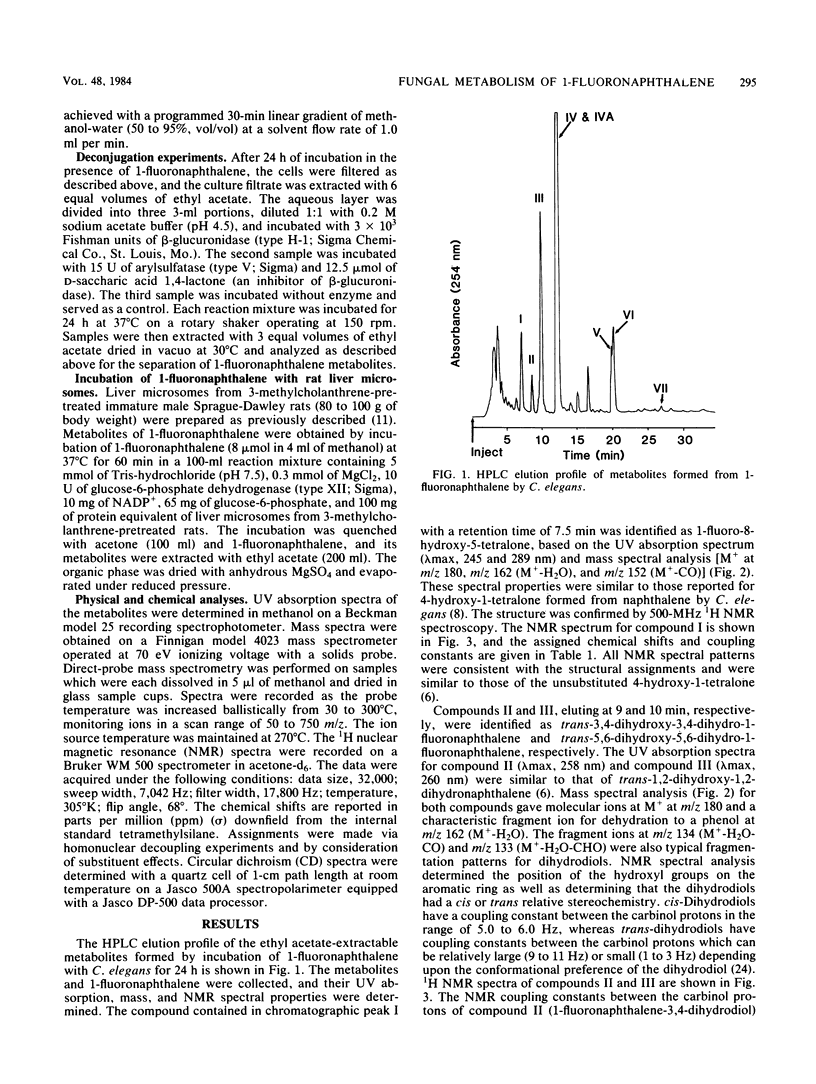
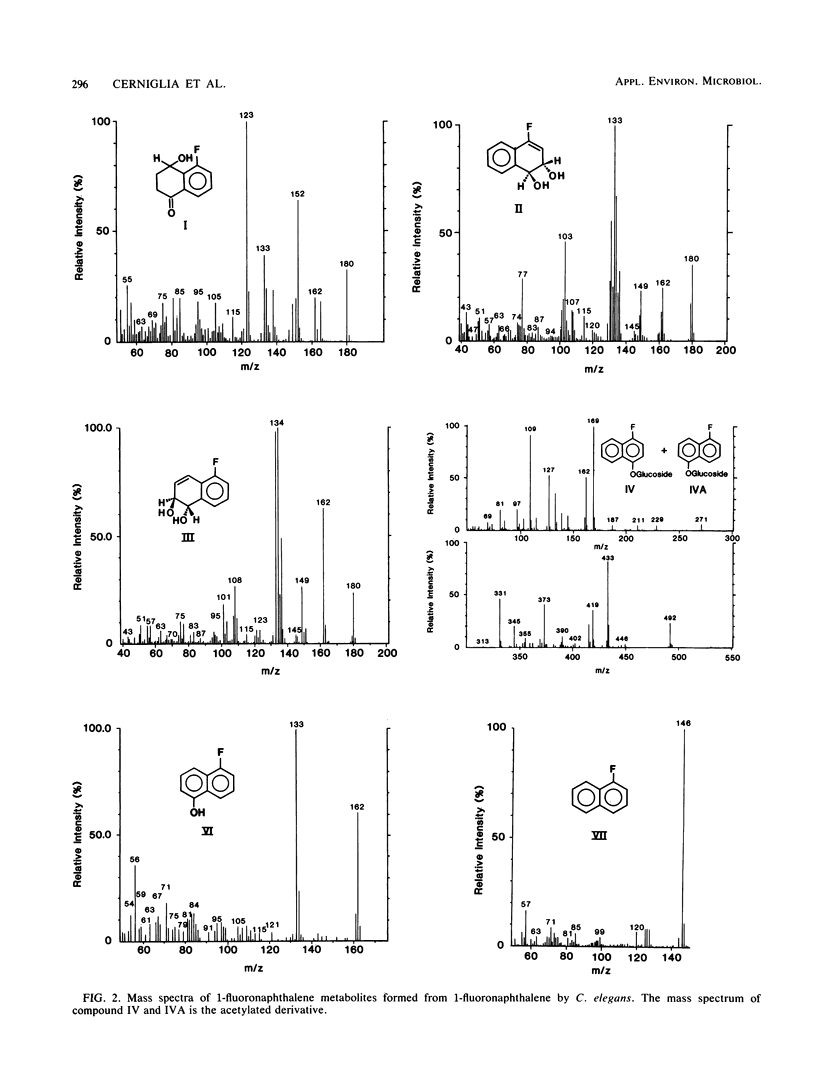
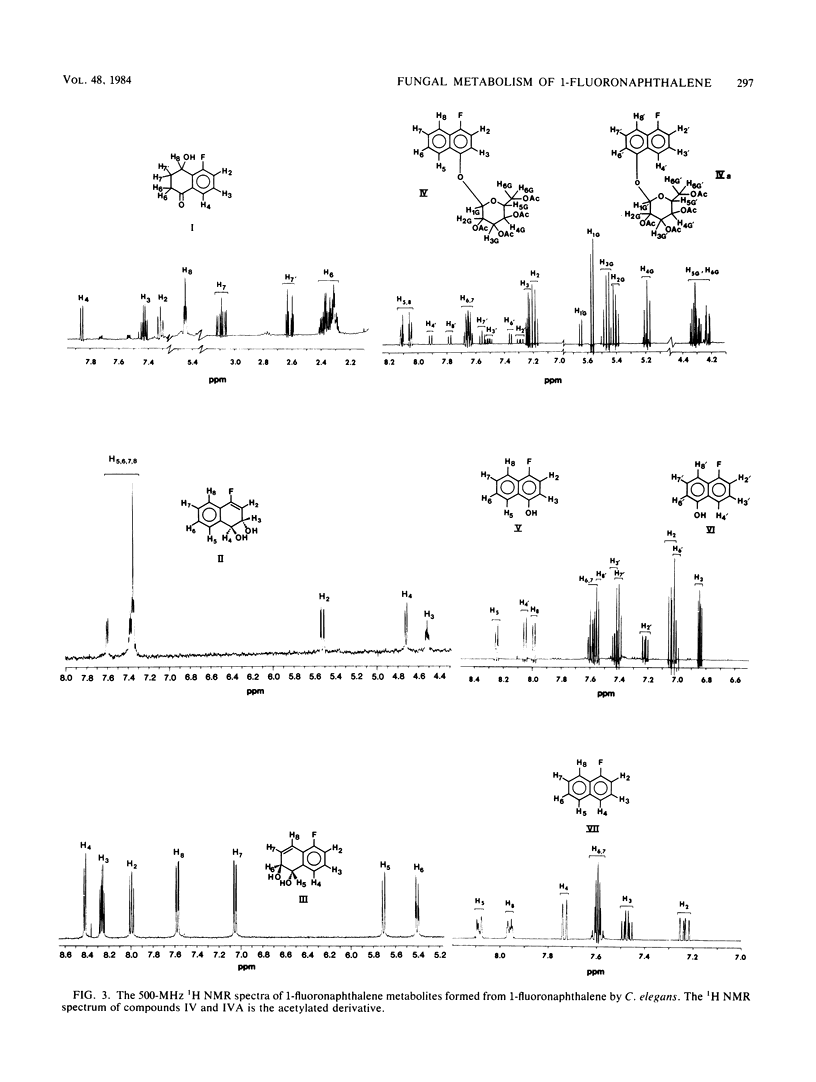
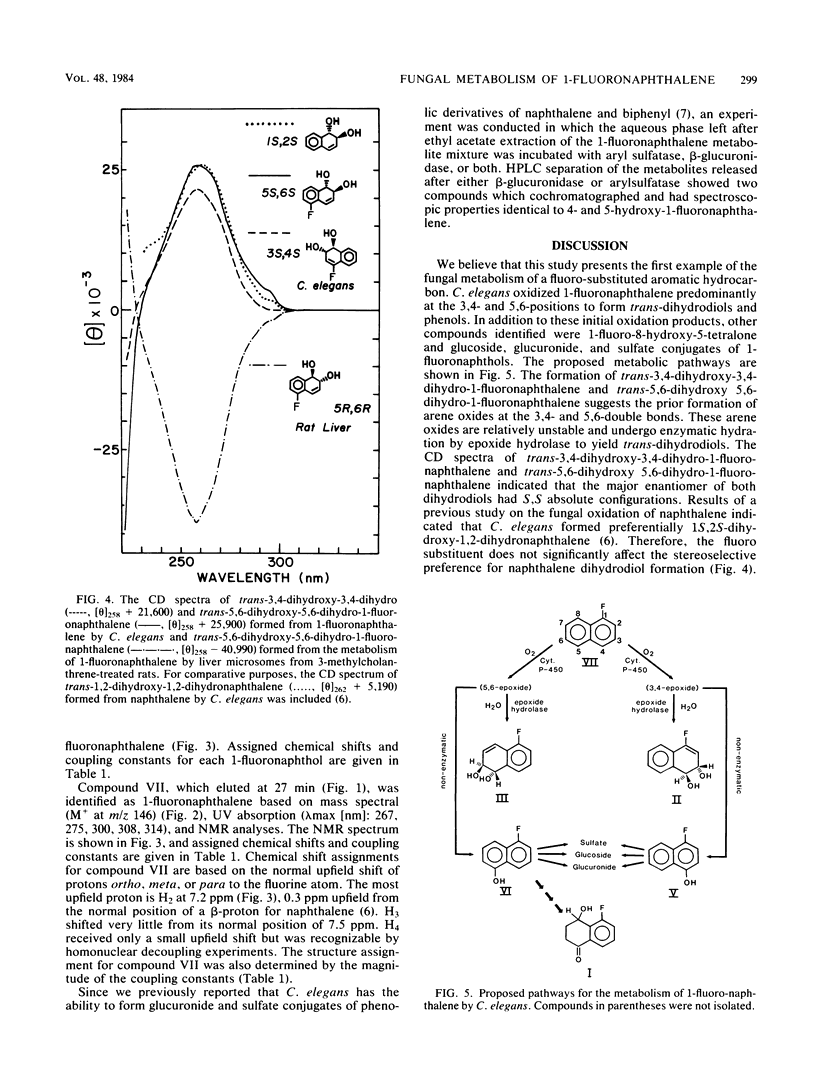
The metabolism of 1-fluoronaphthalene by Cunninghamella elegans ATCC 36112 was studied. The metabolites were isolated by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography and characterized by the application of UV absorption, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance, and mass spectral techniques. C. elegans oxidized 1-fluoronaphthalene predominantly at the 3,4- and 5,6-positions to form trans-3,4-dihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-1-fluoronaphthalene and trans-5,6-dihydroxy-5,6-dihydro-1-fluoronaphthalene. In addition, 1-fluoro-8-hydroxy-5-tetralone, 5-hydroxy-1-fluoronaphthalene, and 4-hydroxy-1-fluoronaphthalene as well as glucoside, sulfate, and glucuronic acid conjugates of these phenols were formed. Circular dichroism spectra of the trans-3,4- and trans-5,6-dihydrodiols formed from 1-fluoronaphthalene indicated that the major enantiomers of the dihydrodiols have S,S absolute stereochemistries. In contrast, the trans-5,6-dihydrodiol formed from 1-fluoronaphthalene from 3-methylcholanthrene-treated rats had Cotton effects that are opposite in sign (R,R) to those formed by C. elegans. The results indicate that the fungal monooxygenase-epoxide hydrolase systems are highly stereoselective in the metabolism of 1-fluoronaphthalene and that a fluoro substituent blocks epoxidation at the fluoro-substituted double bond, decreases oxidation at the aromatic double bond that is peri to the fluoro substituent, and enhances metabolism at the 3,4- and 5,6-positions of 1-fluoronaphthalene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd D. R., Daly J. W., Jerina D. M. Rearrangement of (1- 2 H)- and (2- 2 H)naphthalene 1,2-oxides to 1-naphthol. Mechanism of the NIH shift. Biochemistry. 1972 May 9;11(10):1961–1966. doi: 10.1021/bi00760a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan D. B., Tripp B. W. Determination of hydrocarbons in seawater extracts of crude oil and crude oil fractions. Nature. 1971 Mar 5;230(5288):44–47. doi: 10.1038/230044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Althaus J. R., Evans F. E., Freeman J. P., Mitchum R. K., Yang S. K. Stereochemistry and evidence for an arene oxide-NIH shift pathway in the fungal metabolism of naphthalene. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Apr-May;44(1-2):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Freeman J. P., Mitchum R. K. Glucuronide and sulfate conjugation in the fungal metabolism of aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1070–1075. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1070-1075.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Gibson D. T. Metabolism of naphthalene by Cunninghamella elegans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):363–370. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.363-370.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Gibson D. T. Metabolism of naphthalene by cell extracts of Cunninghamella elegans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Feb;186(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Hebert R. L., Szaniszlo P. J., Gibson D. T. Fungal transformation of naphthalene. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):135–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00402301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou M. W., Yang S. K. Combined reversed-phase and normal-phase high-performance liquid chromatography in the purification and identification of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene metabolites. J Chromatogr. 1979 Dec 20;185:635–654. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)85637-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris J. P., Fasco M. J., Stylianopoulou F. L., Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Jeffrey A. M. Monooxygenase activity in Cunninghamella bainieri: evidence for a fungal system similar to liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 May;156(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Witkop B., Zaltzman-Nirenberg P., Udenfriend S. 1,2-naphthalene oxide as an intermediate in the microsomal hydroxylation of naphthalene. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 6;9(1):147–156. doi: 10.1021/bi00803a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Witkop B., Zaltzman-Nirenberg P., Udenfriend S. The role of arene oxide-oxepin systems in the metabolism of aromatic substrates. 3. Formation of 1,2-naphthalene oxide from naphthalene by liver microsomes. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Nov 6;90(23):6525–6527. doi: 10.1021/ja01025a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Craig W. K., Smith P. J. Water-soluble hydrocarbons from crude oil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1974 Aug;12(2):212–217. doi: 10.1007/BF01684964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. V., Rosazza J. P. Microbial models of mammalian metabolism. Aromatic hydroxylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Apr 2;161(2):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


