Abstract
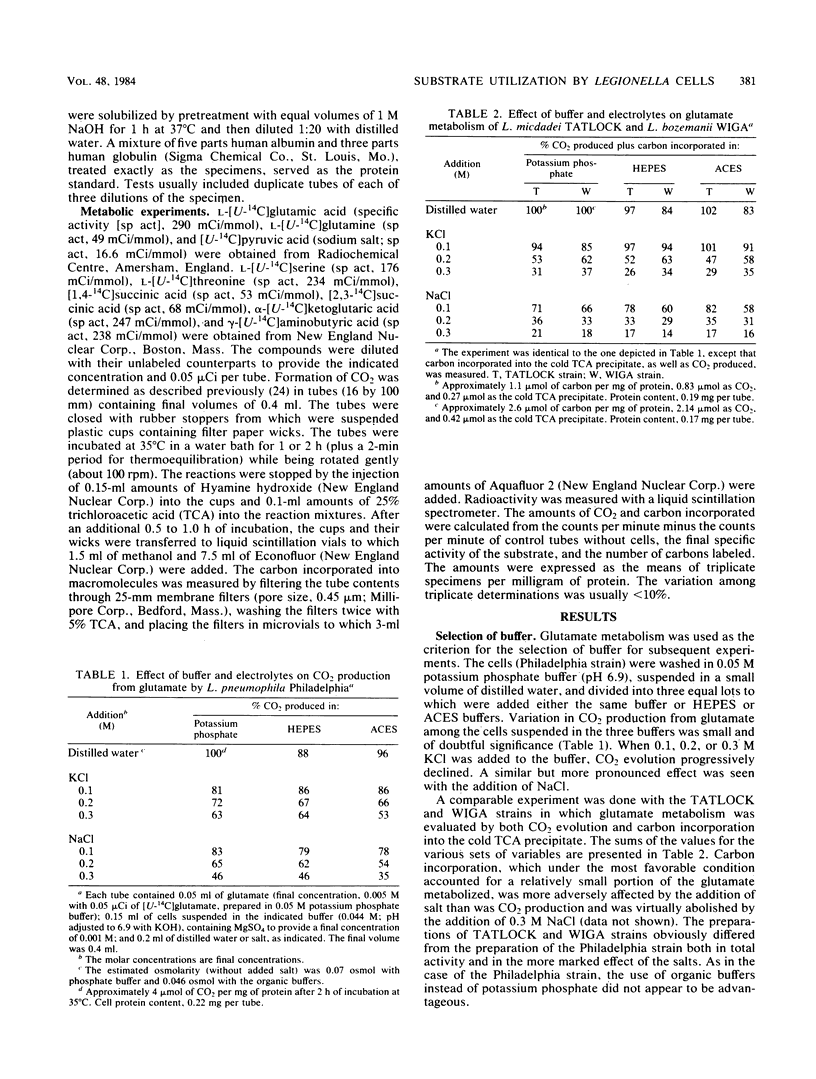
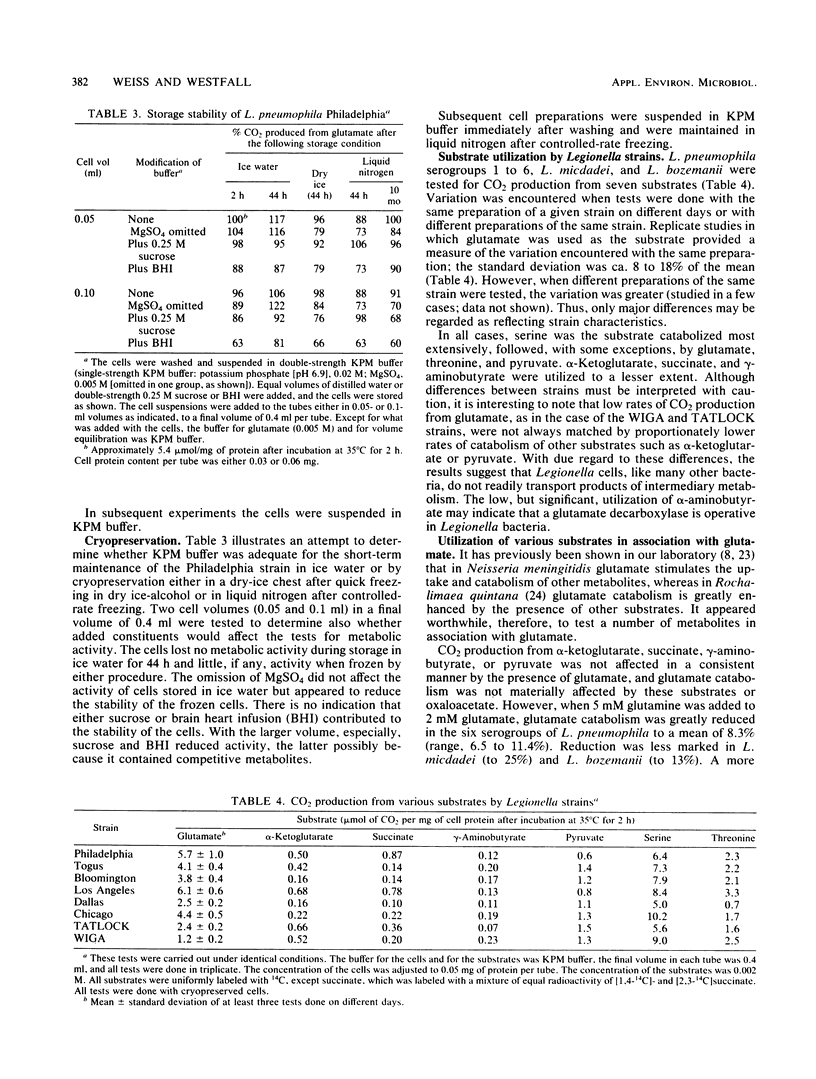
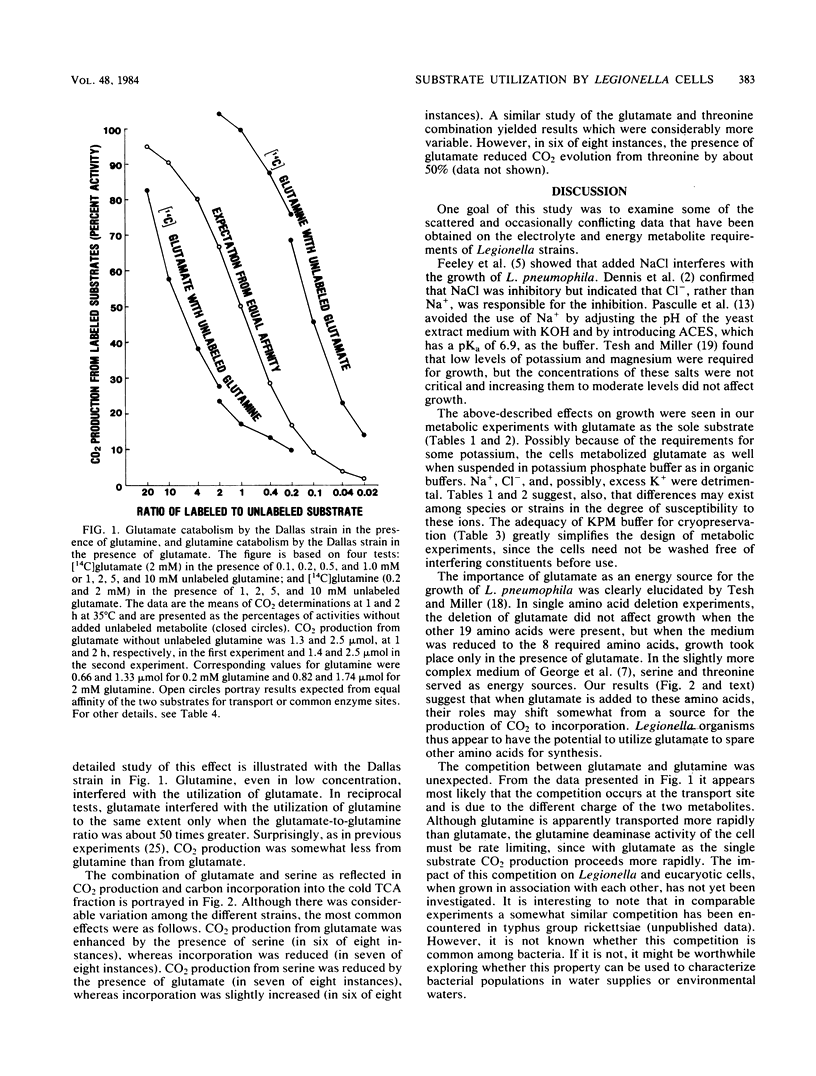
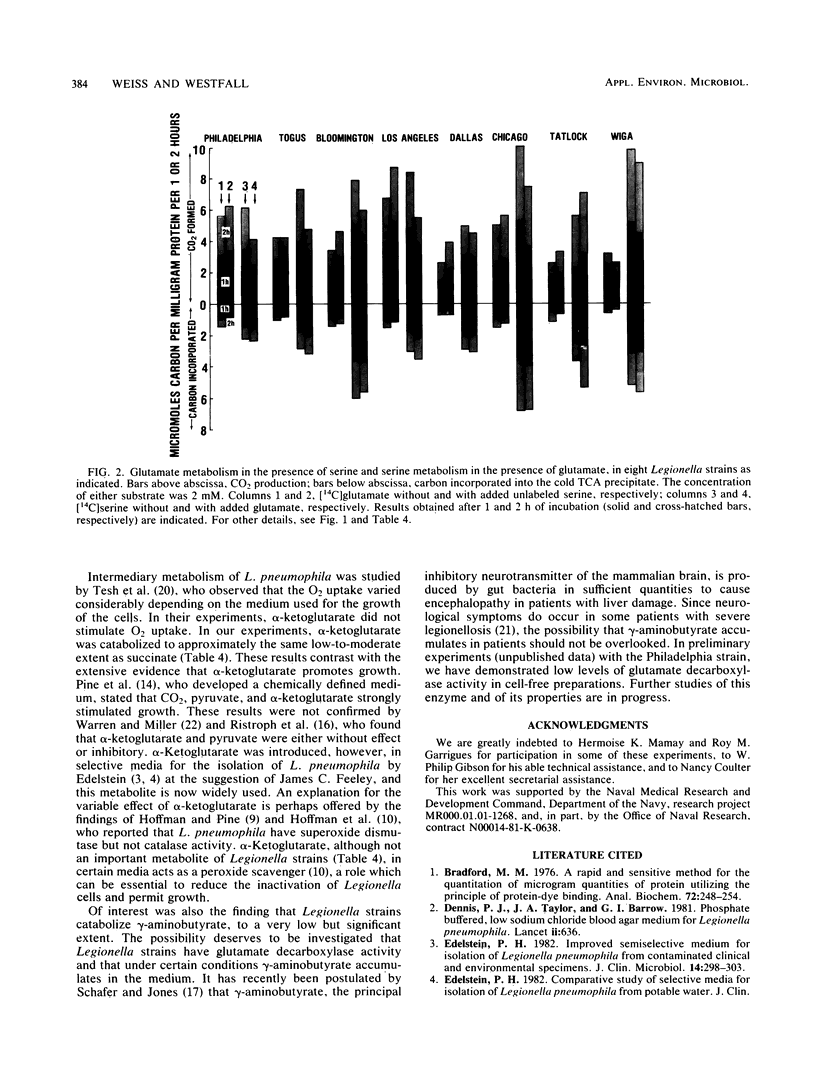
The objective of this study was to evaluate by relatively simple metabolic tests the usefulness of buffers and energy sources commonly used in Legionella growth media. Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1 to 6, Legionella micdadei, and Legionella bozemanii were grown in an enriched charcoal-yeast extract diphasic medium. The cells were washed thrice, suspended in various buffers (pH 6.9) with 1 or 5 mM MgSO4, and used immediately or after controlled-rate cryopreservation. CO2 produced and C incorporated into the cold trichloracetic acid-insoluble fractions from 14C-labeled substrates were determine. Potassium phosphate buffer (0.02 M) was as satisfactory as organic buffers for glutamate metabolism, but the addition of KCl or NaCl reduced activity. Metabolic activity for glutamate was not lost upon cryopreservation, and cryopreserved cells were used to test the utilization of other single or paired substrates. Rates of activity for serine, glutamate, threonine, and pyruvate, in this descending order, were high, and those for alpha-ketoglutarate, succinate, and gamma-aminobutyrate were low. Although glutamine was not used as rapidly as glutamate, when added to glutamate it was preferentially metabolized, possibly because of more rapid transport. When glutamate and serine were combined, glutamate furnished more C for CO2 and less for incorporation, whereas the reverse was true of serine. In conclusion, glutamate as an energy source may in some cases spare other amino acids for synthesis. alpha-Ketoglutarate, a common constituent of Legionella media, may reduce oxygen toxicity but is probably not a chief energy source.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. J., Taylor J. A., Barrow G. I. Phosphate buffered, low sodium chloride blood agar medium for Legionella pneumophila. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):636–636. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92771-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. R., Pine L., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Amino acid requirements of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.286-291.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. C. Effect of glutamate on exogenous citrate catabolism of Neisseria meningitidis and of other species of Neisseria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):819–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.819-823.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Pine L., Bell S. Production of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide in medium used to culture Legionella pneumophila: catalytic decomposition by charcoal. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):784–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.784-791.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladd T. I., Ventullo R. M., Wallis P. M., Costerton J. W. Heterotrophic activity and biodegradation of labile and refractory compounds by groundwater and stream microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):321–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.321-329.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallavia L. P., Weiss E. Catabolic activities of Neisseria meningitidis: utilization of glutamate. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):127–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.127-132.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., George J. R., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Development of a chemically defined liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):615–626. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.615-626.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Hutner S. H., George J. R., Harrell W. K. Metal requirements of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.688-695.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Hedlund K. W., Gowda S. Chemically defined medium for Legionella pneumophila growth. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.115-119.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. F., Jones E. A. Hepatic encephalopathy and the gamma-aminobutyric-acid neurotransmitter system. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):18–20. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh M. J., Miller R. D. Amino acid requirements for Legionella pneumophila growth. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):865–869. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.865-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh M. J., Miller R. D. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in defined media: requirement for magnesium and potassium. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Sep;28(9):1055–1058. doi: 10.1139/m82-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh M. J., Morse S. A., Miller R. D. Intermediary metabolism in Legionella pneumophila: utilization of amino acids and other compounds as energy sources. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1104-1109.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai T. F., Finn D. R., Plikaytis B. D., McCauley W., Martin S. M., Fraser D. W. Legionnaires' disease: clinical features of the epidemic in Philadelphia. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):509–517. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. J., Miller R. D. Growth of Legionnaires disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in chemically defined medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.50-55.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Catabolic Activities of Neisseria meningitidis: Utilization of Succinate. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):133–137. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.133-137.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



