Abstract
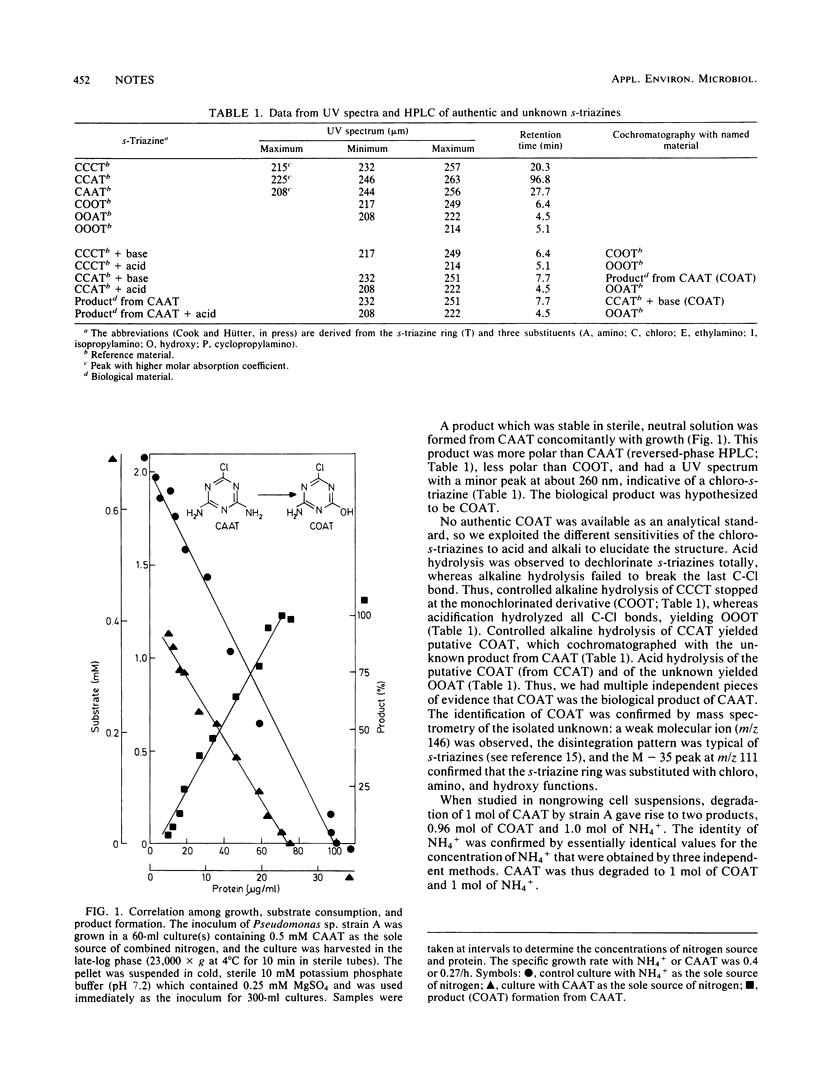
Pseudomonas sp. strain A grew with 2-chloro-1,3,5-triazine-4,6-diamine as the sole and growth-limiting source of nitrogen. The substrate was utilized quantitatively and concomitantly with growth and with excretion of a product which was identified as 2-chloro-4-amino-1,3,5-triazine-6(5H)-one. The reaction yielded 1 mol of organic product and 1 mol of NH4+ per mol of substrate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böhme C., Bär F. Uber den Abbau von Triazin-Herbiciden im tierischen organismus. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1967 Feb;5(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(67)82882-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. M., Beilstein P., Hütter R. Qualitative analysis of waste-water from ametryne production. Int J Environ Anal Chem. 1983;14(2):93–98. doi: 10.1080/03067318308071610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan L. S., Farmer W. J., Goodin J. R., Day B. E. Nonbiological detoxication of the s-triazine herbicides. Residue Rev. 1970;32:267–286. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8464-3_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jutzi K., Cook A. M., Hütter R. The degradative pathway of the s-triazine melamine. The steps to ring cleavage. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):679–684. doi: 10.1042/bj2080679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



