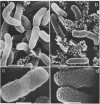
Abstract
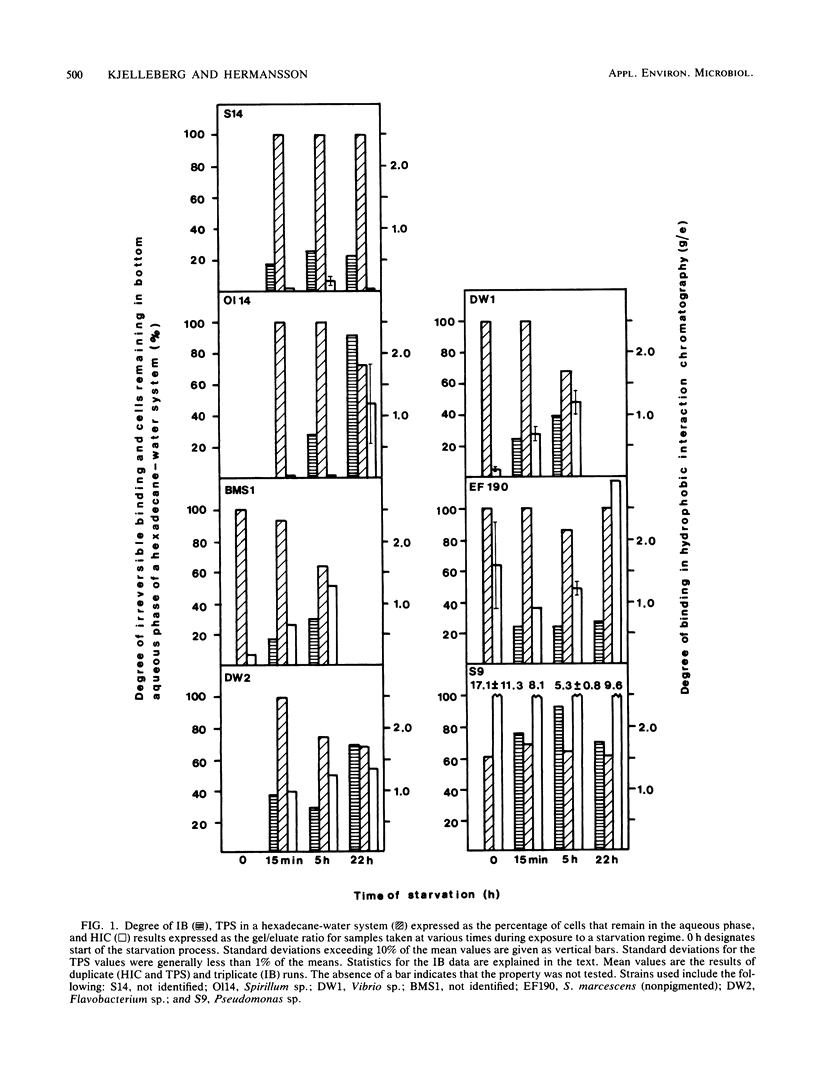
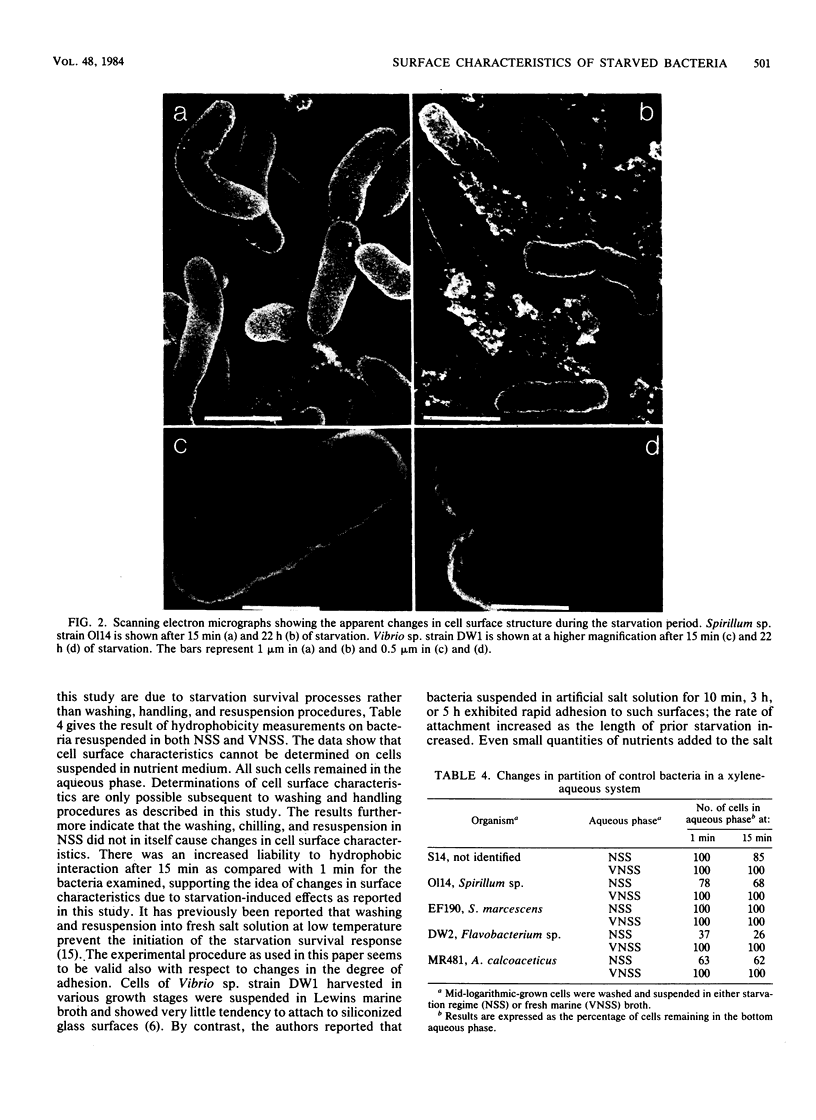
Changes in bacterial surface hydrophobicity, charge, and degree of irreversible binding to glass surfaces of seven marine isolates were followed during starvation. The degree of hydrophobicity was measured by hydrophobic interaction chromatography and by two-phase separation in a hexadecane-water system, whereas changes in charge were measured by electrostatic interaction chromatography. All isolates underwent the starvation-induced responses of fragmentation, which is defined as division without growth, and continuous size reduction, which results in populations with increased numbers of smaller cells. The latter process was also responsible for a significant proportion of the total drop in cell volume; this was observed by noting the biovolume (the average cell multiplied by the number of bacteria) of a population after various times of starvation. Four strains exhibited increases in both hydrophobicity and irreversible binding, initiated after different starvation times. The most hydrophilic and most hydrophobic isolates both showed a small increase in the degree of irreversible binding after only 5 h, followed by a small decrease after 22 h. Their hydrophobicity remained constant, however, throughout the entire starvation period. On the other hand, one strain, EF190, increased its hydrophobicity after 5 h of starvation, although the degree of irreversible binding remained constant. Charge effects could not be generally related to the increase in irreversible binding. Scanning electron micrographs showed a large increase in surface roughness throughout the starvation period for all strains that showed marked changes in physicochemical characteristics.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casida L. E., Jr Small cells in pure cultures of Agromyces ramosus and in natural soil. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):214–216. doi: 10.1139/m77-032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. W., Young L. Y. Enrichment and association of bacteria and particulates in salt marsh surface water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):894–899. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.894-899.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. W., Young L. Y. Enumeration of particle-bound and unattached respiring bacteria in the salt marsh environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.156-160.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks C. W. Sorption of heterotrophic and enteric bacteria to glass surfaces in the continuous culture of river water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):572–578. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.572-578.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey B., Kjelleberg S., Marshall K. C. Responses of marine bacteria under starvation conditions at a solid-water interface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):43–47. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.43-47.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchman D., Mitchell R. Contribution of particle-bound bacteria to total microheterotrophic activity in five ponds and two marshes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):200–209. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.200-209.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Humphrey B. A., Marshall K. C. Initial phases of starvation and activity of bacteria at surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):978–984. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.978-984.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C., Stout R., Mitchell R. Selective sorption of bacteria from seawater. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):1413–1416. doi: 10.1139/m71-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novitsky J. A., Morita R. Y. Survival of a psychrophilic marine Vibrio under long-term nutrient starvation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):635–641. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.635-641.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Interfacial free energy and the hydrophobic effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4175–4176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]