Abstract
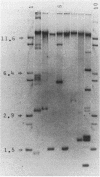
Samples of psychrophilic and psychrotrophic bacteria were collected from sea ice, seawater, sediments, and benthic or ice-associated animals in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. A total of 155 strains were isolated and tested for the presence of plasmids by DNA agarose gel electrophoresis. Thirty-one percent of the isolates carried at least one kind of plasmid. Bacterial isolates taken from sediments showed the highest plasmid incidence (42%), and isolates from seawater showed the lowest plasmid incidence (20%). Plasmids were significantly more frequent in the strains which had been first isolated from low-nutrient media (46%) than in the strains which had been isolated from high-nutrient media (25%). Multiple forms of plasmids were observed in two-thirds of the plasmid-carrying strains. A majority of the plasmids detected were estimated to have a mass of 10 megadaltons or less. Among 48 plasmid-carrying strains, 7 showed antibiotic resistance. It is concluded that bacterial plasmids are ubiquitous in natural microbial assemblages of the pristine marine ecosystem of Antarctica.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton N. F., Day M. J., Bull A. T. Distribution of bacterial plasmids in clean and polluted sites in a South Wales river. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1026–1029. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1026-1029.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hada H. S., Sizemore R. K. Incidence of Plasmids in Marine Vibrio spp. Isolated from an Oil Field in the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):199–202. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.199-202.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita R. Y. Psychrophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):144–167. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.144-167.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Okami Y. Studies on marine microorganisms. II. Actinomycetes in Sagami Bay and their antibiotic substances. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Aug;25(8):461–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore R. K., Colwell R. R. Plasmids carried by antibiotic-resistant marine bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):373–382. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan C. W., Palmisano A. C. Sea Ice Microbial Communities: Distribution, Abundance, and Diversity of Ice Bacteria in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, in 1980. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):788–795. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.788-795.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]