Abstract
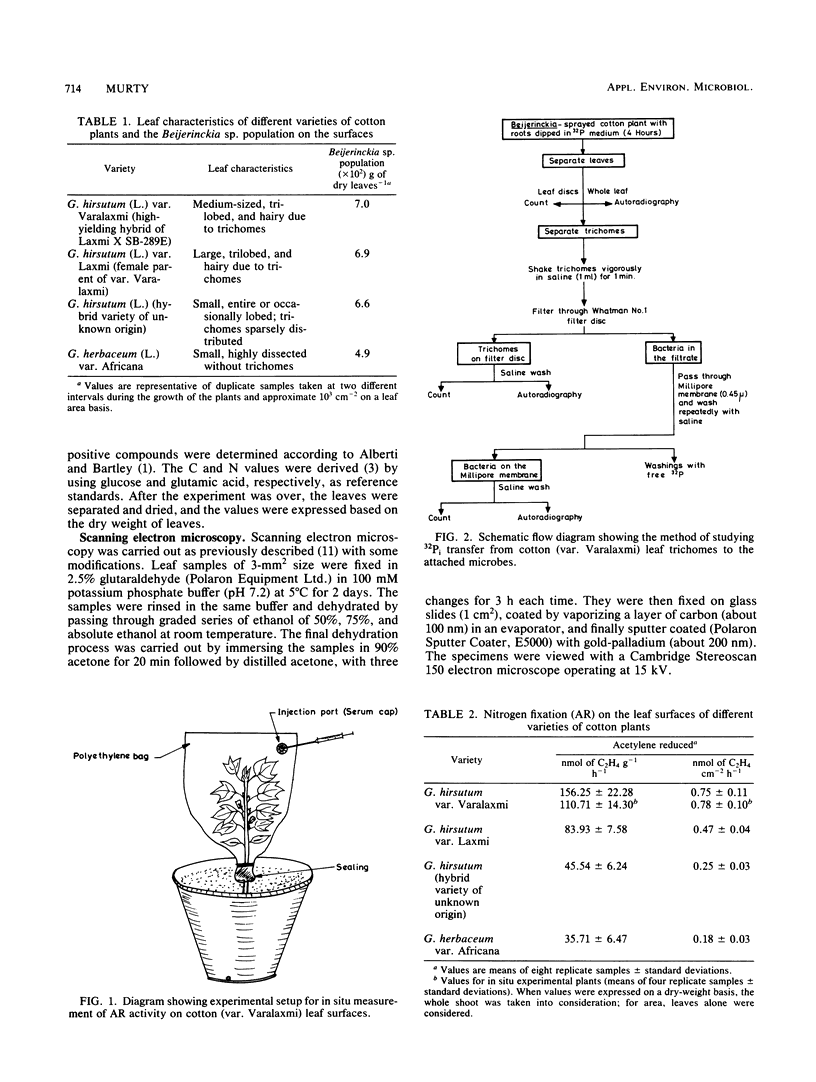
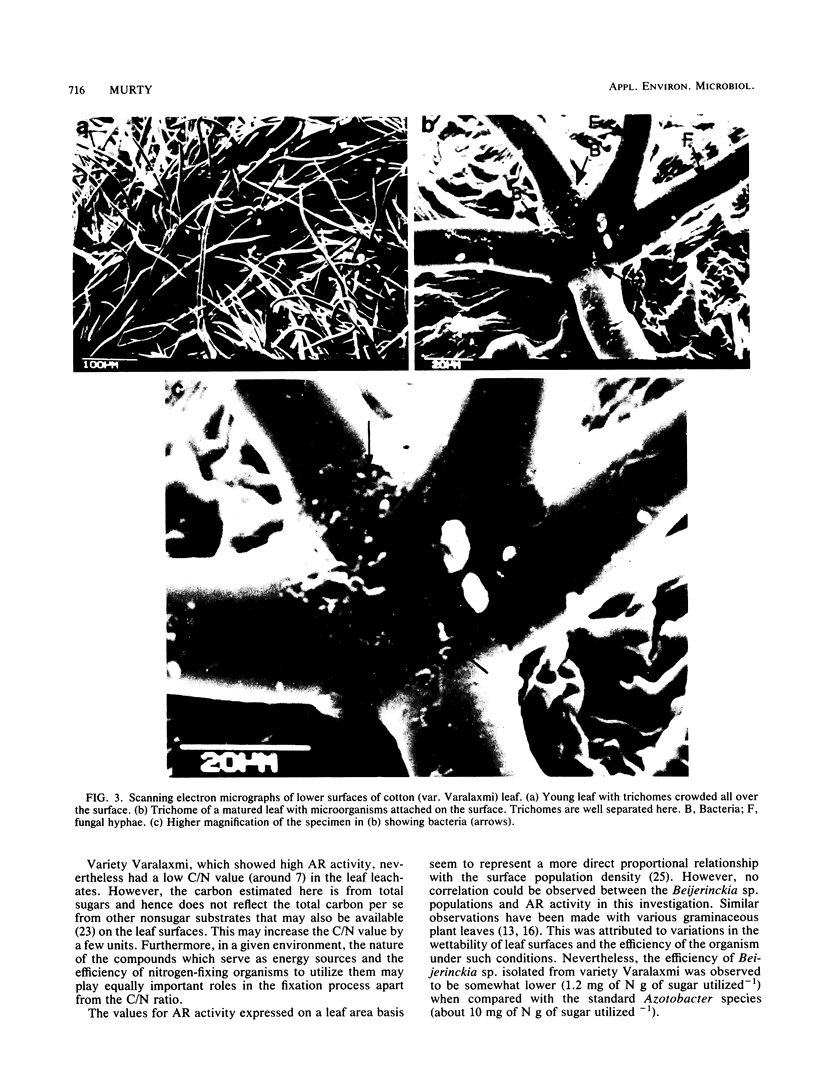
Positive nitrogenase activities ranging from 0.18 to 0.78 nmol of C2H4 cm−2 h−1 were detected on the leaf surfaces of different varieties of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. and G. herbaceum L.) plants. Beijerinckia sp. was observed to be the predominant nitrogen-fixing microorganism in the phyllosphere of these varieties. A higher level of phyllosphere nitrogen-fixing activity was recorded in the variety Varalaxmi despite a low C/N ratio in the leaf leachates. Leaf surfaces of the above variety possessed the largest number of hairy outgrowths (trichomes) which entrapped a majority of microbes. Immersion of plant roots in nutrient medium containing 32Pi led to the accumulation of label in the trichome-borne microorganisms, thereby indicating a possible transfer of nutrients from leaf to microbes via trichomes. Extrapolation of acetylene reduction values suggested that 1.6 to 3.2 kg of N ha−1 might be contributed by diazotrophs in the phyllosphere of the variety Varalaxmi during the entire growth period.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERTI K. G., BARTLEY W. The production of amino acids by cell fractions, particularly rat-liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1963 Apr;87:104–114. doi: 10.1042/bj0870104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber L. E., Tjepkema J. D., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Acetylene reduction (nitrogen fixation) associated with corn inoculated with Spirillum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.108-113.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke L. R., Seeley H. W. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) by epiphytes of freshwater macrophytes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):129–138. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.129-138.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. B. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) in a salt marsh amended with sewage sludge and organic carbon and nitrogen compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):846–852. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.846-852.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito O., Cabrera D., Watanabe I. Fixation of dinitrogen-15 associated with rice plants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):554–558. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.554-558.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okon Y., Albrecht S. L., Burris R. H. Methods for Growing Spirillum lipoferum and for Counting It in Pure Culture and in Association with Plants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):85–88. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.85-88.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Wilson P. W. Formation of the nitrogen-fixing enzyme system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1139/m68-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEMM E. W., WILLIS A. J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):508–514. doi: 10.1042/bj0570508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]