Abstract
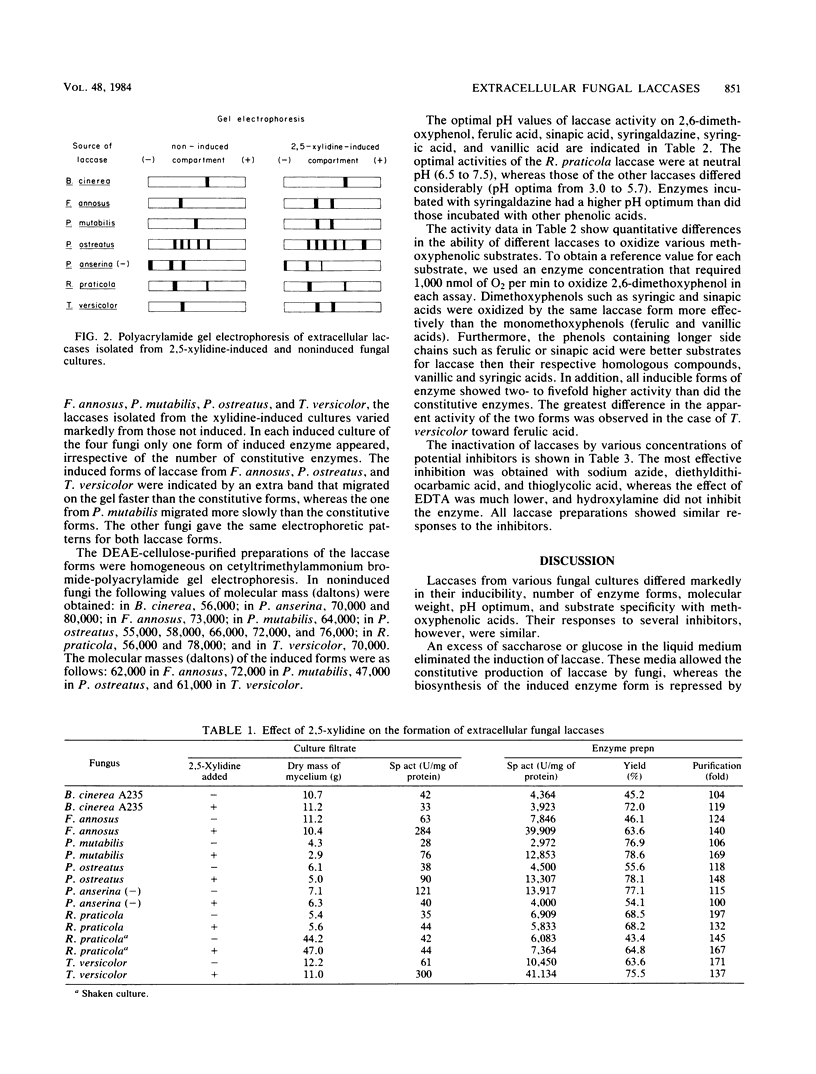
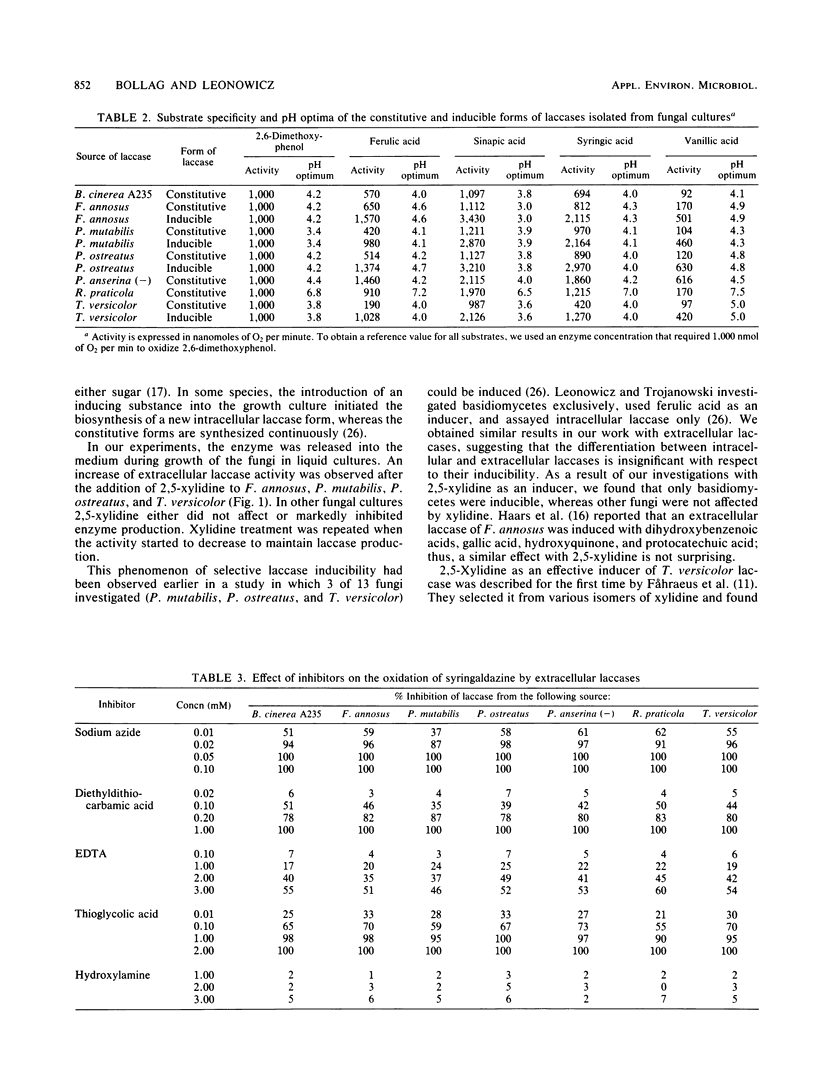
Various basidiomycetes, ascomycetes, and deuteromycetes, grown in a sugar-rich liquid medium, were compared for laccase-producing ability and for the inducing effect of 2,5-xylidine on laccase production. Clear stimulation of the extracellular enzyme formation by xylidine was obtained in the cultures of Fomes annosus, Pholiota mutabilis, Pleurotus ostreatus, and Trametes versicolor, whereas Rhizoctonia praticola and Botrytis cinerea were not affected by the xylidine, and in the case of Podospora anserina a decrease in laccase activity was observed. The laccases were purified, and electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels indicated a particular pattern for each laccase. The bands of the induced forms appeared only with basidiomycetes. The optimal pH of R. praticola laccase was in the neutral region, whereas the optima of all the other exolaccases were significantly lower (between pH 3.0 and 5.7). All laccases oxidized the methoxyphenolic acids under investigation, but there existed quantitative differences in oxidation efficiencies which depended on pH and on the nature (noninduced or induced) of the enzyme. The sensitivity of all enzymes to inhibitors did not differ considerably.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bollag J. M., Sjoblad R. D., Liu S. Y. Characterization of an enzyme from Rhizoctonia praticola which polymerizes phenolic compounds. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Feb;25(2):229–233. doi: 10.1139/m79-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESSER K., DICK S., GIELEN W. DIE PHENOLOXYDASEN DES ASCOMYCETEN PODOSPORA ANSERINA. II. REINIGUNG UND EIGENSCHAFTEN DER LACCASE. Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Jun 2;48:306–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Eriksson K. E. Induction of Neurospora crassa laccase with protein synthesis inhibitors. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):450–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.450-457.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus G., Reinhammar B. Large scale production and purification of laccase from cultures of the fungus Polyporus versicolor and some properties of laccase A. Acta Chem Scand. 1967;21(9):2367–2378. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.21-2367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIKAWA H., SCHUBERT W. J., NORD F. F. INVESTIGATIONS ON LIGNINS AND LIGNIFICATION. XXX. ENZYMIC DEGRADATION OF GUAIACYLGLYCEROL AND RELATED COMPOUNDS BY WHITE-ROT FUNGI. Biochem Z. 1963;338:153–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIKAWA H., SCHUBERT W. J., NORD F. F. Investigations on lignins and lignification. 27. The enzymic degradation of softwood lignin by white-rot fungi. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:131–139. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser P., Kirk T. K., Zeikus J. G. Ligninolytic enzyme system of Phanaerochaete chrysosporium: synthesized in the absence of lignin in response to nitrogen starvation. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.790-797.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Champe S. P. Purification and characterization of the conidial laccase of Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1338–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1338-1345.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonowicz A., Trojanowski J. Induction of laccase by ferulic acid in basidiomycetes. Acta Biochim Pol. 1975;22(4):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonowicz A., Trojanowski J. Induction of laccase in Basidiomycetes: the laccase-coding messenger. Acta Biochim Pol. 1978;25(2):147–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonowicz A., Trojanowski J., Orlicz B. Induction of laccase in Basidiomycetes: apparent activity of the inducible and constitutive forms of the enzyme with phenolic substrates. Acta Biochim Pol. 1978;25(4):369–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marjanen L. A., Ryrie I. J. Molecular weight determinations of hydrophilic proteins by cationic detergent electrophoresis. Application to membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 18;371(2):442–450. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitoris H. P., Van Breemen J. F., Van Bruggen E. F., Esser K. The phenoloxidases of the ascomycete Podospora anserina. X. Electron microscopic studies on the structure of laccases I, II and III. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 21;271(2):286–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


