Abstract
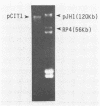
A plasmid of ca. 100 kilobases was detected in a Pseudomonas species which was isolated from soil by growth on aniline as the sole carbon and energy source. The plasmid was shown to be involved in aniline metabolism.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachofer R., Oltmanns O., Lingens F. Isolation and characterization of a Nocardia-like soil-bacterium, growing on carboxanilide fungicides. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Mar 26;90(2):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00414516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmids in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Shaw E. J., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of an R factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1244-1249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski U., Janke D., Prauser H., Fritsche W. Degradation of aniline and monochloroanilines by Rhodococcus sp. An 117 and a pseudomonad: a comparative study. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1983;23(4):235–246. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surovtseva E. G., Vol'nova A. I. Anilin kak edinstvennyi istochnik ugleroda, azota i énergii dlia Alcaligenes faecalis. Mikrobiologiia. 1980 Jan-Feb;49(1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Furuse C., Sakaizumi S. Transduction of various R factors by phage P1 in Escherichia coli and by phage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1791–1795. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1791-1795.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]