Abstract
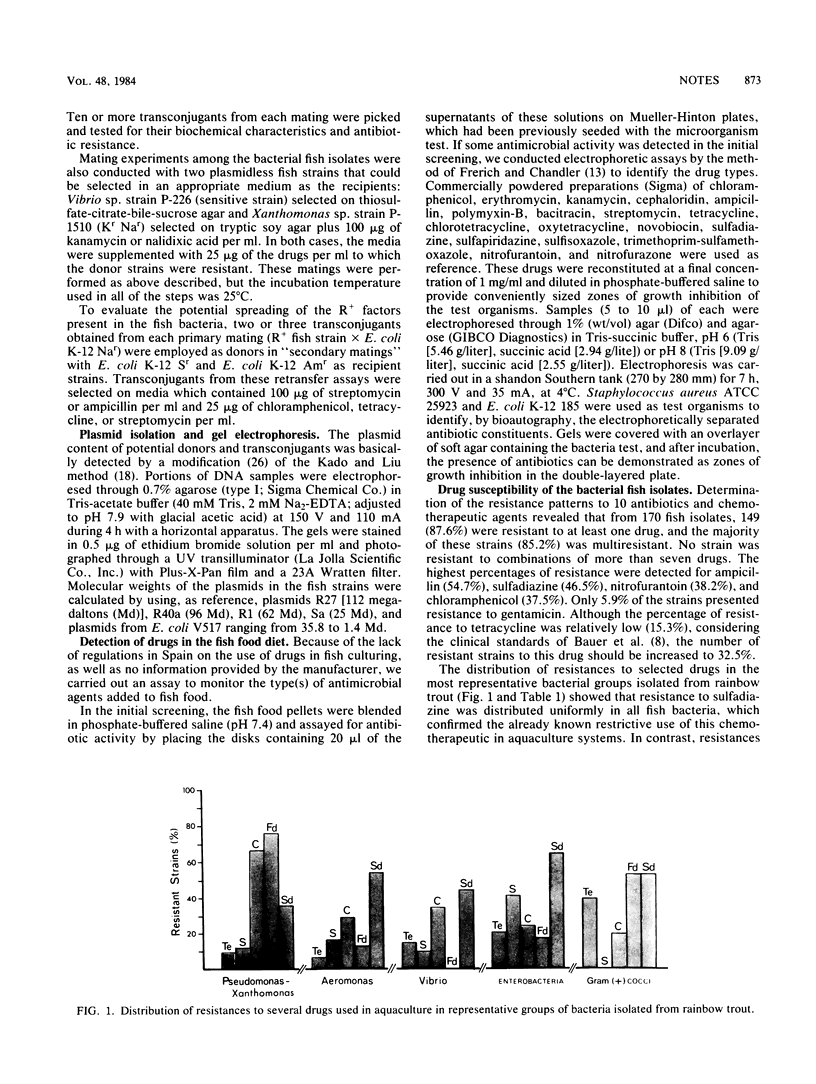
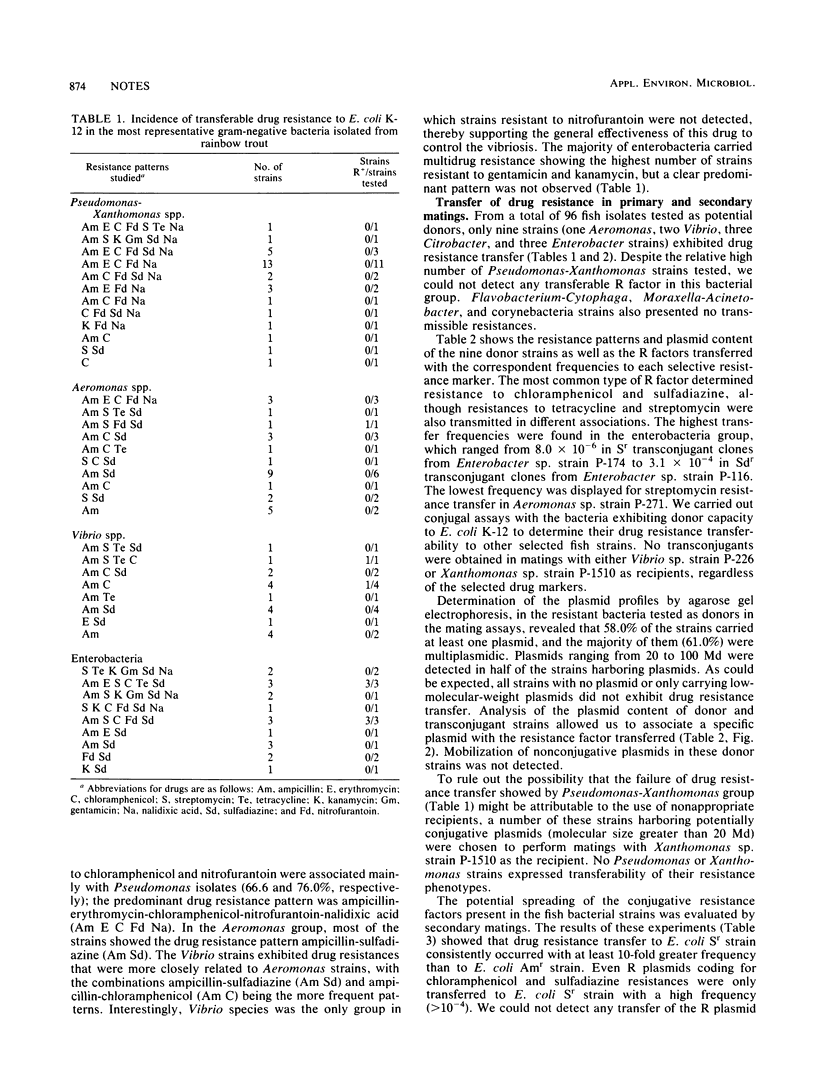
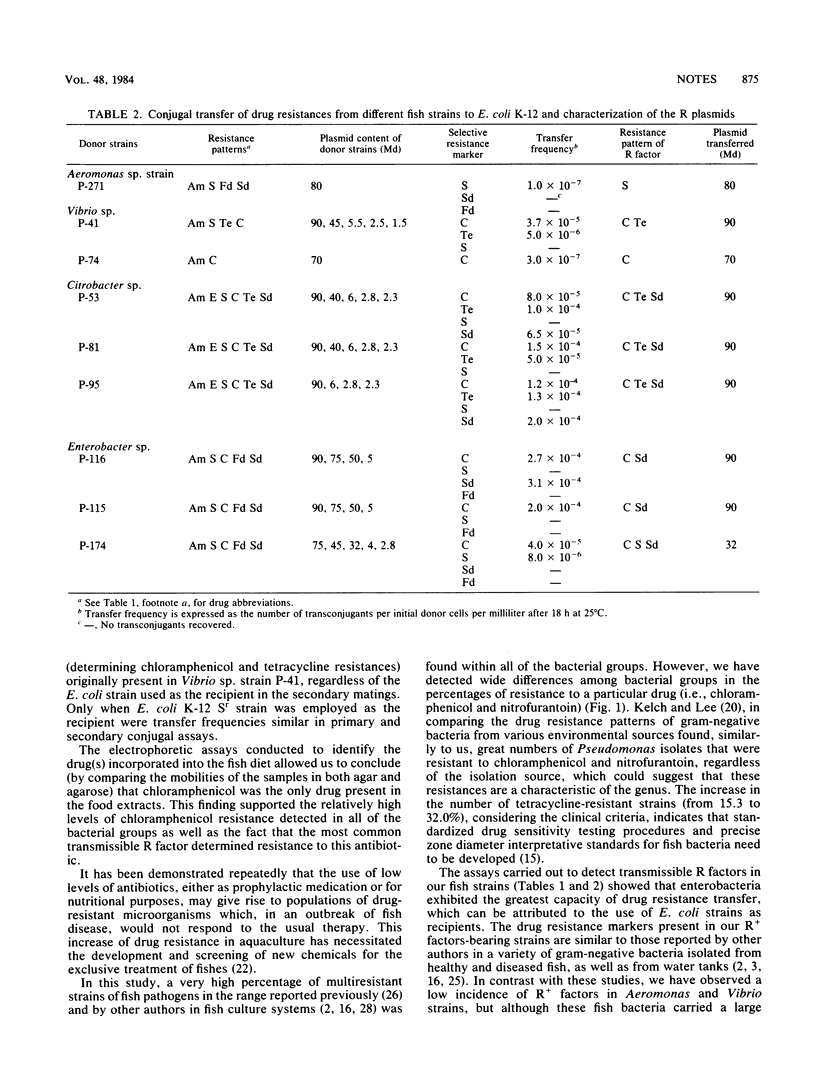
The occurrence of drug resistance and plasmid-mediated transferability was investigated in 170 strains belonging to eight bacterial groups isolated from cultured rainbow trout. It was found that 87.6% of the strains were resistant to at least one drug, with the highest percentages of resistance being detected for ampicillin (54.7%), sulfadiazine (46.5%), nitrofurantoin (38.2%), and chloramphenicol (37.0%). Six enterobacteria, two Vibrio, and one Aeromonas isolate transferred resistance factors to Escherichia coli K-12. The most common transmissible R factor determined resistance to chloramphenicol and sulfadiazine, demonstrating an association between a specific plasmid and the resistance pattern transferred. The presence of chloramphenicol in fish food was detected by bioassay. In general, transfer frequencies were similar in primary and secondary matings, which indicate the potential water-borne dissemination of these R plasmids.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altherr M. R., Kasweck K. L. In situ studies with membrane diffusion chambers of antibiotic resistance transfer in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):838–843. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.838-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Schiewe M. H., Falkow S. Evidence for plasmid contribution to the virulence of fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):509–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.509-513.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Shipley P. L. Plasmid-mediated factors associated with virulence of bacteria to animals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:465–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerichs G. N., Chandler M. D. The identification and assay of antibiotics in live virus vaccines by electrophoresis in gel. J Biol Stand. 1982 Jul;10(3):205–211. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(82)80021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Palchaudhuri S., Maas W. K. Naturally occurring plasmid carrying genes for enterotoxin production and drug resistance. Science. 1977 Oct 14;198(4313):198–199. doi: 10.1126/science.333581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan G. W., Hadley W. K. Human infection with Edwardsiella tarda. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Feb;70(2):283–288. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Aeromonas hydrophila: ecology and toxigenicity of isolates from an estuary. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;50(2):359–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelch W. J., Lee J. S. Antibiotic resistance patterns of gram-negative bacteria isolated from environmental sources. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):450–456. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.450-456.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Cabelli V. J. R-plasmid transfer frequencies from environmental isolates of Escherichia coli to laboratory and fecal strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):756–764. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.756-764.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Colwell R. R., Hetrick F. M. Characterization of plasmids in bacterial fish pathogen. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.184-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Bartlett K. H. Aquarium pets as a source of antibiotic-resistant salmonellae. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Apr;25(4):535–541. doi: 10.1139/m79-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wantanabe T., Aoki T., Ogata Y., Egusa S. Anbtibiotics and drug resistance in animals. R factors related to fish culturing. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:383–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]