Abstract
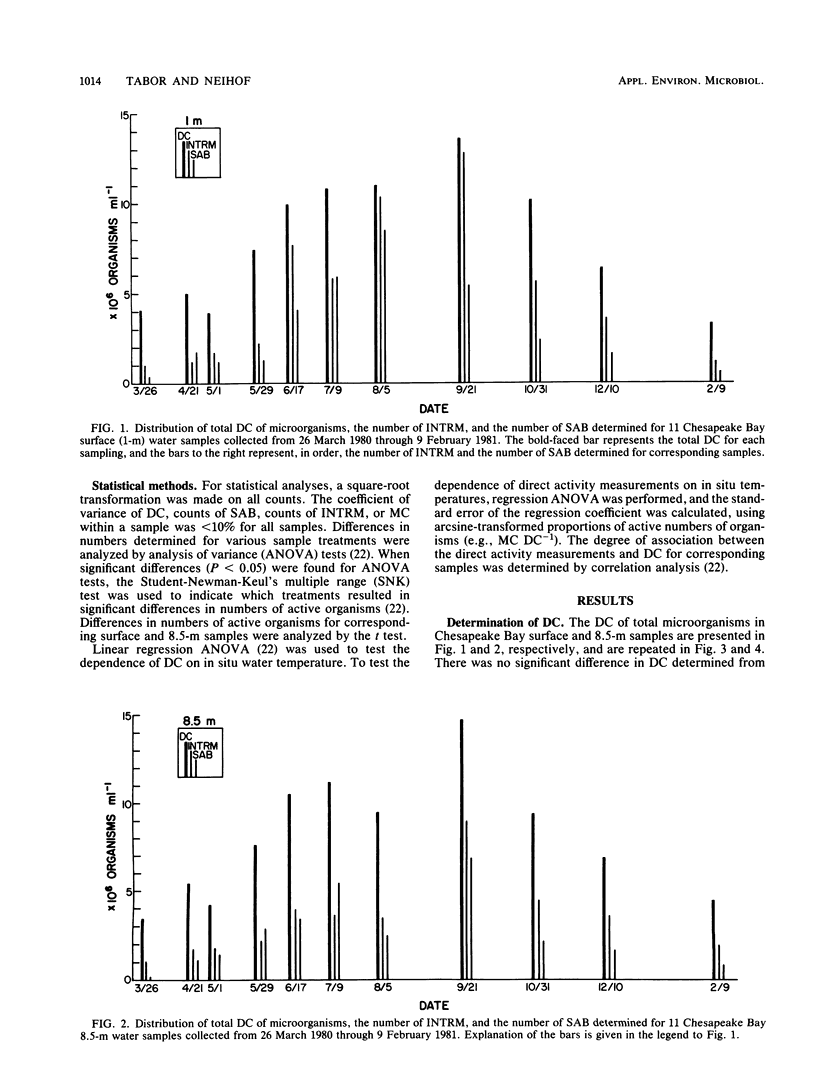
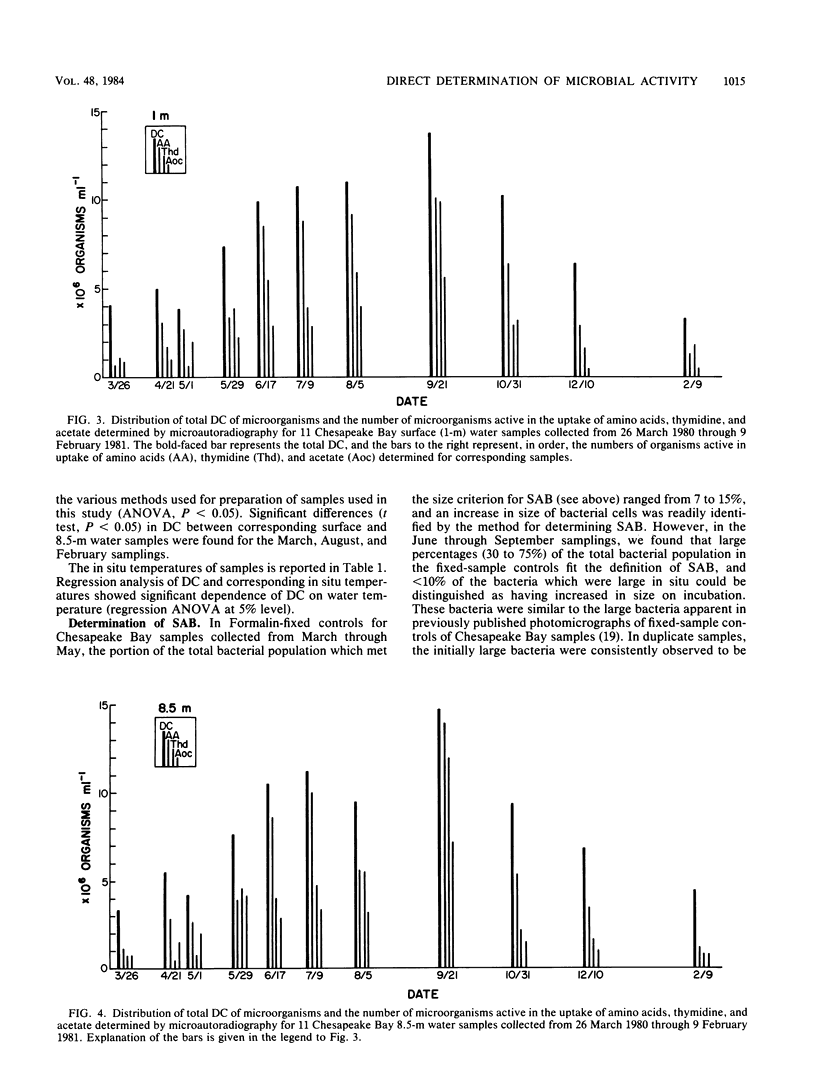
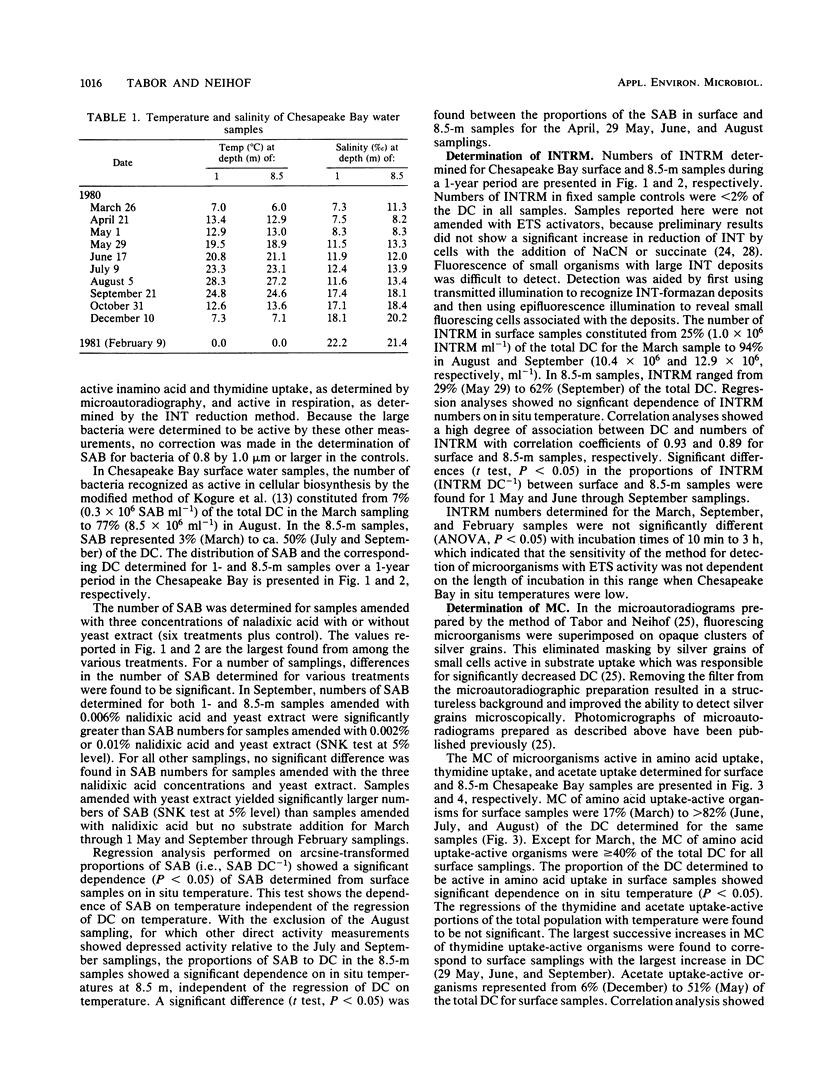
We used three methods in determination of the metabolically active individual microorganisms for Chesapeake Bay surface and near-bottom populations over a period of a year. Synthetically active bacteria were recognized as enlarged cells in samples amended with nalidixic acid and yeast extract and incubated for 6 h. Microorganisms with active electron transport systems were identified by the reduction of a tetrazolium salt electron acceptor. Microorganisms active in uptake of amino acids, thymidine, and acetate were determined by microautoradiography. In conjunction with enumeration of active organisms, a total direct count was made for each sample preparation by epifluorescence microscopy. For the majority of samples, numbers of amino acid uptake-active organisms were greater than numbers of organisms determined to be active by other direct measurements. Within a sample, the numbers of uptake-active organisms (amino acids or thymidine) and electron transport system-active organisms were significantly different for 68% of the samples. Numbers of synthetically active bacteria were generally less than numbers determined by the other direct activity measurements. The distribution of total counts in the 11 samplings showed a seasonal pattern, with significant dependence on in situ water temperature, increasing from March to September and then decreasing through February. Synthetically active bacteria and amino acid uptake-active organisms showed a significant dependence on in situ temperature, independent of the function of temperature on total counts. Numbers of active organisms determined by at least one of the methods used exceeded 25% of the total population of all samplings, and from June through September, >85% of the total population was found to be active by at least one direct activity measurement. Thus, active rather than dormant organisms compose a major portion of the microbial population in this region of Chesapeake Bay.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker K. H., Mills A. L. Determination of the Number of Respiring Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Cells in Water Samples by Using Combined Fluorescent Antibody-2-(p-Iodophenyl)-3-(p-Nitrophenyl)-5-Phenyltetrazolium Chloride Staining. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):338–344. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.338-344.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Schmidt E. L. Autoradiography and immunofluorescence combined for autecological study of single cell activity with Nitrobacter as a model system. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):676–684. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.676-684.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1112-1118.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. W., Young L. Y. Enumeration of particle-bound and unattached respiring bacteria in the salt marsh environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.156-160.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogure K., Simidu U., Taga N. A tentative direct microscopic method for counting living marine bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):415–420. doi: 10.1139/m79-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogure K., Simidu U., Taga N. Distribution of viable marine bacteria in neritic seawater around Japan. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Mar;26(3):318–323. doi: 10.1139/m80-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki J. S., Remsen C. C. Comparison of two direct-count methods for determining metabolizing bacteria in freshwater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1132–1138. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1132-1138.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Reil L. A. Autoradiography and epifluorescence microscopy combined for the determination of number and spectrum of actively metabolizing bacteria in natural water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):506–512. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.506-512.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro A. L., Brock T. D. Distinction between bacterial and algal utilization of soluble substances in the sea. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Apr;51(1):35–42. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Officer C. B., Biggs R. B., Taft J. L., Cronin L. E., Tyler M. A., Boynton W. R. Chesapeake bay anoxia: origin, development, and significance. Science. 1984 Jan 6;223(4631):22–27. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4631.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor P. S., Neihof R. A. Improved method for determination of respiring individual microorganisms in natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1249–1255. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1249-1255.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor P. S., Neihof R. A. Improved microautoradiographic method to determine individual microorganisms active in substrate uptake in natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):945–953. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.945-953.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. T. Measurement and significance of specific activity in the heterotrophic bacteria of natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):297–305. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.297-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Iturriaga R., Becker-Birck J. Simultaneous determination of the total number of aquatic bacteria and the number thereof involved in respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):926–935. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.926-935.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


