Abstract
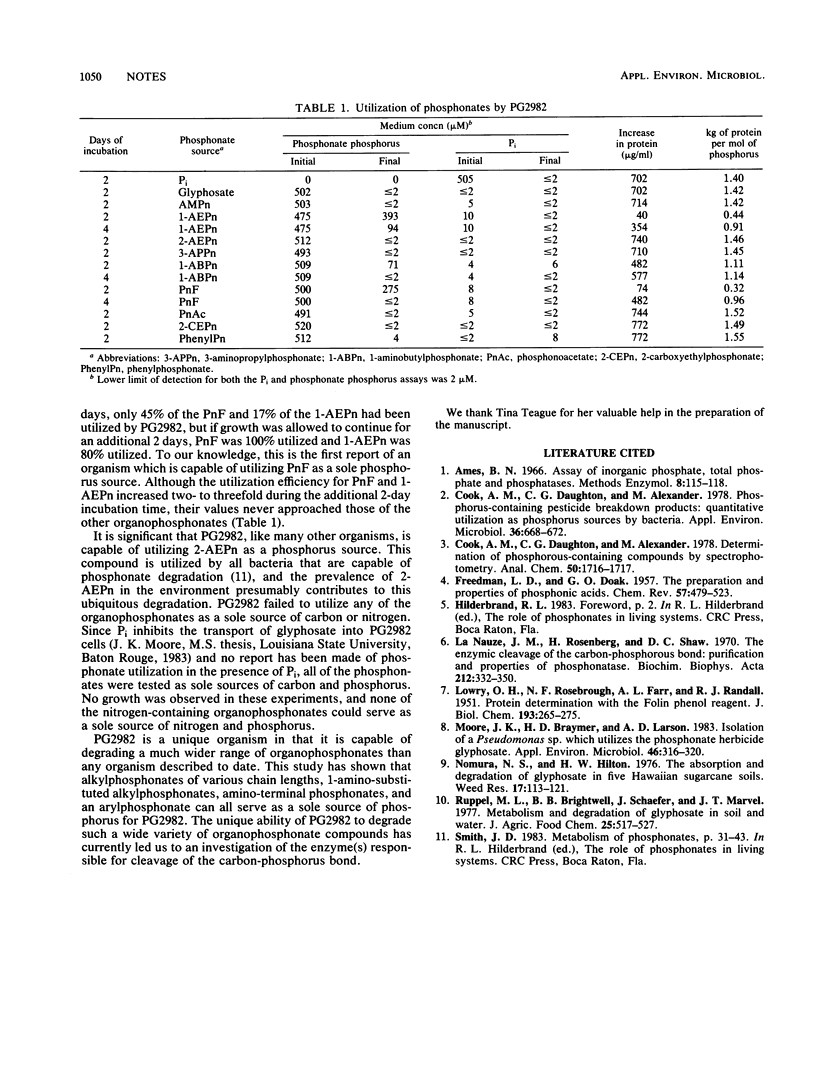
The glyphosate-degrading Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982 was found to utilize each of 10 organophosphonate compounds as a sole phosphorus source. Representative compounds tested included alkylphosphonates, 1-amino-substituted alkylphosphonates, amino-terminal phosphonates, and an arylphosphonate. This report demonstrates that PG2982 is capable of utilizing a wider range of structurally different organophosphonate compounds than any organism described to date.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cook A. M., Daughton C. G., Alexander M. Phosphorus-containing pesticide breakdown products: quantitative utilization as phosphorus sources by bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):668–672. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.668-672.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Nauze J. M., Rosenberg H., Shaw D. C. The enzymic cleavage of the carbon-phosphorus bond: purification and properties of phosphonatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 15;212(2):332–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. K., Braymer H. D., Larson A. D. Isolation of a Pseudomonas sp. Which Utilizes the Phosphonate Herbicide Glyphosate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):316–320. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.316-320.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueppel M. L., Brightwell B. B., Schaefer J., Marvel J. T. Metabolism and degradation of glyphosphate in soil and water. J Agric Food Chem. 1977 May-Jun;25(3):517–528. doi: 10.1021/jf60211a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


