Abstract
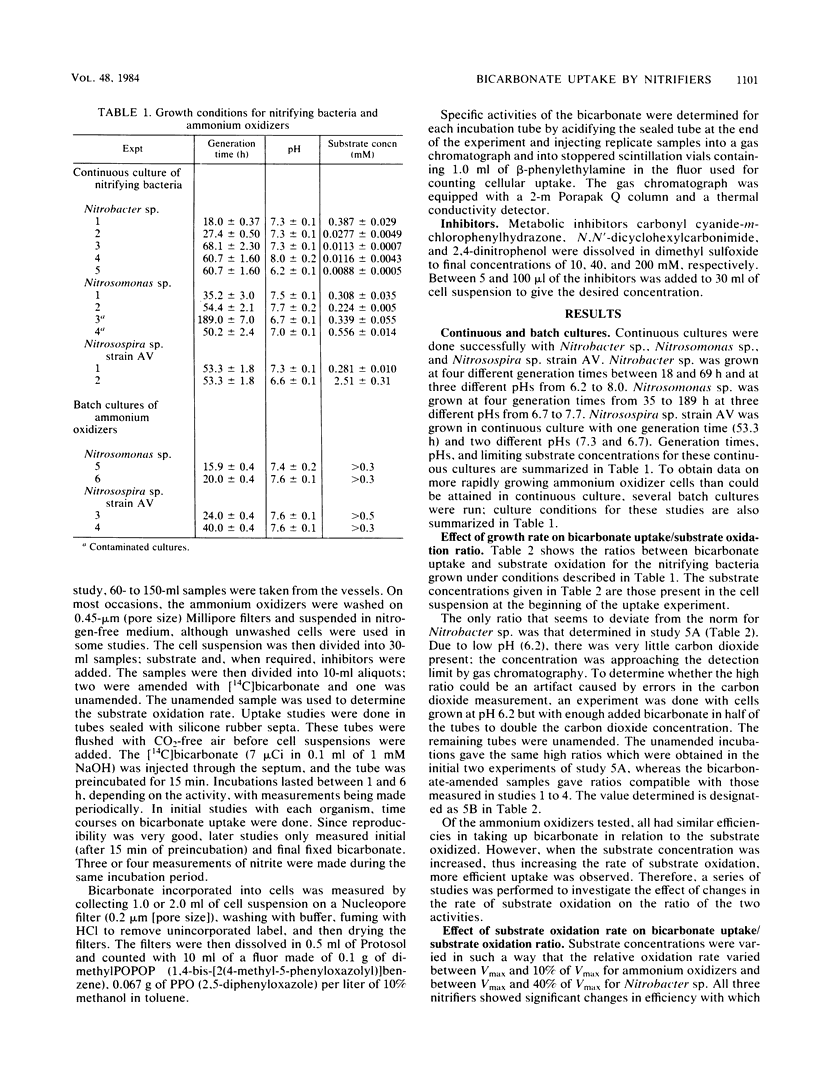
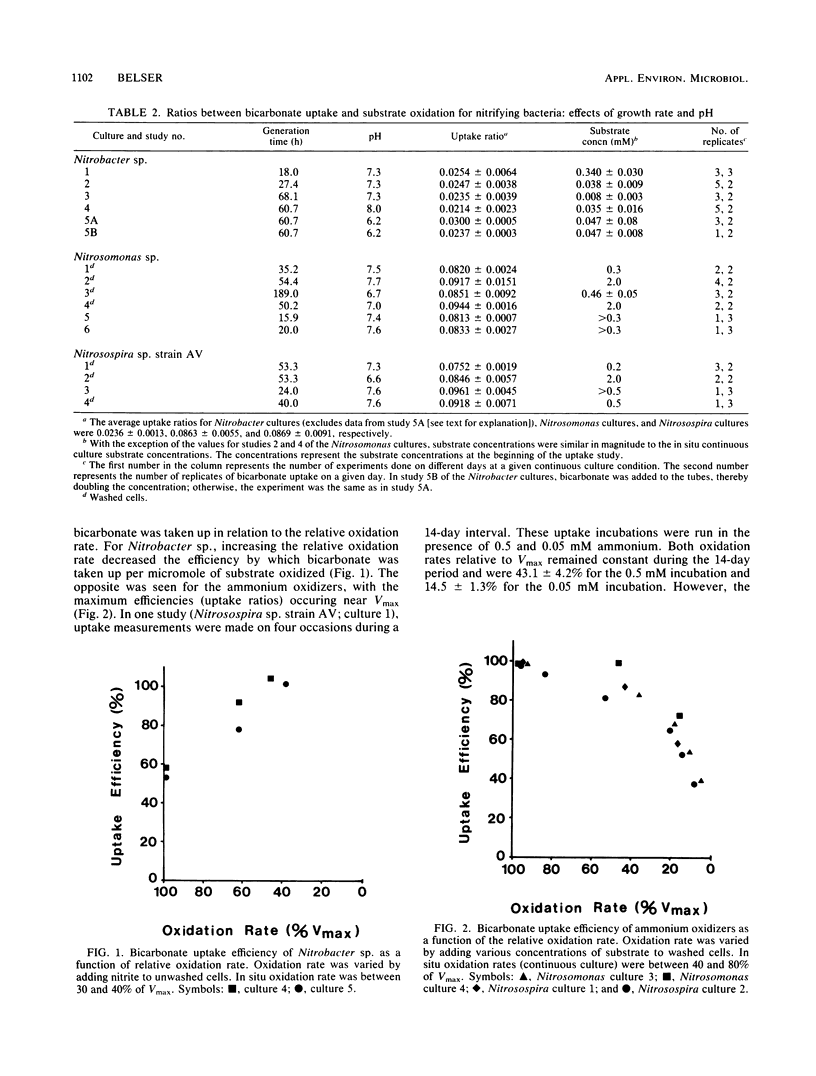
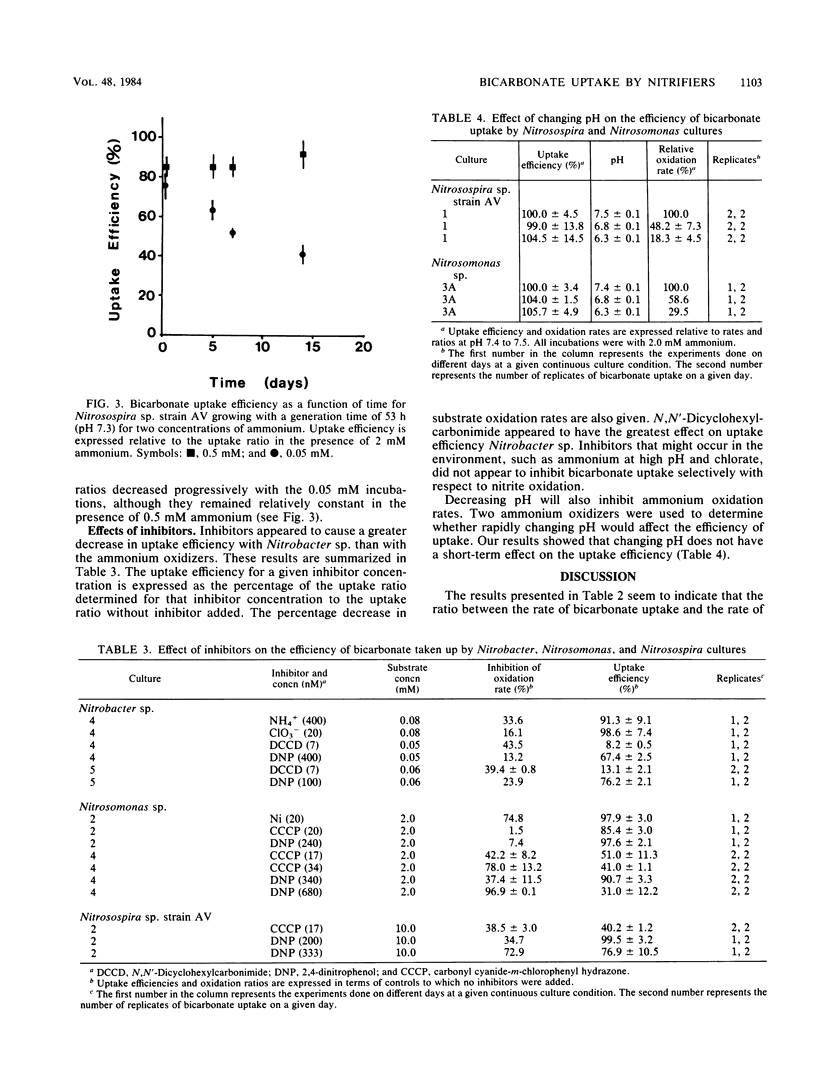
The ratios of bicarbonate uptake to substrate oxidation were measured for three genera of nitrifying bacteria. The ratios for the two ammonium oxidizers tested were essentially the same; 0.0863 ± 0.0055 and 0.0868 ± 0.0091 μmol of bicarbonate were taken up per umol ammonium oxidized for Nitrosomonas europaea and a Nitrosospira strain, respectively. For Nitrobacter sp., a ratio of 0.0236 ± 0.0013 μmol of bicarbonate taken up per umol of nitrite oxidized was obtained. Cells were grown in substrate-limited continuous culture and in batch culture, with generation times ranging between 16 and 189 h for the ammonium oxidizers and 18 and 69 h for Nitrobacter sp. All ratios appeared to be independent of growth rates and pH. However, short-term changes in substrate concentration and certain metabolic inhibitors significantly changed the efficiency of bicarbonate uptake. The significance of these results to the application of the nitrapyrin-sensitive bicarbonate uptake method for measuring nitrification rates in natural samples is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belser L. W., Mays E. L. Specific inhibition of nitrite oxidation by chlorate and its use in assessing nitrification in soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):505–510. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.505-510.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goreau T. J., Kaplan W. A., Wofsy S. C., McElroy M. B., Valois F. W., Watson S. W. Production of NO(2) and N(2)O by Nitrifying Bacteria at Reduced Concentrations of Oxygen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):526–532. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.526-532.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen K. The growth and respiration of Nitrosocystis oceanus at different partial pressures of oxygen. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Mar;42(3):387–396. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G. H. Apparent and measured rates of nitrification in the hypolimnion of a mesotrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):542–547. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.542-547.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


