Abstract
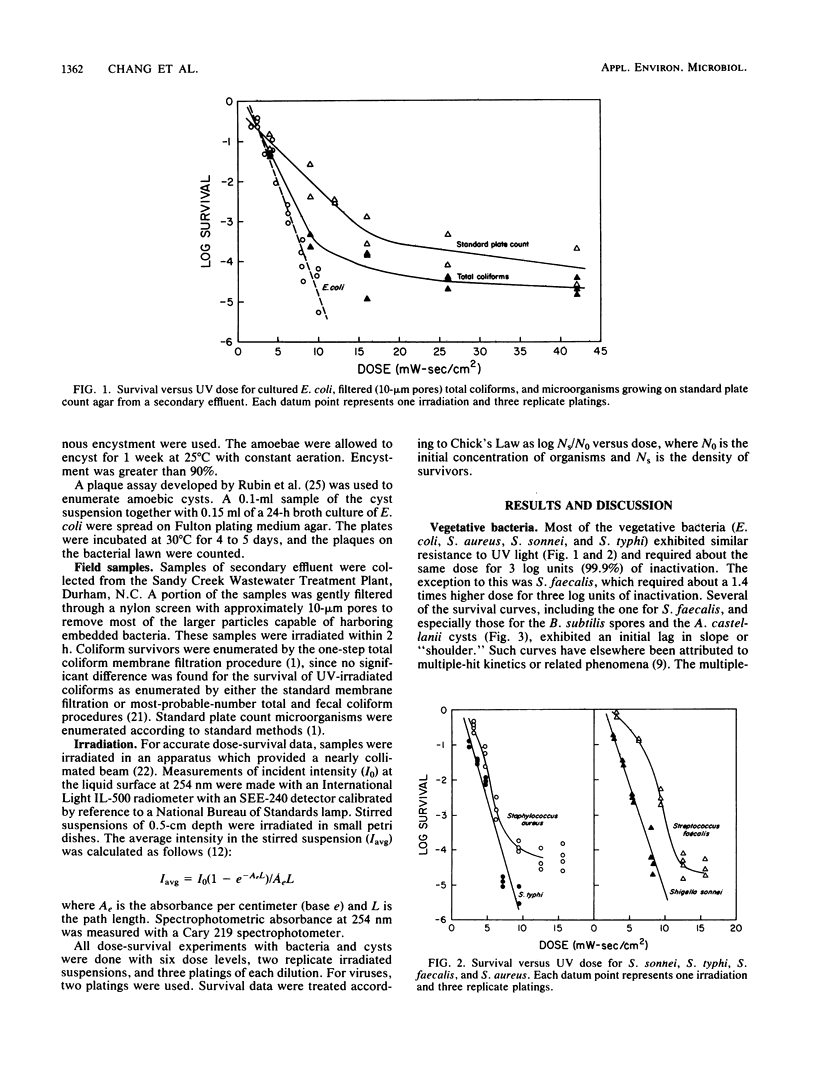
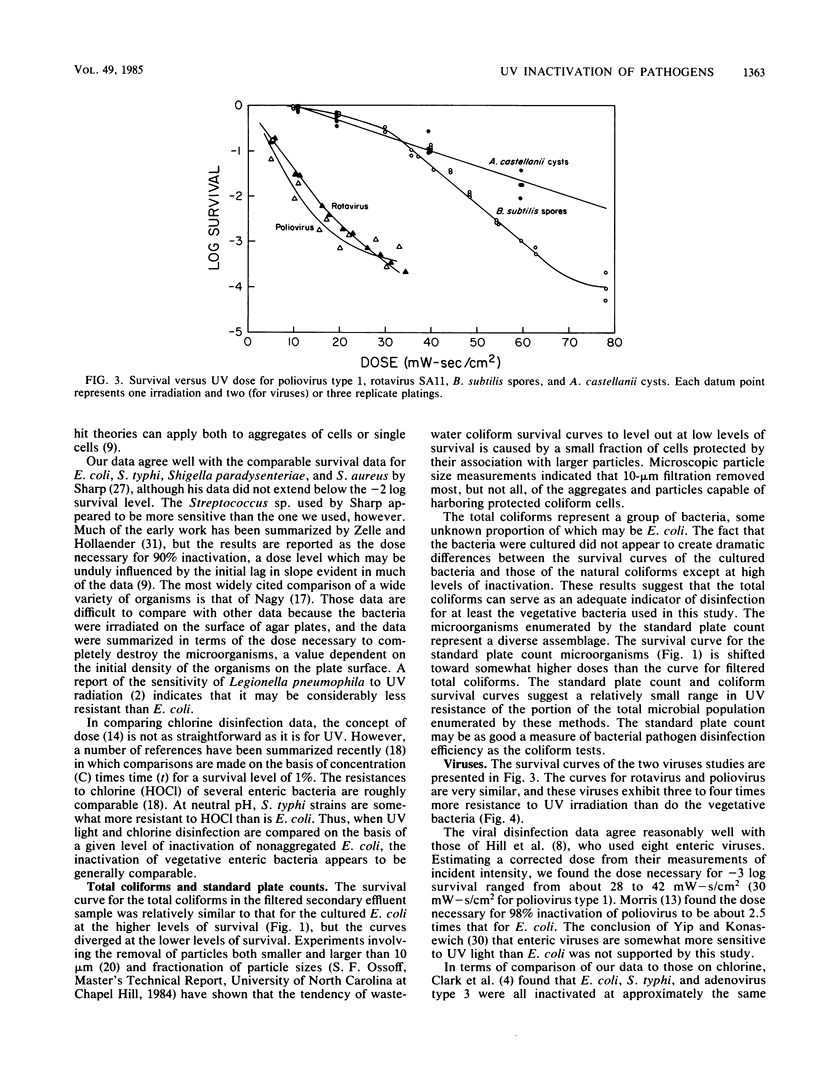
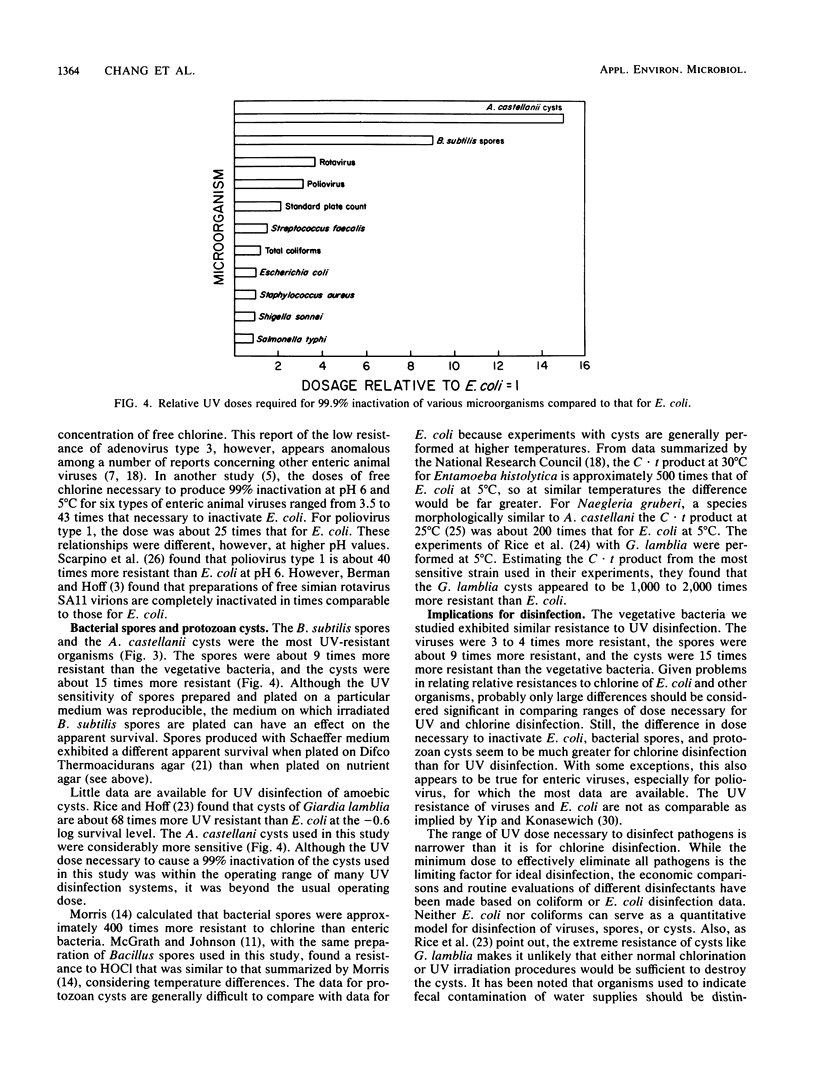
Survival was measured as a function of the dose of germicidal UV light for the bacteria Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Shigella sonnei, Streptococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtilis spores, the enteric viruses poliovirus type 1 and simian rotavirus SA11, the cysts of the protozoan Acanthamoeba castellanii, as well as for total coliforms and standard plate count microorganisms from secondary effluent. The doses of UV light necessary for a 99.9% inactivation of the cultured vegetative bacteria, total coliforms, and standard plate count microorganisms were comparable. However, the viruses, the bacterial spores, and the amoebic cysts required about 3 to 4 times, 9 times, and 15 times, respectively, the dose required for E. coli. These ratios covered a narrower relative dose range than that previously reported for chlorine disinfection of E. coli, viruses, spores, and cysts.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antopol S. C., Ellner P. D. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to ultraviolet radiation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):347–348. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.347-348.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman D., Hoff J. C. Inactivation of simian rotavirus SA11 by chlorine, chlorine dioxide, and monochloramine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):317–323. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.317-323.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE N. A., KABLER P. W., STEVENSON R. E. The inactivation of purified type 3 adenovirus in water by chlorine. Am J Hyg. 1956 Nov;64(3):314–319. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Gerba C. P., Smith E. M. Simian rotavirus SA11 replication in cell cultures. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):810–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.810-815.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. F., Jr, Hamblet F. E., Benton W. H., Akin E. W. Ultraviolet devitalization of eight selected enteric viruses in estuarine water. Appl Microbiol. 1970 May;19(5):805–812. doi: 10.1128/am.19.5.805-812.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOROWITZ H. J. Absorption effects in volume irradiation of microorganisms. Science. 1950 Mar 3;111(2879):229–229. doi: 10.1126/science.111.2879.229-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J. The practical use of ultraviolet radiation for disinfection purposes. Med Lab Technol. 1972 Jan;29(1):41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. A., Haynes R. H. Changes in the ultraviolet sensitivity of Escherichia coli during growth in batch cultures. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1379–1385. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1379-1385.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munakata N., Rupert C. S. Genetically controlled removal of "spore photoproduct" from deoxyribonucleic acid of ultraviolet-irradiated Bacillus subtilis spores. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):192–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.192-198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualls R. G., Chang J. C., Ossoff S. F., Johnson J. D. Comparison of methods of enumerating coliforms after UV disinfection. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):699–701. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.699-701.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualls R. G., Johnson J. D. Bioassay and dose measurement in UV disinfection. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):872–877. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.872-877.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice E. W., Hoff J. C. Inactivation of Giardia lamblia cysts by ultraviolet irradiation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):546–547. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.546-547.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice E. W., Hoff J. C., Schaefer F. W., 3rd Inactivation of Giardia cysts by chlorine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):250–251. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.250-251.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp D. G. The Lethal Action of Short Ultraviolet Rays on Several Common Pathogenic Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1939 Apr;37(4):447–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.37.4.447-460.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. W., DeGraeve G. M. Residual toxicity of several disinfectants in domestic wastewater. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1978 Jan;50(1):46–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


