Abstract
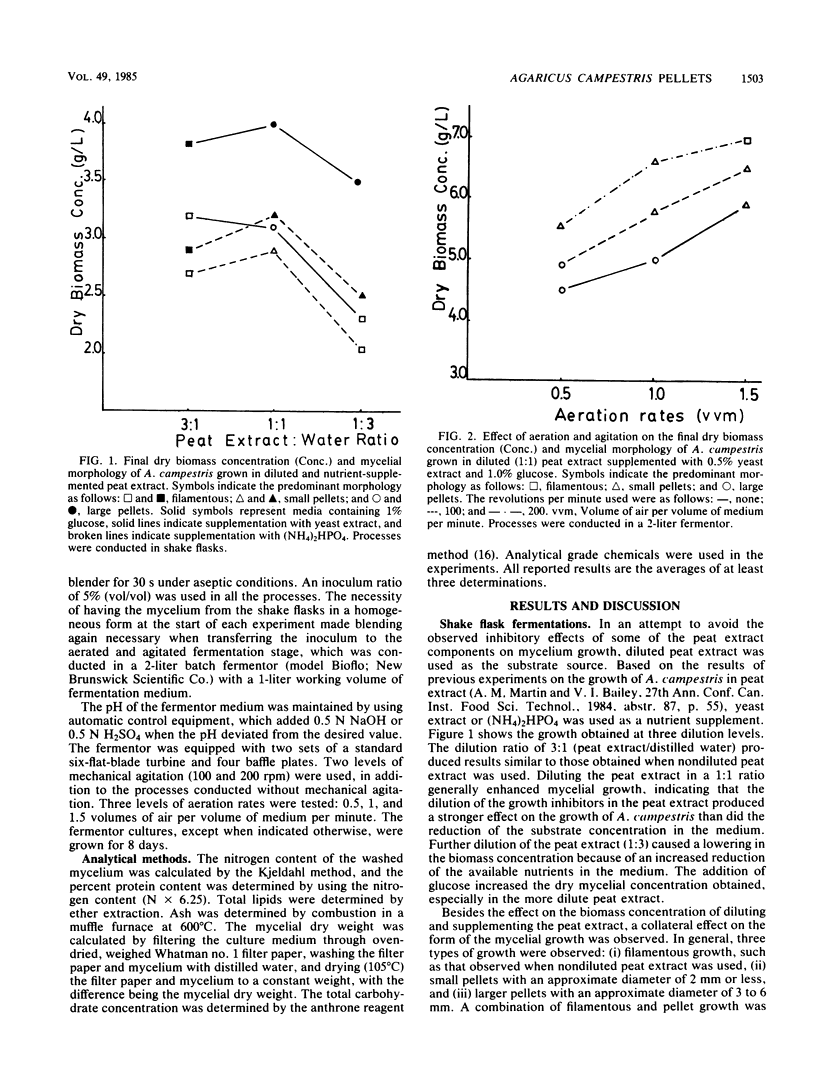
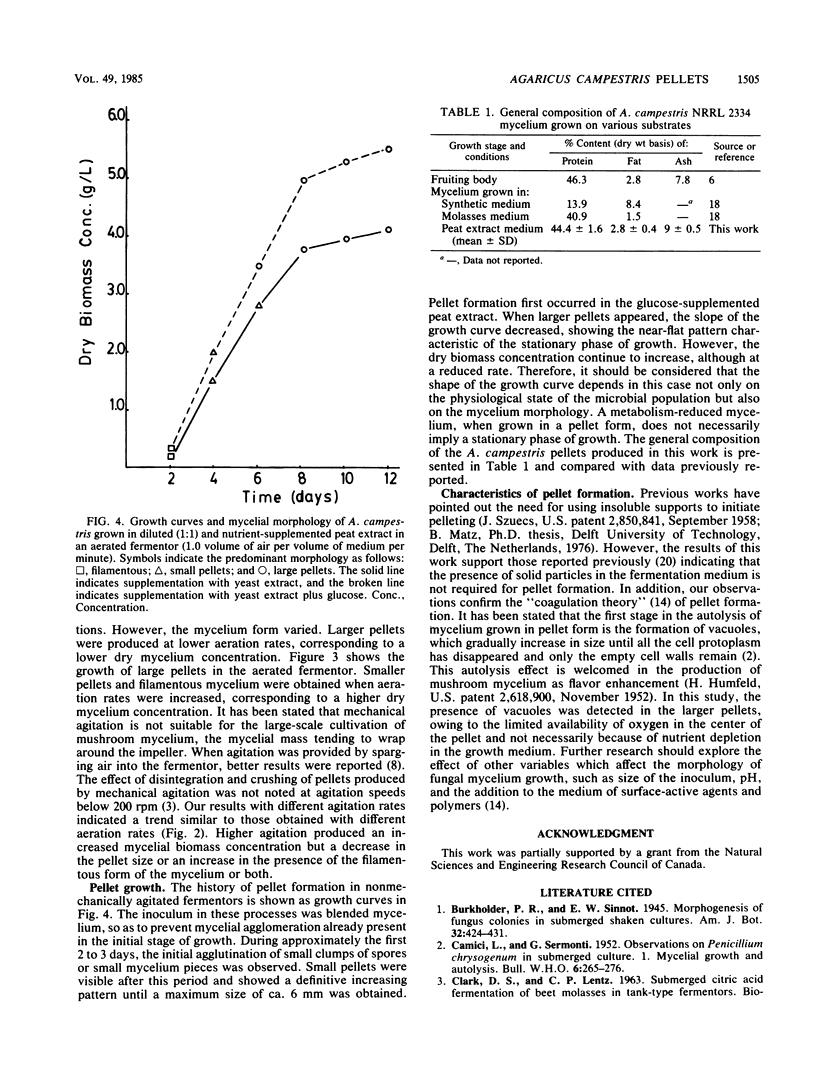
The production of pellets of the fungus Agaricus campestris NRRL 2334 was studied in submerged fermentation with peat extract as the main substrate source. Pellets up to 6 mm in diameter were obtained when the peat extract was diluted to reduce the concentration of growth inhibitors. Yeast extract and yeast extract plus glucose were the most effective nutrient supplements in the diluted peat extract media and stimulated the formation of large pellets which contained 44.4% crude protein, 2.8% fat, and 9% ash (dry weight basis). No solid supports were required for the growth of the pellets. The effects on the growth morphology of several dilution ratios of the peat extract, rates of agitation and aeration, and time were investigated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMICI L., SERMONTI G., CHAIN E. B. Observations on Penicillium chrysogenum in submerged culture. 1. Mycelial growth and autolysis. Bull World Health Organ. 1952;6(1-2):265–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK D. S. Submerged citric acid fermentation of ferrocyanide-treated beet molasses: morphology of pellets of Aspergillus niger. Can J Microbiol. 1962 Feb;8:133–136. doi: 10.1139/m62-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humfeld H. The Production of Mushroom Mycelium (Agaricus campestris) in Submerged Culture. Science. 1948 Apr 9;107(2780):373–373. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2780.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L. Quantitative Determination of Carbohydrates With Dreywood's Anthrone Reagent. Science. 1948 Mar 5;107(2775):254–255. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2775.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUSSER F., SPENCER J. F., SALLANS H. R. Protein and fat content of some mushrooms grown in submerged culture. Appl Microbiol. 1958 Jan;6(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/am.6.1.1-4.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEEL R., MARTIN S. M., LENTZ C. P. A standard inoculum for citric acid production in submerged culture. Can J Microbiol. 1954 Dec;1(3):150–157. doi: 10.1139/m55-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worgan J. T. Culture of the higher fungi. Prog Ind Microbiol. 1968;8:73–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



