Abstract
A method was developed to grow Legionella pneumophila in continuous culture. A chemostat was used to simulate nutrient-limited, submaximal growth in the natural environmental and to provide a precisely controlled growth regimen. Cultures grew under forced aeration under conditions yielding up to 38% saturation of dissolved oxygen; supplemental CO2 (5%) at the same gas flow rates as ambient air had no effect on culture growth. Pleomorphism was observed during growth under all conditions. Pigment was produced only at D less than 0.03 h-1. Catalase was produced at higher growth rates but not at higher temperatures. The pathogenicity was unaffected by altering either the growth rate or the growth temperature.
Full text
PDF
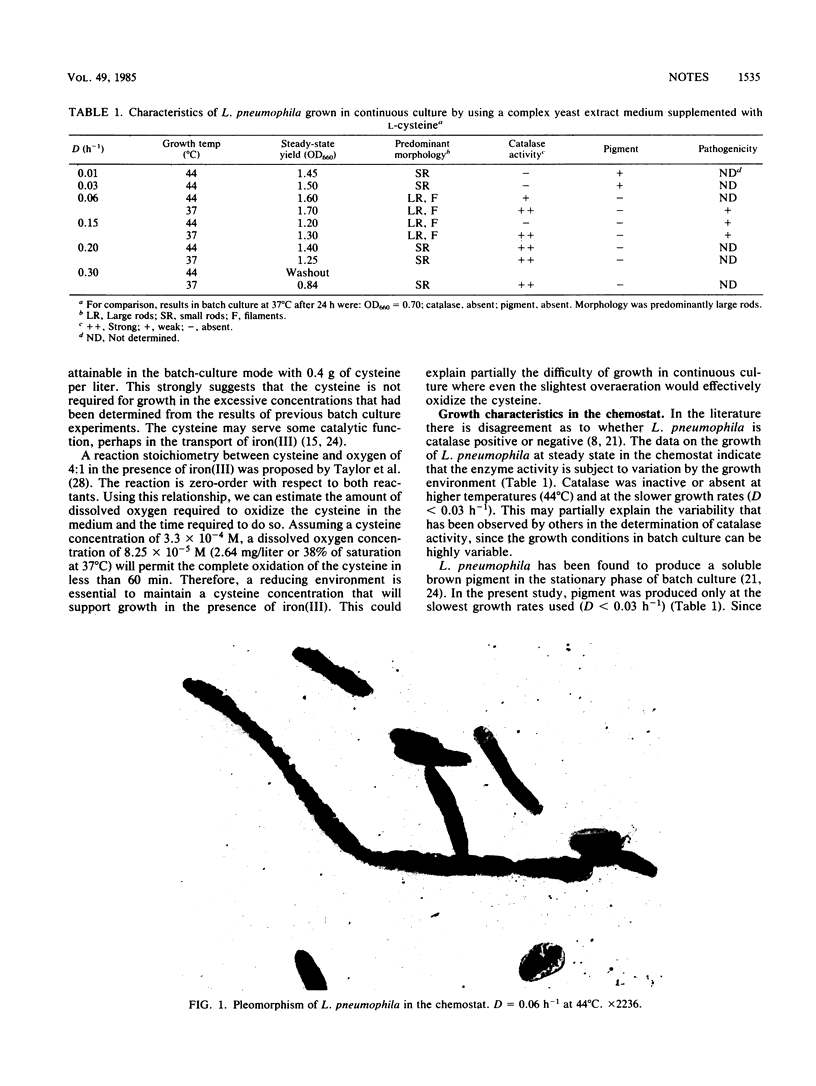


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. D., Matin A., Roberts P. V. Effect of antecedent growth conditions on sensitivity of Escherichia coli to chlorine dioxide. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):814–819. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.814-819.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Snyder I. S. Cyanobacterial stimulation of growth and oxygen uptake by Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):528–531. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.528-531.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester B., Poulos E. G., Demaray M. J., Albin E., Prilucik T. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 from blood with nonsupplemented blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):195–197. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.195-197.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Whittaker R. E., Kreiling R. L., Howell C. L. Efficacy of ozone in eradication of Legionella pneumophila from hospital plumbing fixtures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1330–1333. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1330-1333.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T. Iron metabolism in humans and plants. Am Sci. 1982 Nov-Dec;70(6):626–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Thacker L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from nonepidemic-related aquatic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1239–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1239-1242.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill C. O., Suisted J. R. The effects of temperature and growth rate on the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in bacterial lipids. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Jan;104(1):31–36. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Patton C. M., Feeley J. C., Johnson S. E., Gorman G., Martin W. T., Skaliy P., Mallison G. F., Politi B. D., Mackel D. C. Isolation of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium from environmental samples. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):664–666. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B., Dees S. B., McDougal L. K., Dodd D. J. Characteristics of environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.109-115.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Cherry W. B., Milan D. Isolation of Legionella pneumophilia from cooling tower water by filtration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1202–1205. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1202-1205.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Cherry W. B., Tyndall R. L., Fliermans C. B., Gough S. B., Lambert M. A., McDougal L. K., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J. Legionella oakridgensis: unusual new species isolated from cooling tower water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):536–545. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.536-545.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., George J. R., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Development of a chemically defined liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):615–626. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.615-626.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Neilands J. B., Balows A. Absence of siderophore activity in Legionella species grown in iron-deficient media. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):324–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.324-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Hedlund K. W., Allen R. G. Liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):19–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.19-21.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Hedlund K. W., Gowda S. Chemically defined medium for Legionella pneumophila growth. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.115-119.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Rolfe R. D., Edelstein P. H., Finegold S. M. Comparison of liquid growth media for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):623–627. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.623-627.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. E., Yan J. F., Wang J. L. The iron(3)-catalyzed oxidation of cysteine by molecular oxygen in the aqueous phase. An example of a two-thirds-order reaction. J Am Chem Soc. 1966 Apr 20;88(8):1663–1667. doi: 10.1021/ja00960a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B. Glycine-containing selective medium for isolation of Legionellaceae from environmental specimens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):768–772. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.768-772.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. L., Blaser M. J., Cravens J., Johnson M. A. Growth, survival, and resistance of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):614–618. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. J., Miller R. D. Growth of Legionnaires disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in chemically defined medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.50-55.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



