Abstract
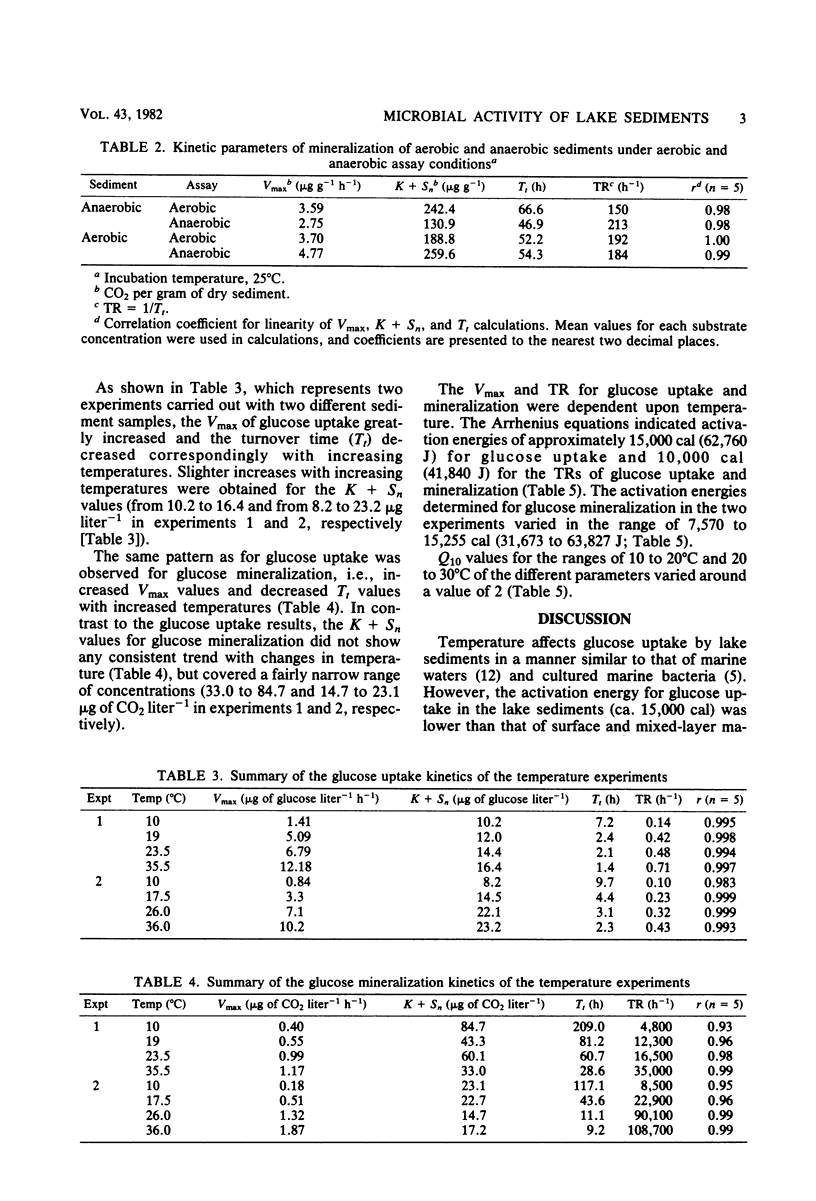
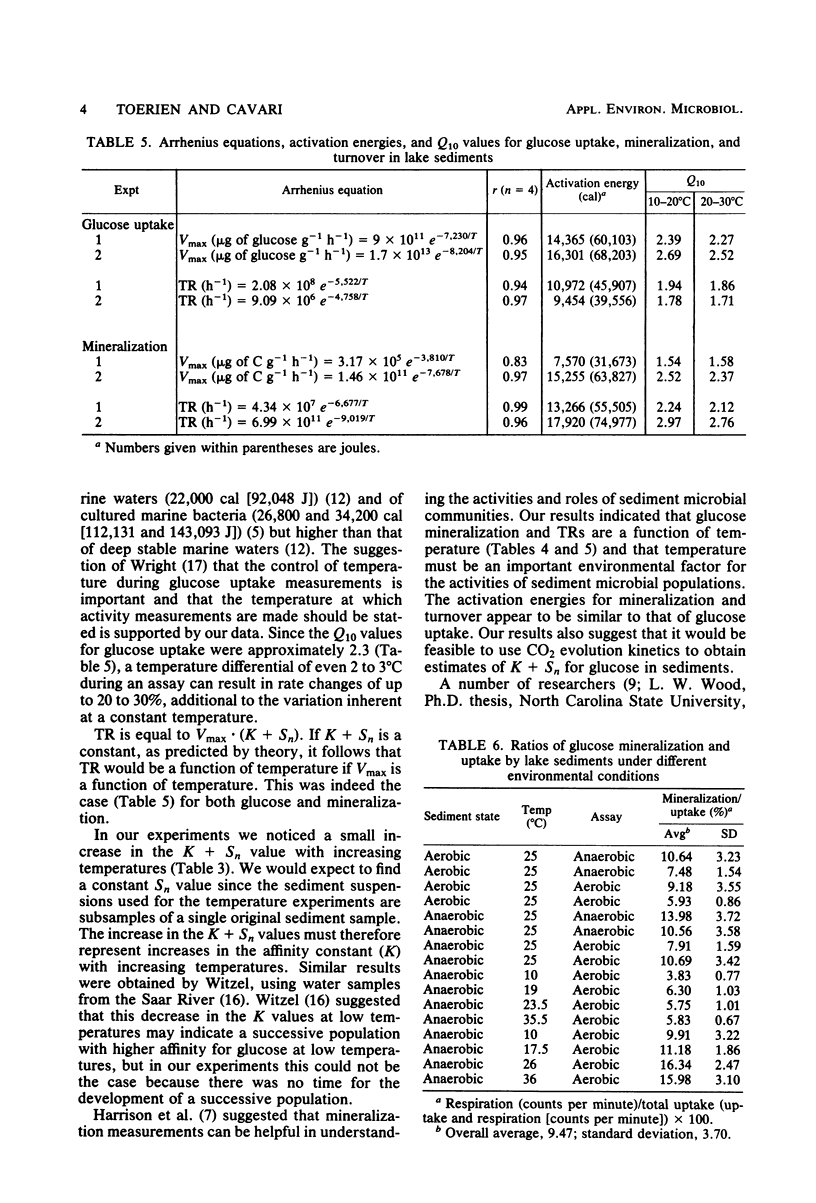
The Vmax and turnover rates (TR) of [U-14C]glucose uptake and mineralization of Lake Kinneret (Israel) sediment are temperature dependent. The following activation energies were determined: glucose uptake, ∼15,000 cal (62,760 J); TR of glucose uptake, ∼10,000 cal (41,840 J); glucose mineralization, 7,500 to 15,000 cal (31,380 to 62,760 J); and TR of glucose mineralization, ∼15,000 cal. Q10 values varied as follows: glucose uptake, ∼2.3; TR of glucose uptake, ∼1.8; and glucose mineralization, ∼2.5. K + Sn values increased slightly with temperature and might reflect an increased K with increased temperatures. Glucose respiration/uptake ratios were low (9.5 to 12%) and were apparently not greatly influenced by the presence or absence of oxygen or by different assay temperatures. Aerobic or anaerobic sediments assayed under either aerobic or anaerobic conditions did not exhibit greatly different Vmax, TR, or K + Sn values.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hamilton R. D., Morgan K. M., Strickland J. D. The glucose uptake kinetics of some marine bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Oct;12(5):995–1003. doi: 10.1139/m66-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. J., Wright R. T., Morita R. Y. Method for measuring mineralization in lake sediments. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):698–702. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.698-702.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Effect of temperature on mineralization by heterotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):584–587. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.584-587.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzel K. P. Temperature compensation of [u-C]glucose incorporation by microbial communities in a river with a fluctuating thermal regime. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):790–796. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.790-796.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. T. Measurement and significance of specific activity in the heterotrophic bacteria of natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):297–305. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.297-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


