Abstract
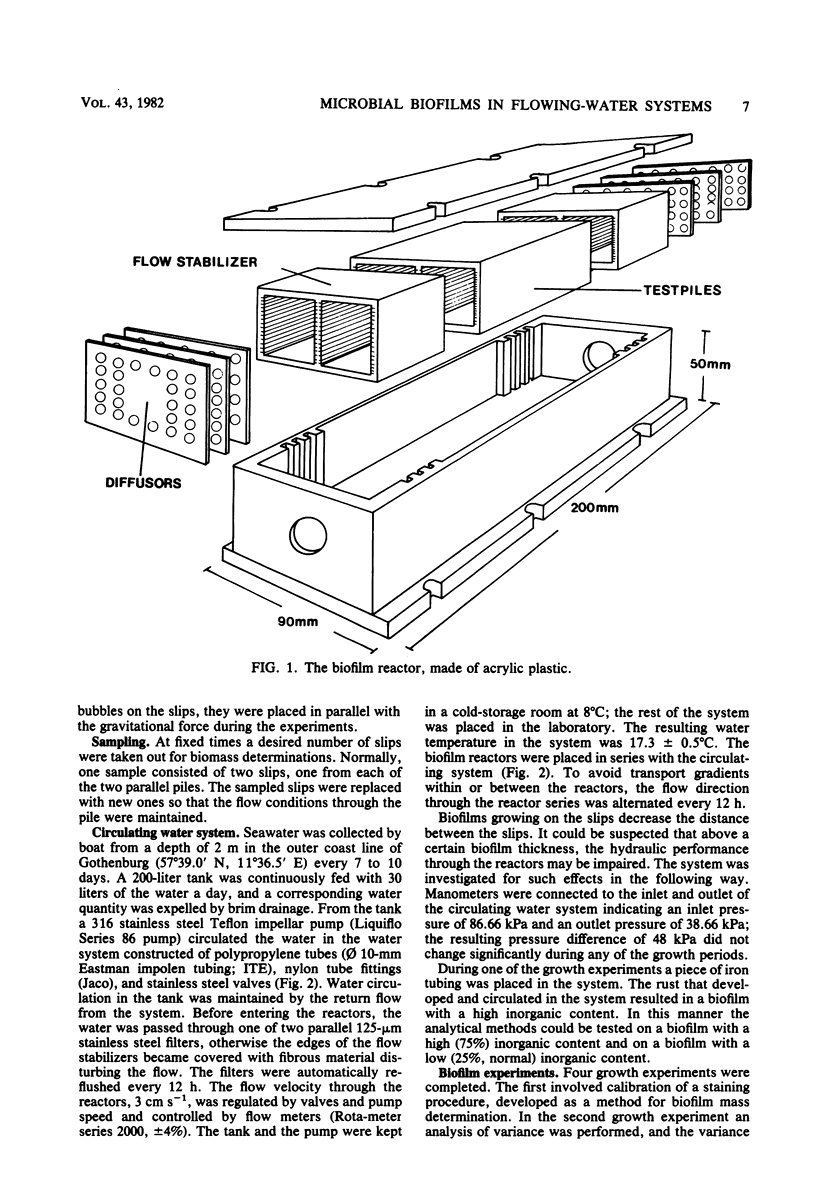
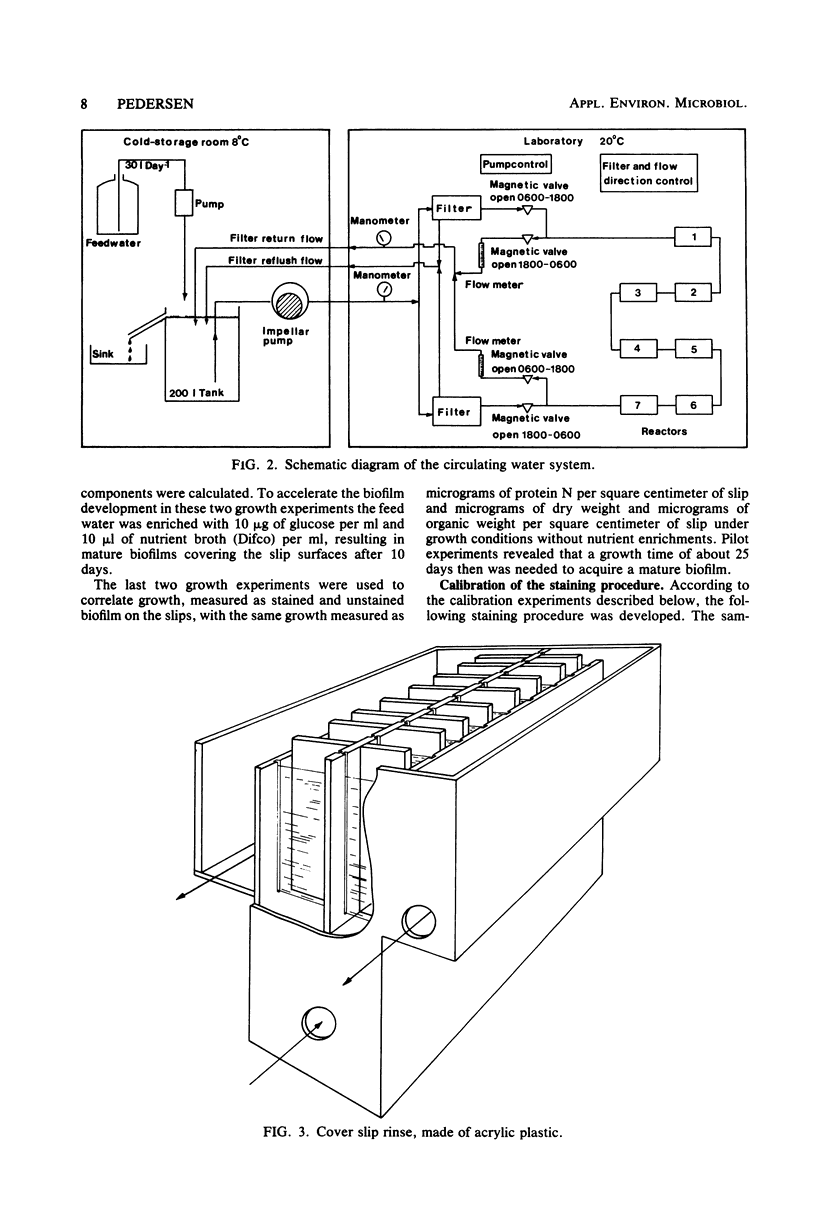
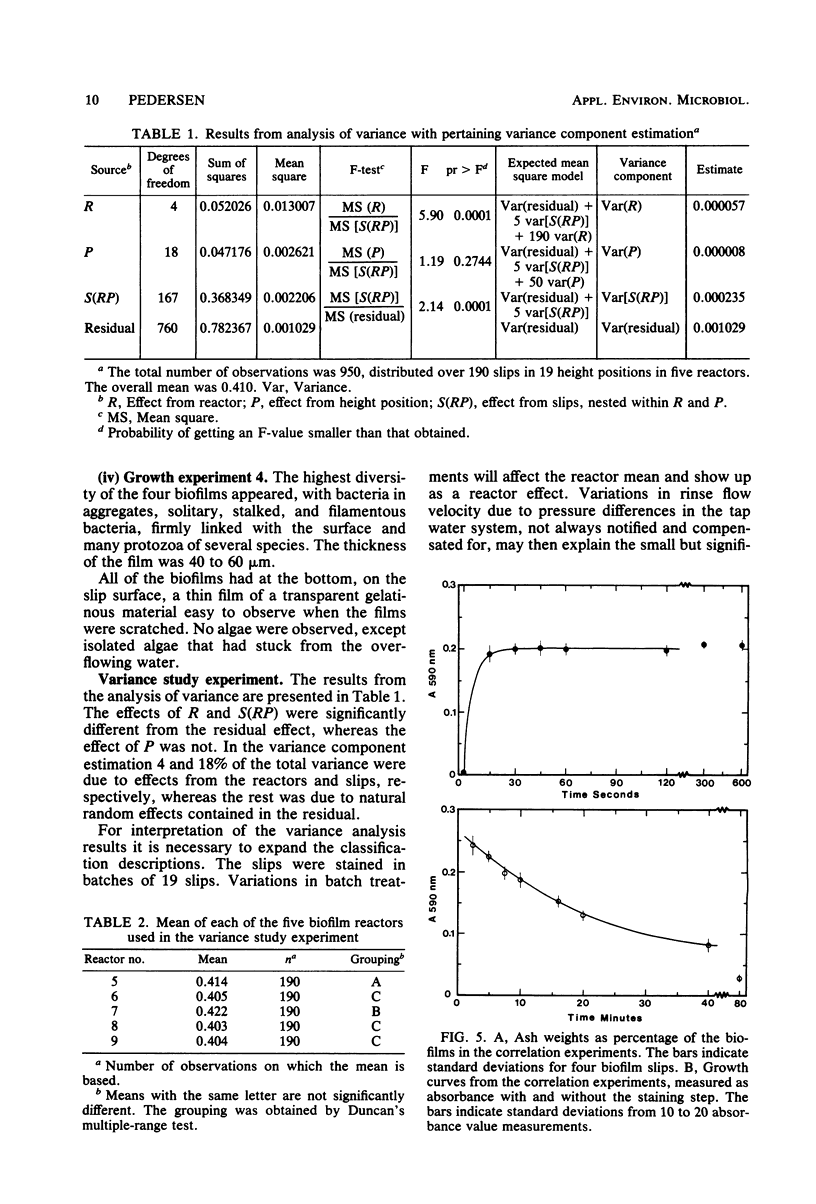
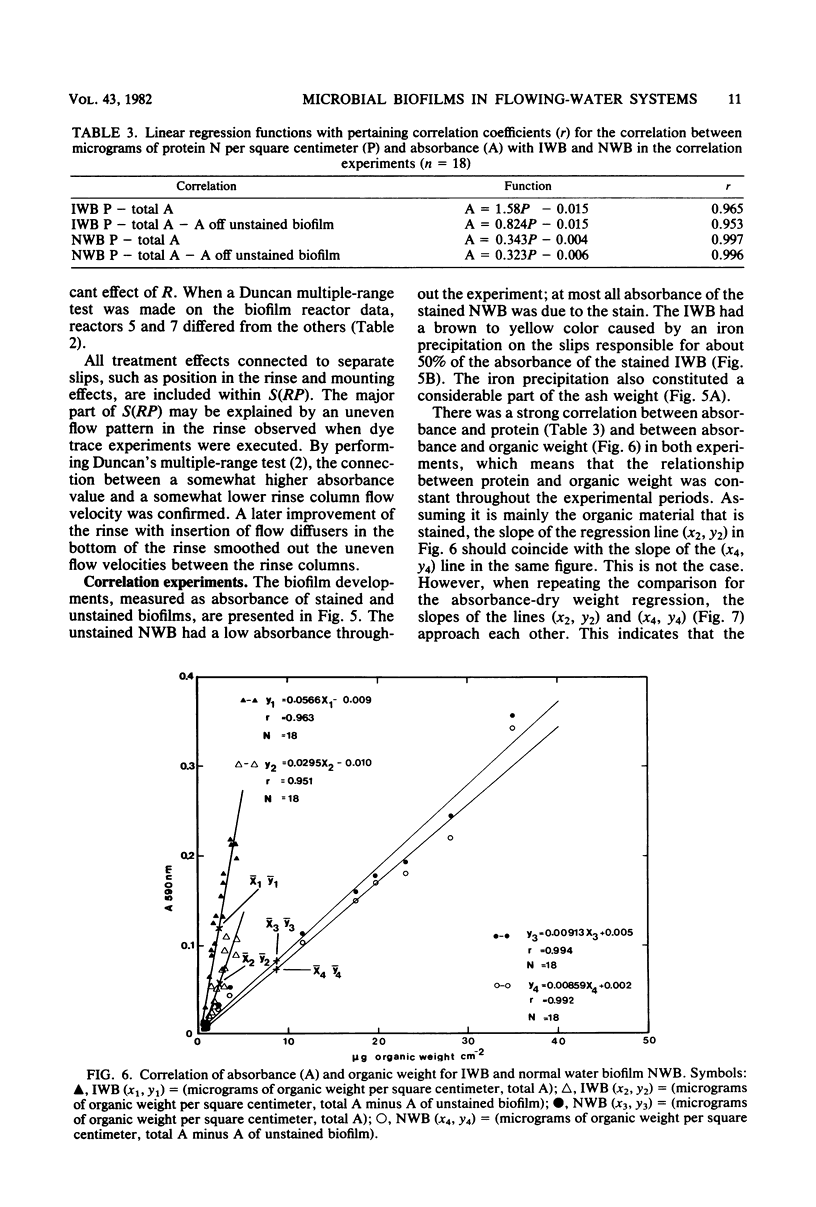
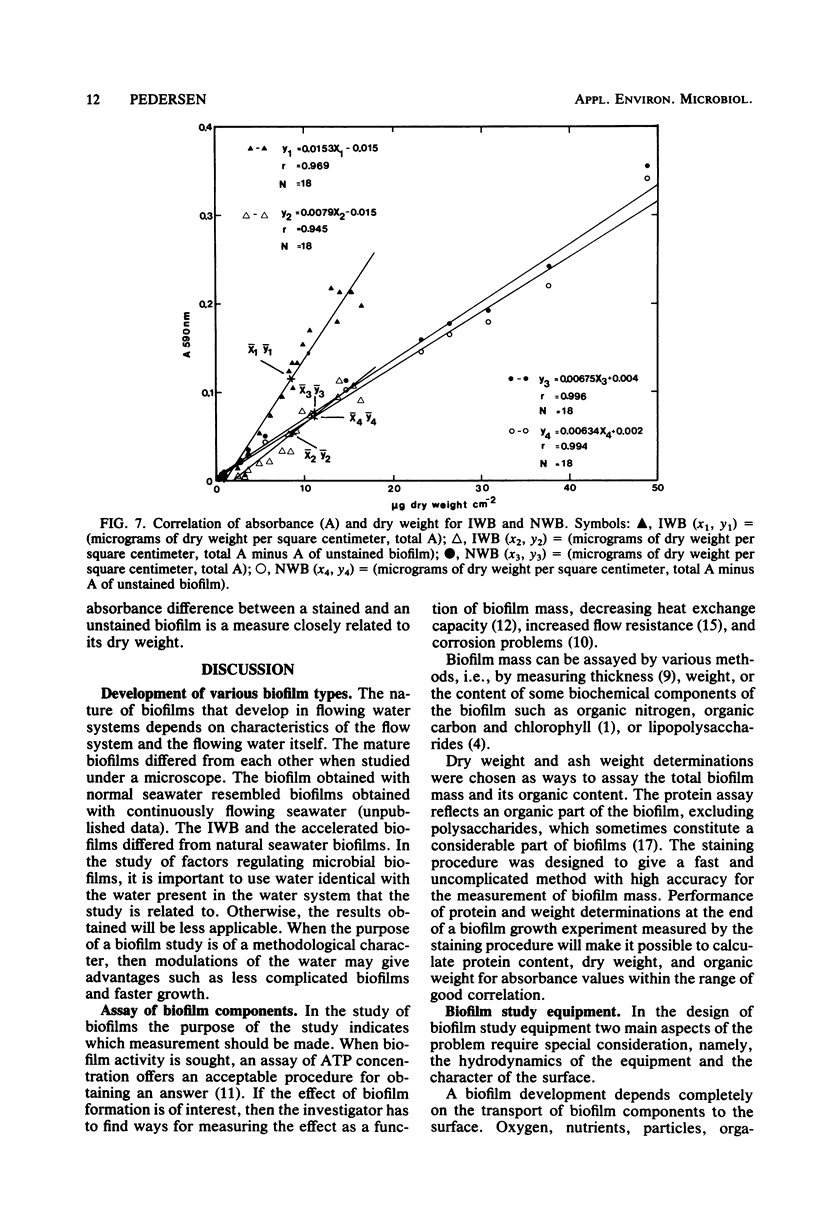
A method for the study of microbial biofilms in flowing-water systems was developed with special reference to the flow conditions in electrochemical concentration cells. Seawater was circulated in a semiclosed flow system through biofilm reactors (3 cm s−1) with microscope cover slips arranged in lamellar piles parallel with the flow. At fixed time intervals cover slips with their biofilm were removed from the pile, stained with crystal violet, and mounted on microscope slides. The absorbances of the slides were measured at 590 nm and plotted against time to give microbial biofilm development. From calibration experiments a staining time of 1 min and a rinse time of 10 min in a tap water flow (3 cm s−1) were considered sufficient. When an analysis of variance was performed on biofilm development data, 78% of the total variance was found to be due to random natural effects; the rest could be explained by experimental effects. The absorbance values correlated well with protein N, dry weight, and organic weight in two biofilm experiments, one with a biofilm with a high (75%) and one with a low (∼25%, normal) inorganic content. Comparisons of regression lines revealed that the absorbance of the stained biofilms was an estimate closely related to biofilm dry weight.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aftring R. P., Taylor B. F. Assessment of microbial fouling in an ocean thermal energy conversion experiment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Oct;38(4):734–739. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.4.734-739.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter S. C., Sullivan J. D., Williams J., Watson S. W. Influence of substrate wettability on the attachment of marine bacteria to various surfaces. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):298–308. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.298-308.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsey T. E., McDonald P. W., Roels O. A. A heated Biuret-Folin protein assay which gives equal absorbance with different proteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):156–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn R. C., Ray A. D. Effects of thickness on bacterial film. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1973 Nov;45(11):2302–2320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Motta E. J. Kinetics of growth and substrate uptake in a biological film system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):286–293. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.286-293.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


