Abstract
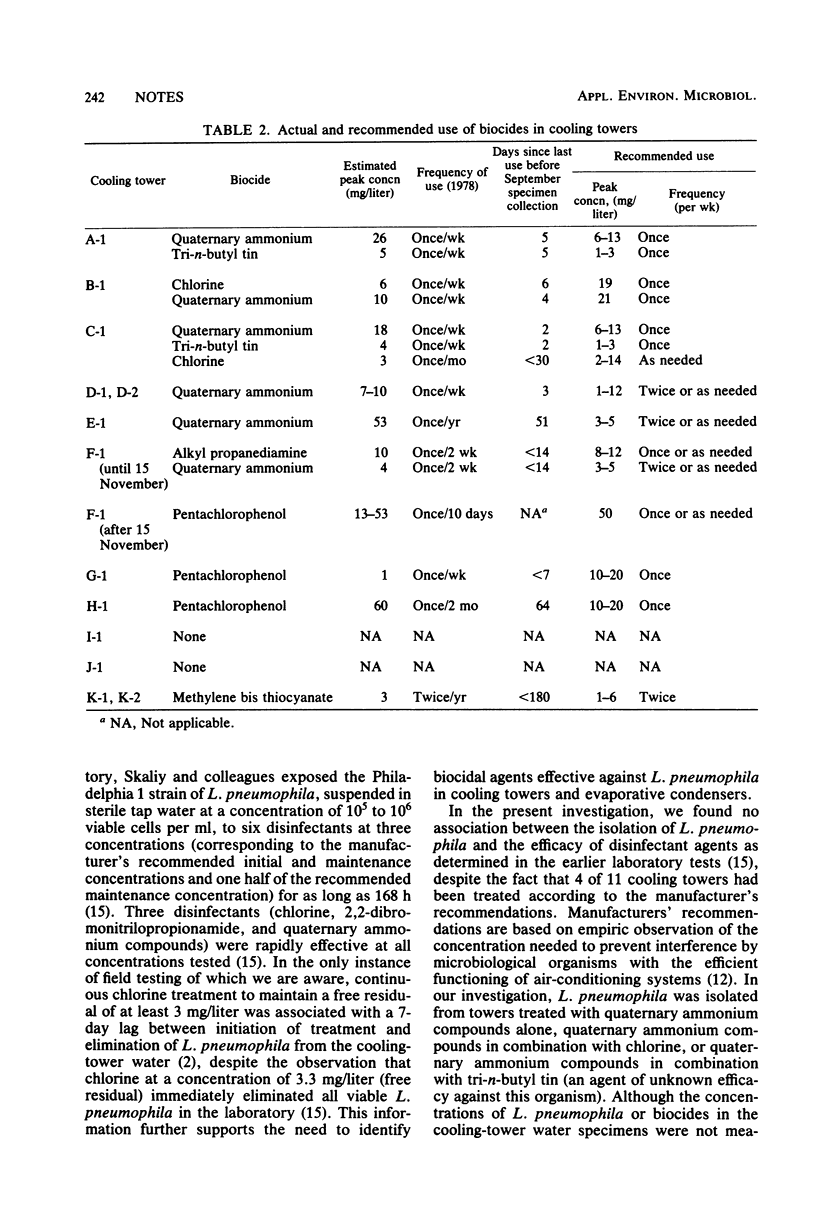
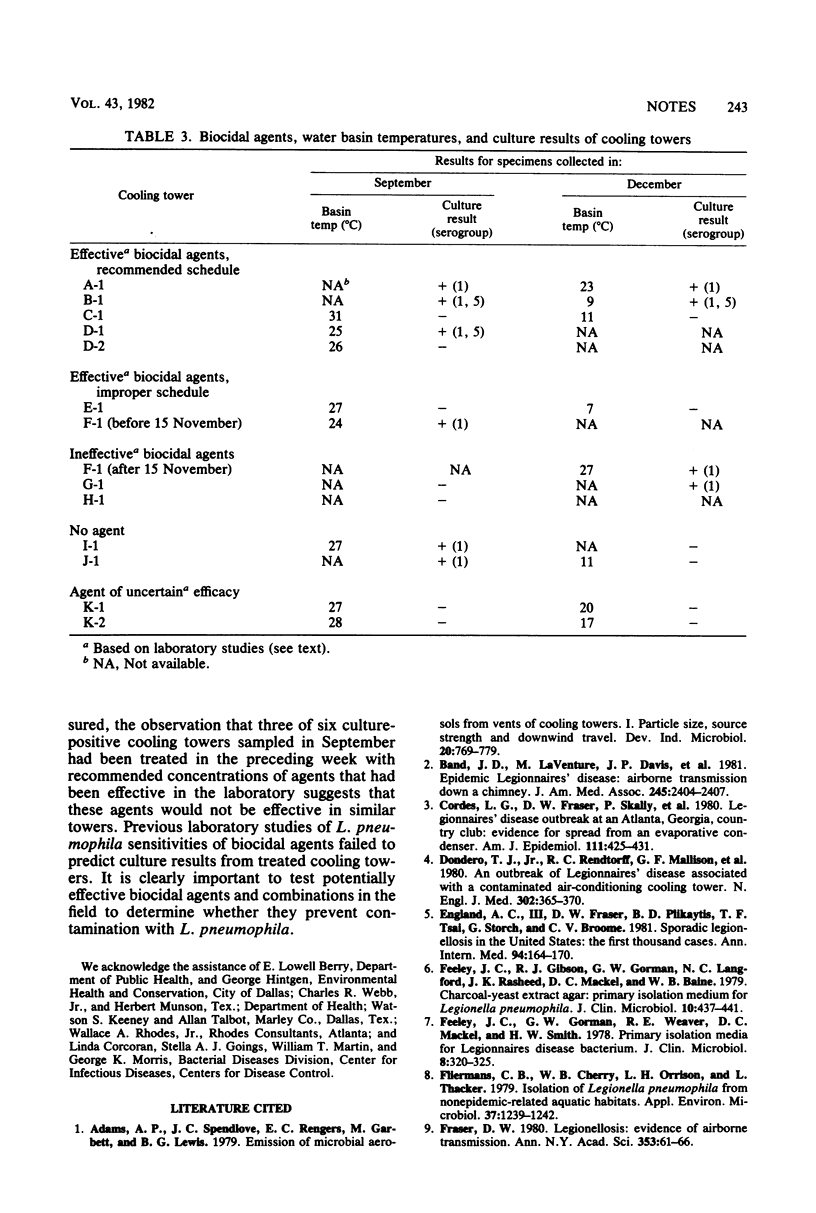
The disinfection of cooling towers based on manufacturers' treatment protocols, as employed in units installed at various public gathering places in Dallas, Tex. (hotels, municipal auditorium), and at the city health department, was evaluated for effectiveness in controlling Legionella pneumophila and compared with previous laboratory studies. In specimens collected in September and December, 1978, L. pneumophila was isolated from 2 of 4 specimens from untreated cooling towers, 2 of 4 specimens from towers treated with agents deemed ineffective in earlier laboratory tests, 6 of 11 specimens from towers treated with putatively effective agents, and 0 of 4 specimens from towers treated with an agent unknown efficacy. These results suggest the need for further studies to identify biocidal agents effective in eliminating L. pneumophila from air-conditioning cooling towers.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Band J. D., LaVenture M., Davis J. P., Mallison G. F., Skaliy P., Hayes P. S., Schell W. L., Weiss H., Greenberg D. J., Fraser D. W. Epidemic Legionnaires' disease. Airborne transmission down a chimney. JAMA. 1981 Jun 19;245(23):2404–2407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes L. G., Fraser D. W., Skaliy P., Perlino C. A., Elsea W. R., Mallison G. F., Hayes P. S. Legionnaires' disease outbreak at an Atlanta, Georgia, Country Club: evidence for spread from an evaporative condenser. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Apr;111(4):425–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondero T. J., Jr, Rendtorff R. C., Mallison G. F., Weeks R. M., Levy J. S., Wong E. W., Schaffner W. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a contaminated air-conditioning cooling tower. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 14;302(7):365–370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002143020703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England A. C., 3rd, Fraser D. W., Plikaytis B. D., Tsai T. F., Storch G., Broome C. V. Sporadic legionellosis in the United States: the first thousand cases. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):164–170. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Thacker L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from nonepidemic-related aquatic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1239–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1239-1242.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W. Legionellosis: evidence of airborne transmission. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;353:61–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb18906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Orenstein W., Parkin W. E., Beecham H. J., Sharrar R. G., Harris J., Mallison G. F., Martin S. M., McDade J. E. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick T. H., Gregg M. B., Berman B., Mallison G., Rhodes W. W., Jr, Kassanoff I. Pontiac fever. An epidemic of unknown etiology in a health department: I. Clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Feb;107(2):149–160. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. P. Cooling towers and evaporative condensers. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):667–670. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Patton C. M., Feeley J. C., Johnson S. E., Gorman G., Martin W. T., Skaliy P., Mallison G. F., Politi B. D., Mackel D. C. Isolation of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium from environmental samples. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):664–666. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Weaver R. E., Dees S. B., Cherry W. B. Cellular fatty acid composition of isolates from Legionnaires disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):140–143. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.140-143.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaliy P., Thompson T. A., Gorman G. W., Morris G. K., McEachern H. V., Mackel D. C. Laboratory studies of disinfectants against Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):697–700. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.697-700.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


