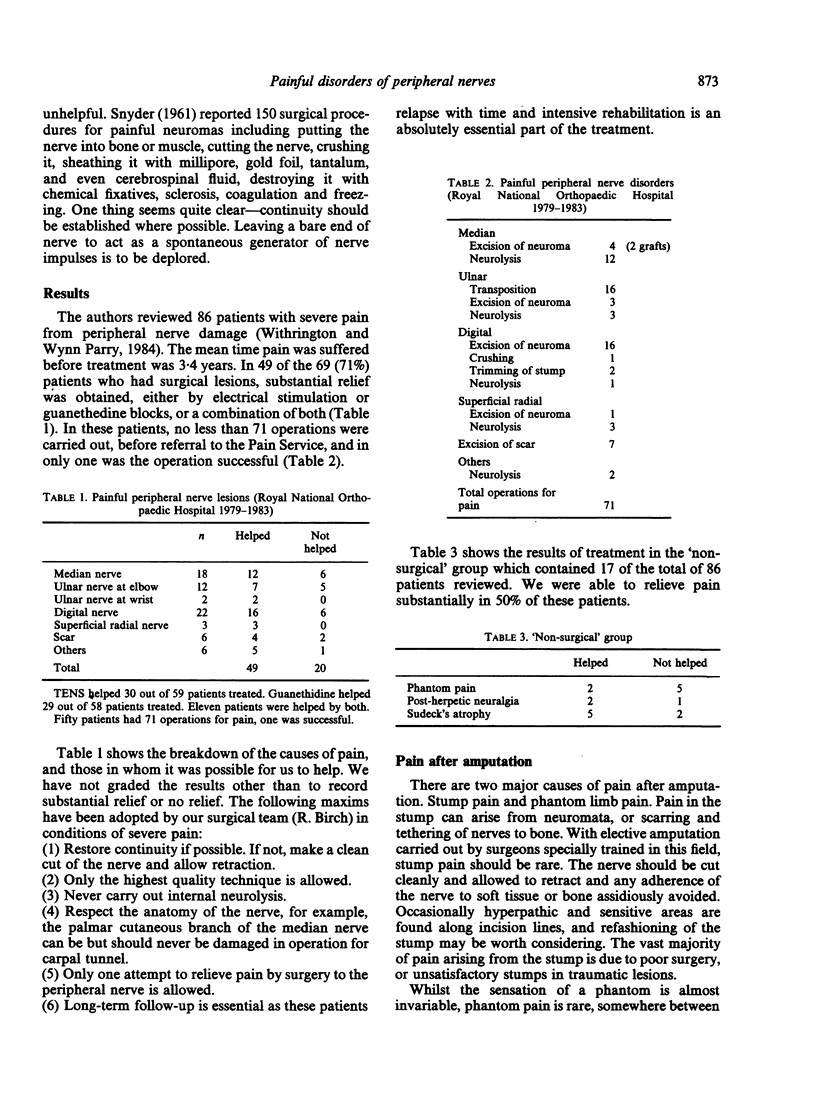
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. S., Black R. G., Abraham J., Ward A. A., Jr Neuronal hyperactivity in experimental trigeminal deafferentation. J Neurosurg. 1971 Oct;35(4):444–452. doi: 10.3171/jns.1971.35.4.0444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. N., Long D. M. Peripheral nerve stimulation in the treatment of intractable pain. J Neurosurg. 1976 Dec;45(6):692–699. doi: 10.3171/jns.1976.45.6.0692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton V. M. Pain control with the aid of transcutaneous nerve stimulation. Physiotherapy. 1982 Mar;68(3):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannington-Kiff J. G. Intravenous regional sympathetic block with guanethidine. Lancet. 1974 May 25;1(7865):1019–1020. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbal R., Devor M., Tuchendler O., Lieblich I. Autotomy following nerve injury: genetic factors in the development of chronic pain. Pain. 1980 Dec;9(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(80)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen T. S., Krebs B., Nielsen J., Rasmussen P. Phantom limb, phantom pain and stump pain in amputees during the first 6 months following limb amputation. Pain. 1983 Nov;17(3):243–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(83)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Nathan P. W. Painful peripheral states and sympathetic blocks. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Jul;41(7):664–671. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.7.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nashold B. S., Jr, Ostdahl R. H. Dorsal root entry zone lesions for pain relief. J Neurosurg. 1979 Jul;51(1):59–69. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.1.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan P. W. Painful legs and moving toes: evidence on the site of the lesion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Oct;41(10):934–939. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.10.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordenbos W., Wall P. D. Implications of the failure of nerve resection and graft to cure chronic pain produced by nerve lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Dec;44(12):1068–1073. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.12.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J. L., Torebjörk H. E. Paraesthesiae from ectopic impulse generation in human sensory nerves. Brain. 1980 Dec;103(4):835–853. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.4.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scadding J. W., Wall P. D., Parry C. B., Brooks D. M. Clinical trial of propranolol in post-traumatic neuralgia. Pain. 1982 Nov;14(3):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(82)90135-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper J. W., Booth D. M. Treatment of painful neuromas of sensory nerves in the hand: a comparison of traditional and newer methods. J Hand Surg Am. 1976 Sep;1(2):144–151. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(76)80008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D., Gutnick M. Properties of afferent nerve impulses originating from a neuroma. Nature. 1974 Apr 26;248(5451):740–743. doi: 10.1038/248740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D., Sweet W. H. Temporary abolition of pain in man. Science. 1967 Jan 6;155(3758):108–109. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3758.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. C., Heroy W. W., Goodman E. N. Causalgia Following Gunshot Injuries of Nerves : Role of Emotional Stimuli and Surgical Cure through Interruption of Diencephalic Efferent Discharge by Sympathectomy. Ann Surg. 1948 Aug;128(2):161–183. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194808000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


