Abstract
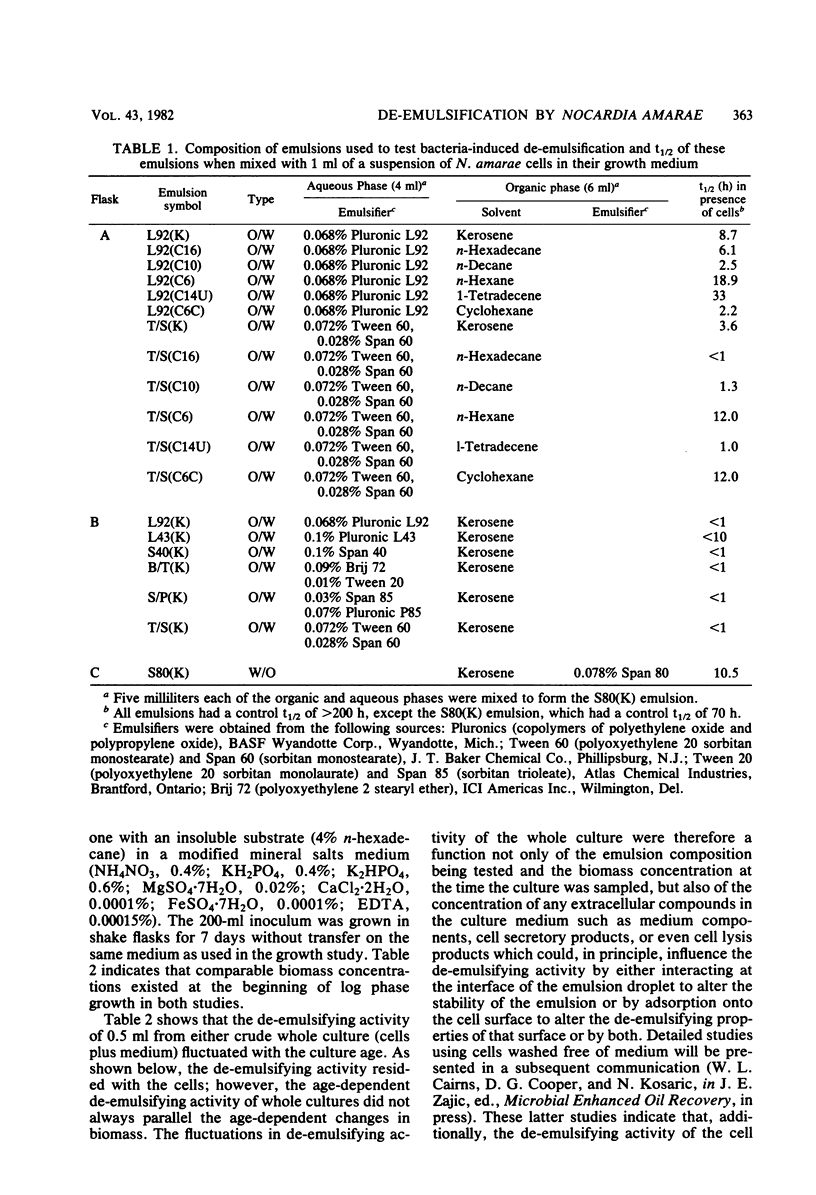
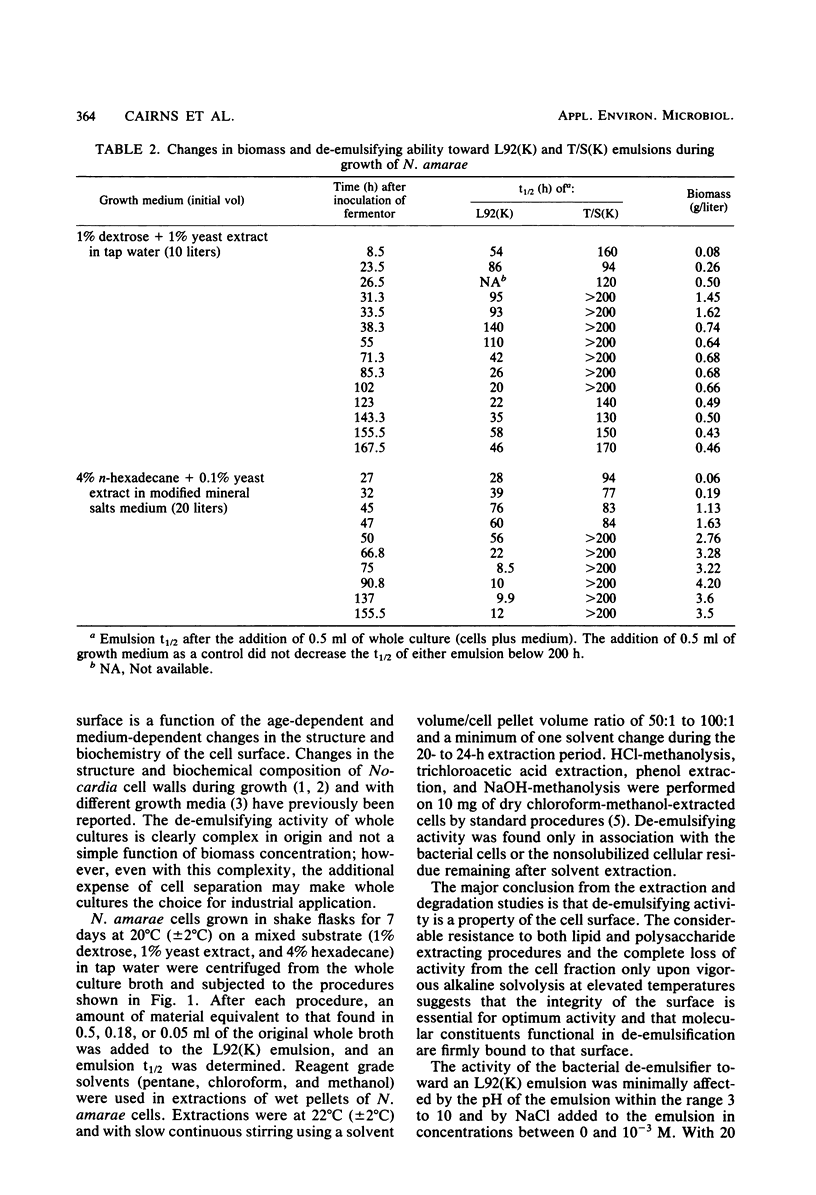
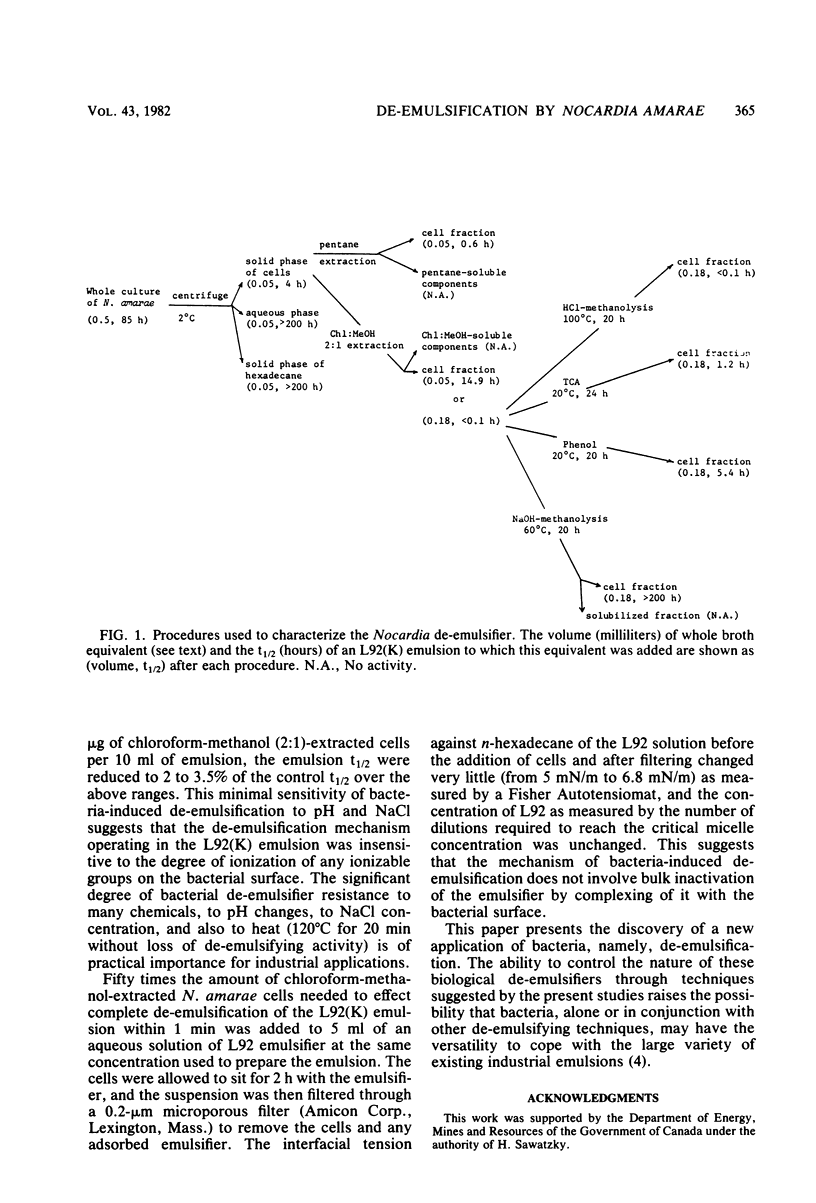
Nocardia amarae grown in a liquid medium induced coalescence of emulsions which differed in type, composition of the organic phase, and structure of stabilizing emulsifiers. De-emulsifying activity varied with the type of growth medium, culture age, and postharvest treatment. Based on extraction and degradation studies, it was concluded that de-emulsifying properties are due to the bacterial cell surface. Thus, bacteria may provide a new source of de-emulsifying agents.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaman B. L., Kim K. S., Salton M. R., Barksdale L. Amino acids of the cell wall of Nocardia rubra. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):941–943. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.941-943.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Shankel D. M. Ultrastructure of Nocardia cell growth and development on defined and complex agar media. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):876–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.876-884.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L. Structural and biochemical alterations of Nocardia asteroides cell walls during its growth cycle. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1235–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1235-1253.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


