Abstract
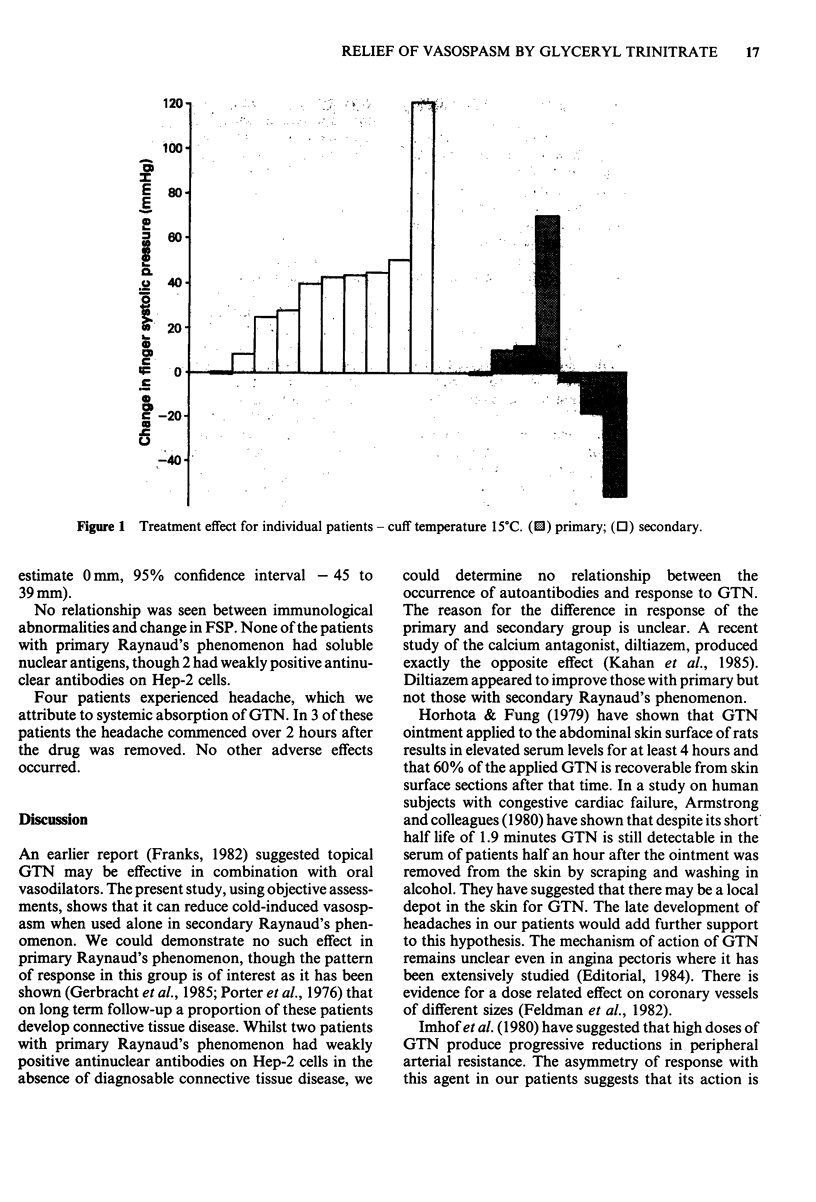
An objective response to topical glyceryl trinitrate was shown by digital plethysmography in a study of 17 patients with Raynaud's phenomenon. Improvement was significant (P less than 0.005) in those in whom the disease was secondary to an underlying connective tissue disorder. The response suggests that the effect of this drug is mediated locally.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong P. W., Armstrong J. A., Marks G. S. Pharmacokinetic-hemodynamic studies of nitroglycerin ointment in congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1980 Oct;46(4):670–676. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(80)90519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. L., Marx J. D., Pepine C. J., Conti C. R. Analysis of coronary responses to various doses of intracoronary nitroglycerin. Circulation. 1982 Aug;66(2):321–327. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.2.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks A. G., Jr Topical glyceryl trinitrate as adjunctive treatment in Raynaud's disease. Lancet. 1982 Jan 9;1(8263):76–77. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbracht D. D., Steen V. D., Ziegler G. L., Medsger T. A., Jr, Rodnan G. P. Evolution of primary Raynaud's phenomenon (Raynaud's disease) to connective tissue disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Jan;28(1):87–92. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horhota S. T., Fung H. L. Percutaneous nitroglycerin absorption in rats. J Pharm Sci. 1979 May;68(5):608–612. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imhof P. R., Ott B., Frankhauser P., Chu L. C., Hodler J. Difference in nitroglycerin dose-response in the venous and arterial beds. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(6):455–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00874655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan A., Amor B., Menkes C. J. A randomised double-blind trial of diltiazem in the treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Jan;44(1):30–33. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Lassen N. A. Measurement of digital blood pressure after local cooling. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Nov;43(5):907–910. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.5.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L. Raynaud phenomena and finger systolic pressure during cooling. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;38(8):765–770. doi: 10.1080/00365517809104885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen N., Nielsen S. L. Prevalence of primary Raynaud phenomena in young females. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;38(8):761–764. doi: 10.1080/00365517809104884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter J. M., Bardana E. J., Jr, Baur G. M., Wesche D. H., Andrasch R. H., Rösch J. The clinical significance of Raynaud's syndrome. Surgery. 1976 Dec;80(6):756–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



