Abstract
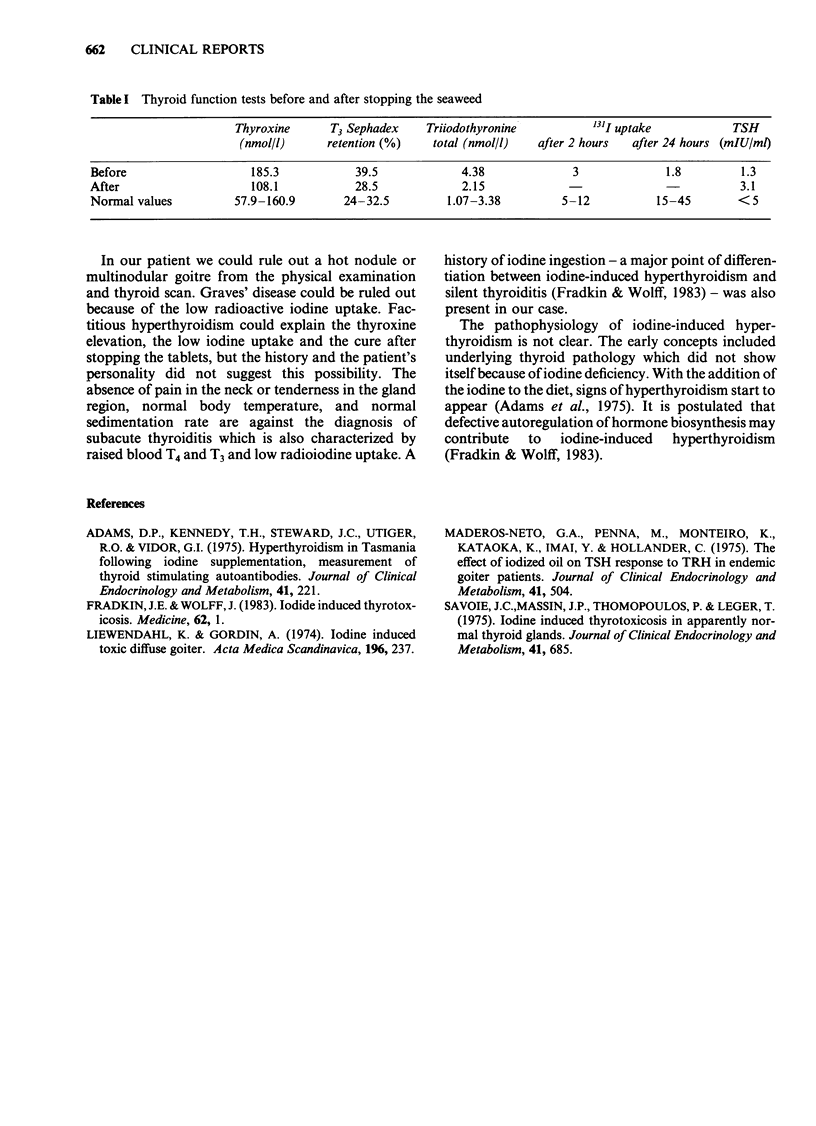
Iodine-induced hyperthyroidism can develop even in the presence of an otherwise normal gland. One of the less common sources of iodine is tablets of seaweed, sold over the counter without prescription. We report the case of a 72 year old female who developed clinical and laboratory evidence of hyperthyroidism while ingesting sea-kelp (Vitalia) tablets. Six months after stopping the tablets, the symptoms and laboratory evidence of hyperthyroidism had disappeared. No evidence of pre-existing thyroid disease was found.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. D., Kennedy T. H., Stewart J. C., Utiger R. D., Vidor G. I. Hyperthyroidism in Tasmania following iodide supplementation: measurements of thyroid-stimulating autoantibodies and thyrotropin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Aug;41(2):221–228. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradkin J. E., Wolff J. Iodide-induced thyrotoxicosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Jan;62(1):1–20. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198301000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liewendahl K., Gordin A. Iodine-induced toxic diffuse goitre. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Sep;196(3):237–239. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1974.tb01001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros-Neto G. A., Penna M., Monteiro K., Kataoka K., Imai Y., Hollander C. The effect of iodized oil on the TSH response to TRH in endemic goiter patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Sep;41(3):504–510. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-3-504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savoie J. C., Massin J. P., Thomopoulos P., Leger F. Iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis in apparently normal thyroid glands. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Oct;41(4):685–691. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-4-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


