Abstract
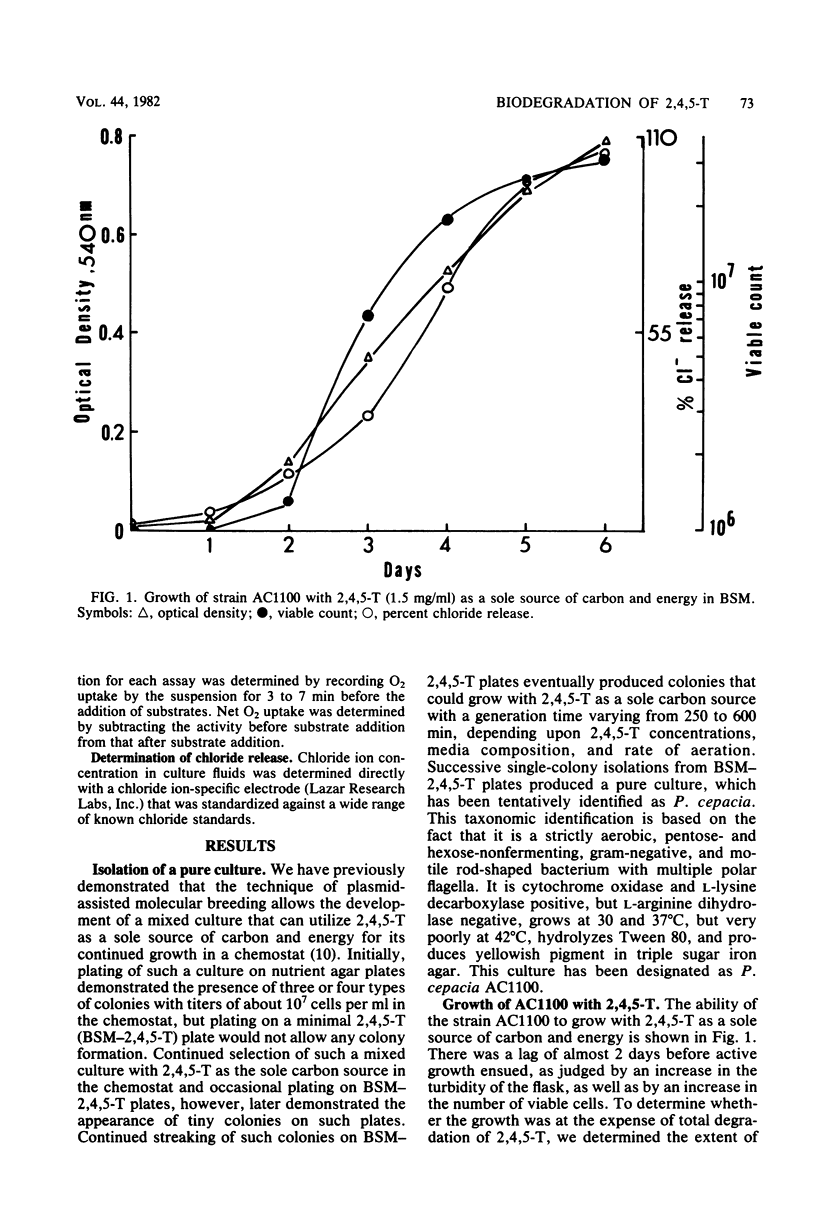
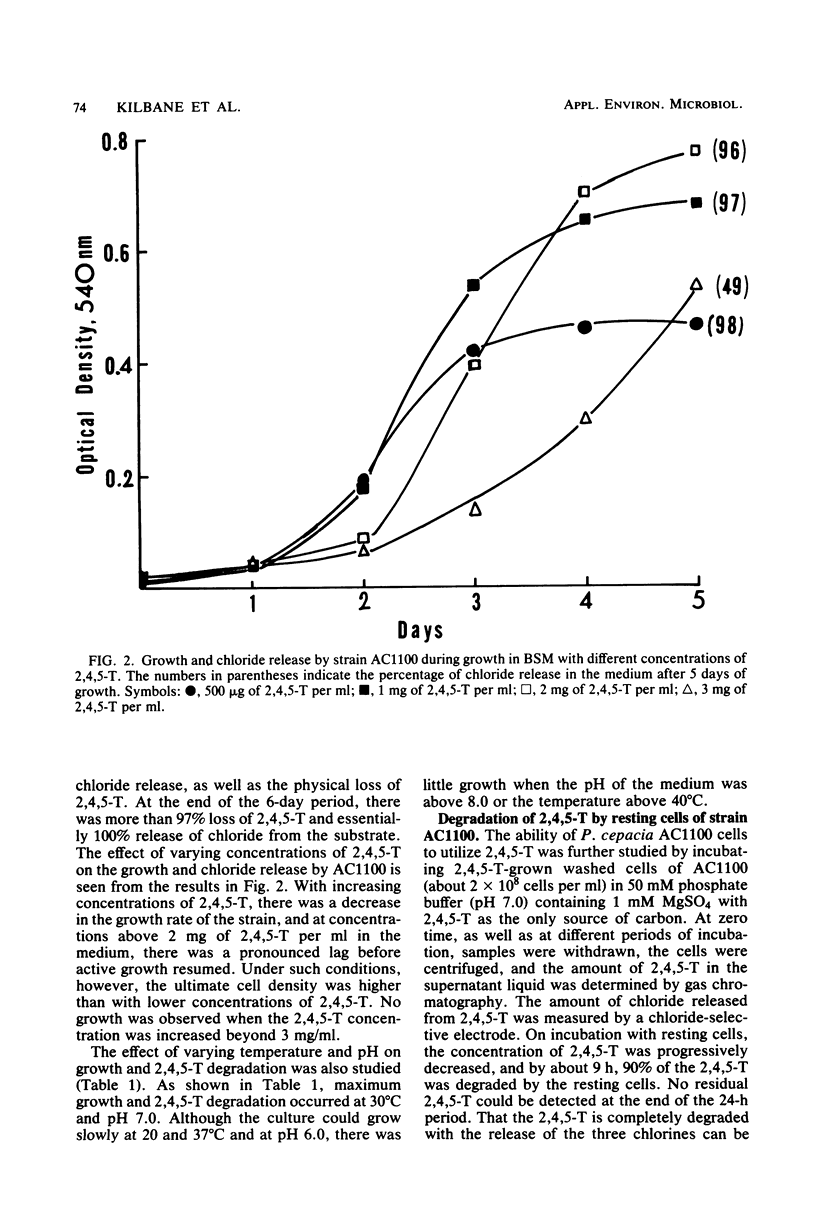
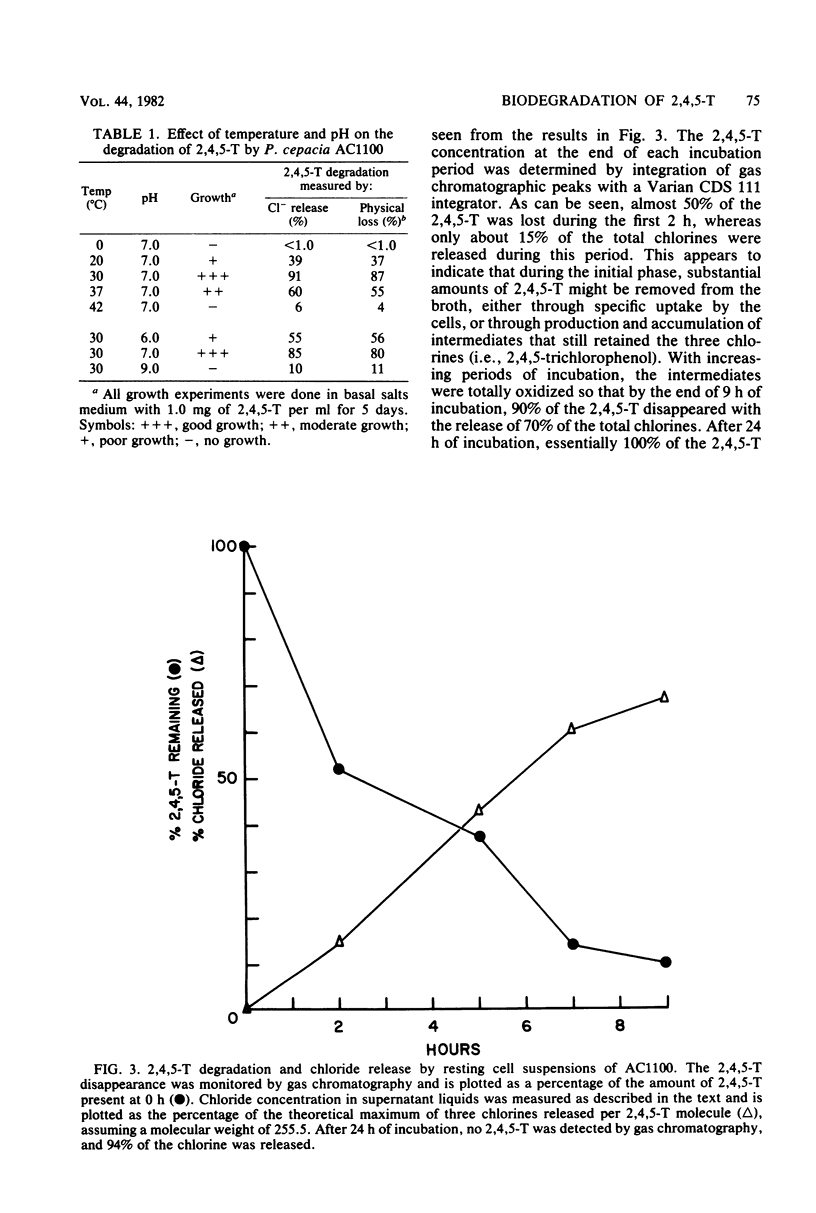
A pure culture of Pseudomonas cepacia, designated AC1100, that can utilize 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) as its sole source of carbon and energy was isolated. An actively growing culture of AC1100 was able to degrade more than 97% of 2,4,5-T, present at 1 mg/ml, within 6 days as determined by chloride release, gas chromatographic, and spectrophotometric analyses. The ability of AC1100 to oxidize a variety of chlorophenols and related compounds is also reported.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. Biodegradation of chemicals of environmental concern. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):132–138. doi: 10.1126/science.7444456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant W. F. The genotoxic effects of 2,4,5-T. Mutat Res. 1979;65(2):83–119. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(79)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanify J. A., Metcalf P., Nobbs C. L., Worsley K. J. Aerial spraying of 2,4,5-T and human birth malformations: an epidemiological investigation. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):349–351. doi: 10.1126/science.7209535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J. Isolation, mapping, and examination of effects of TnA insertions in ColE1 plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):482–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.482-491.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg S. T., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmid-assisted molecular breeding: new technique for enhanced biodegradation of persistent toxic chemicals. Science. 1981 Dec 4;214(4525):1133–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.7302584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Feary T. W., Blevins W. T. Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency in pleiotropic carbohydrate-negative mutant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):999–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.999-1009.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



