Abstract
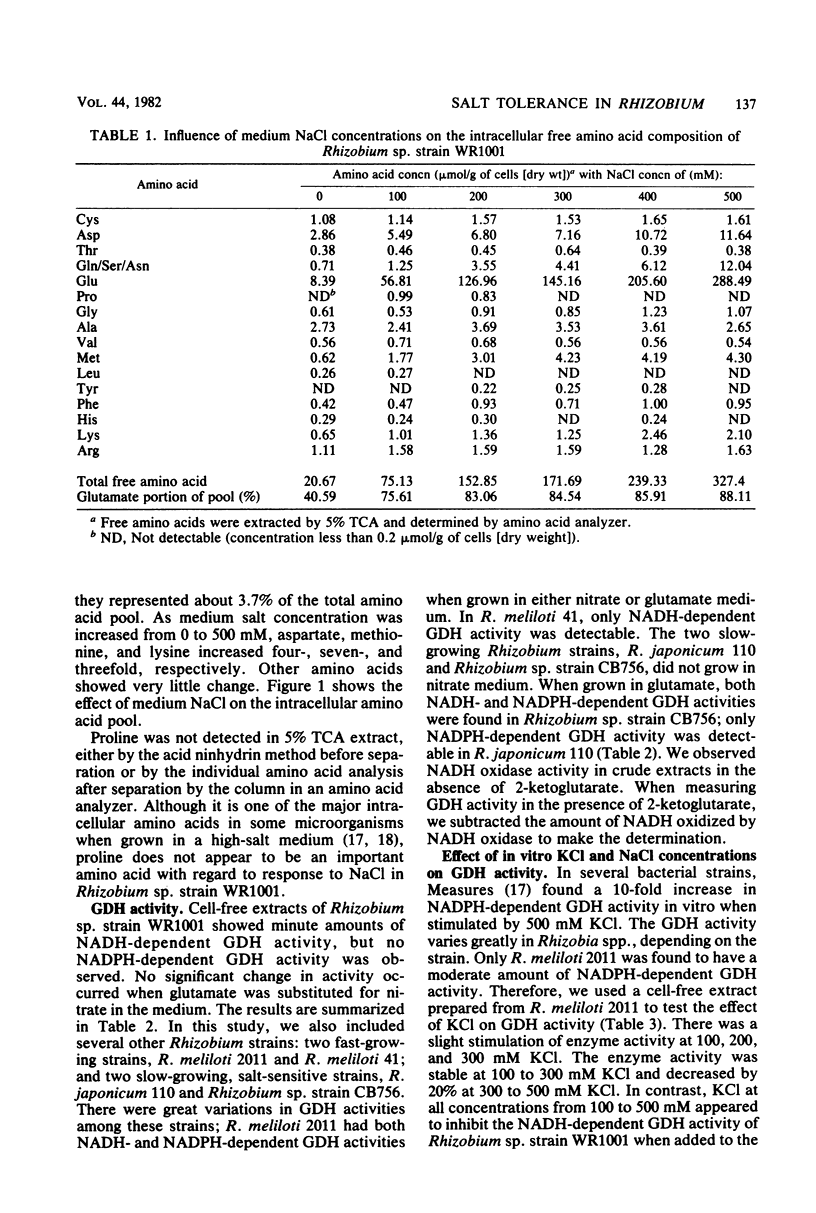
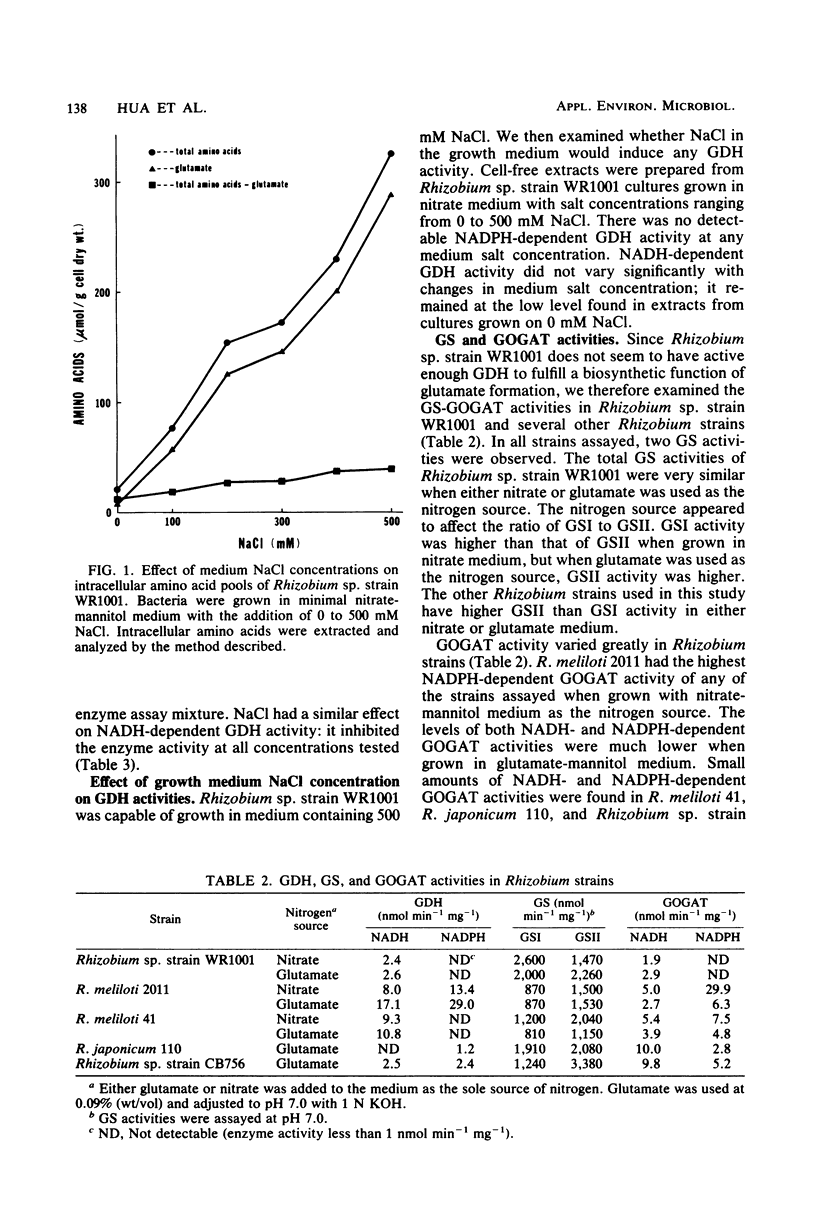
Rhizobium sp. strain WR1001, isolated from the Sonoran Desert by Eskew and Ting, was found to be able to grow in defined medium containing NaCl up to 500 mM, a concentration approaching that of sea water. Therefore, it is a valuable strain for studying the biochemical basis of salt tolerance. Intracellular free glutamate was found to increase rapidly in response to osmotic stress by NaCl. It accounted for 88% of the amino acid pool when the bacterium was grown in 500 mM NaCl. The role of glutamate dehydrogenase in glutamate biosynthesis was examined in several Rhizobium strains. Both NADH- and NADPH-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase activities in various Rhizobium strains were observed. The range of activity differed considerably depending on the particular strain. KCl (500 mM) did not stimulate glutamate dehydrogenase activity, as reported in a number of bacterial strains by Measures. The low activity of glutamate dehydrogenase in Rhizobium sp. strain WR1001 apparently cannot fulfill a biosynthetic function of glutamate formation in response to medium NaCl concentrations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D. Microbial water stress. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):803–846. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.803-846.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Dilworth M. J. Ammonia assimilation by rhizobium cultures and bacteroids. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):39–48. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrow R. A., Knotts R. R. Two forms of glutamine synthetase in free-living root-nodule bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 23;78(2):554–559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dendinger S. M., Brenchley J. E. Temperature-sensitive glutamate dehydrogenase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1043–1047. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1043-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. L., Keister D. L. Comparative properties of glutamine synthetases I and II in Rhizobium and Agrobacterium spp. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):641–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.641-648.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig R. A. Control of ammonium assimilation in Rhizobium 32H1. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):114–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.114-123.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H. Specific proline accumulation in an acrA mutant of Escherichia coli K12 grown in salt-hypertonic medium. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Aug;113(2):425–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-2-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osburne M. S., Signer E. R. Ammonium assimilation in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1234–1240. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1234-1240.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S., Miller R. E., Valentine R. C. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate control of the enzymes of glutamine metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2922–2926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinborn J., Roughley R. J. Sodium chloride as a cause of low numbers of Rhizobium in legume inoculants. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;37(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinborn J., Roughley R. J. Toxicity of sodium and chloride ions to Rhizobium spp. in broth and peat culture. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;39(2):133–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upchurch R. G., Elkan G. H. Comparison of colony morphology, salt tolerance, and effectiveness in Rhizobium japonicum. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1118–1122. doi: 10.1139/m77-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav N. K., Vyas S. R. Salt and pH tolerance of rhizobia. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1973;18(3):242–247. doi: 10.1007/BF02872863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zablotowicz R. M., Focht D. D. Physiological Characteristics of Cowpea Rhizobia: Evaluation of Symbiotic Efficiency in Vigna unguiculata. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):679–685. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.679-685.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



