Abstract
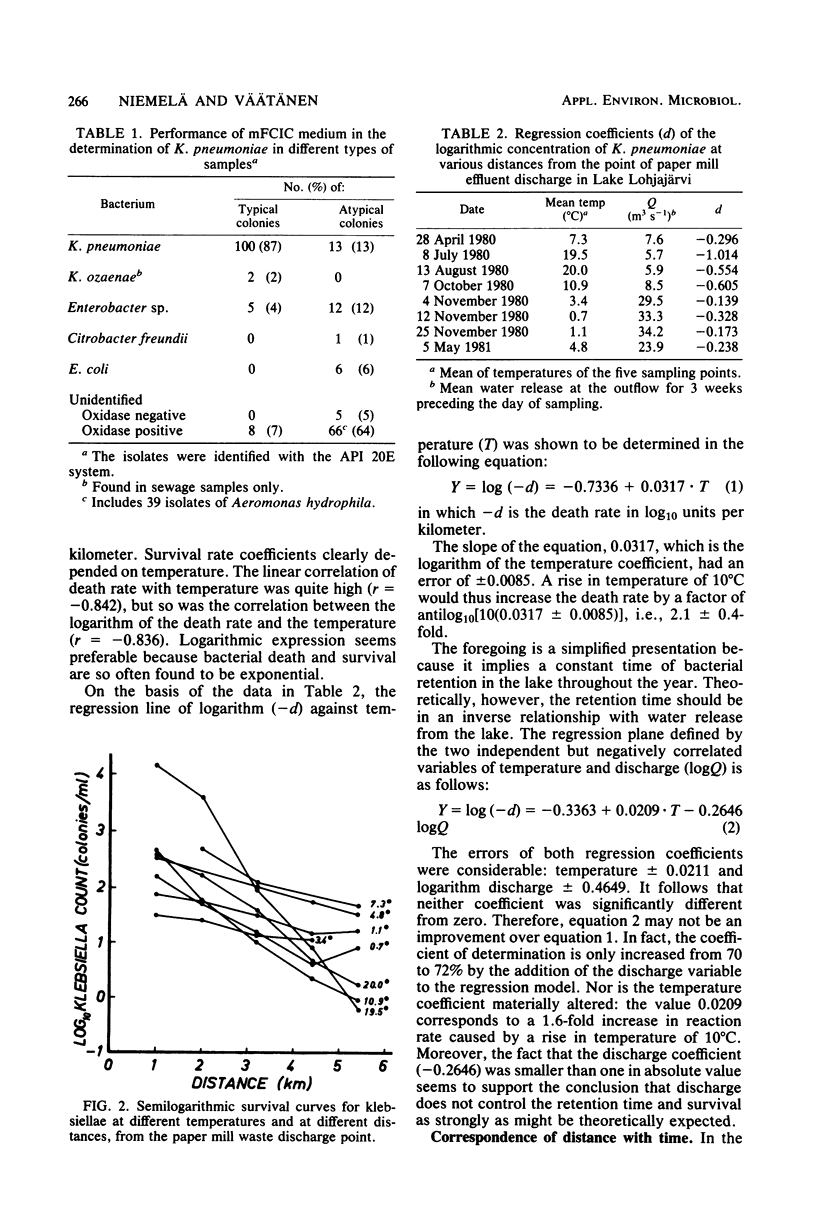
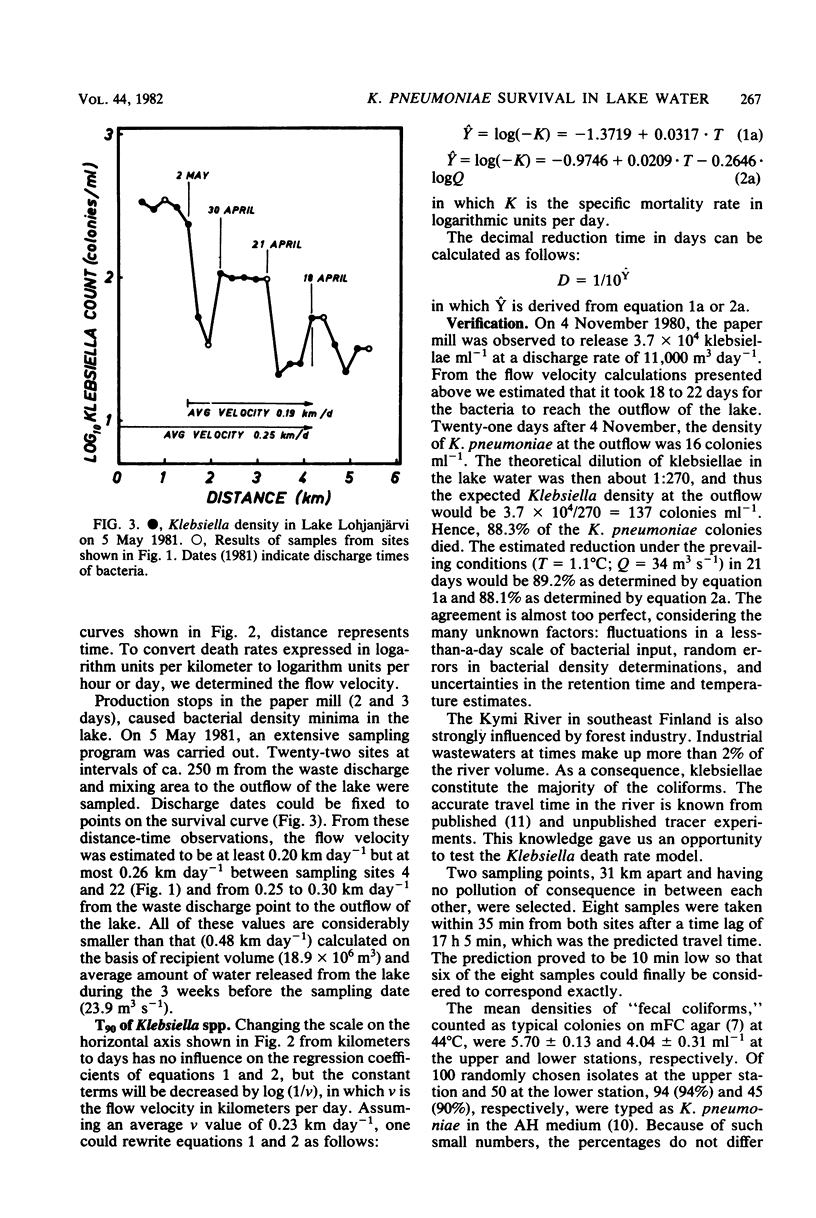
We investigated survival of Klebsiella pneumoniae in freshwater, by determining bacterial densities at eight temperatures between 0 and 20 degrees C at various distances from the discharge area in a lake receiving bacteria mainly from a paper mill. An mFC-inositol-carbenicillin-agar medium was used for Klebsiella enumeration by the membrane filter method. About 90% of the bacteria forming typical colonies on this medium were identified as Klebsiella species. About 10% of the bacteria were false positive, and, an equal percentage were false negative. Semilogarithmic plots of bacterial densities as a function of distance were found to be linear, with slopes depending on water temperature. The average velocity of the flow was estimated from the travel-of-bacterial-density minima caused by production stops. Regression equations were calculated for the dependence of death rate on temperature alone and on both temperature and discharge. The temperature coefficient (Q10) of the death rate was estimated to be 2.1 +/- 0.4. The decimal reduction time (T90) of K. pneumoniae at 0 degrees C was calculated to be about 24 days, and that at 20 degrees C was slightly over 5 days. The regression model was verified by independent observations. Factors affecting the reliability of the estimates were evaluated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagley S. T., Seidler R. J. Primary Klebsiella identification with MacConkey-inositol-carbenicillin agar. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):536–538. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.536-538.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagley S. T., Seidler R. J. Significance of fecal coliform-positive Klebsiella. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1141–1148. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1141-1148.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. M., Michaels G., Klein R. D., Roth I. L. Isolation of Klebsiella pneumoniae from lake water. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Dec;22(12):1762–1767. doi: 10.1139/m76-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan D. W., Razzell W. E. Klebsiella biotypes among coliforms isolated from forest environments and farm produce. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Dec;24(6):933–938. doi: 10.1128/am.24.6.933-938.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntley B. E., Jones A. C., Cabelli V. J. Klebsiella densities in waters receiving wood pulp effluents. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1976 Jul;48(7):1766–1771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Seidler R. J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R. Medium for the presumptive identification of Aeromonas hydrophila and Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):1023–1026. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.1023-1026.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knittel M. D., Seidler R. J., Eby C., Cabe L. M. Colonization of the botanical environment by Klebsiella isolates of pathogenic origin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):557–563. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.557-563.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson A. H., Sparell L. Acetylene reduction (nitrogen fixation) by enterobacteriaceae isolated from paper mill process waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Aug;32(2):197–205. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.2.197-205.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjogren R. E., Gibson M. J. Bacterial survival in a dilute environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1331–1336. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1331-1336.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stramer S. L. Presumptive identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae on m-FC medium. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Dec;22(12):1774–1776. doi: 10.1139/m76-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot H. W., Jr, Seidler R. J. Cyclitol utilization associated with the presence of Klebsielleae in botanical environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):909–915. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.909-915.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



