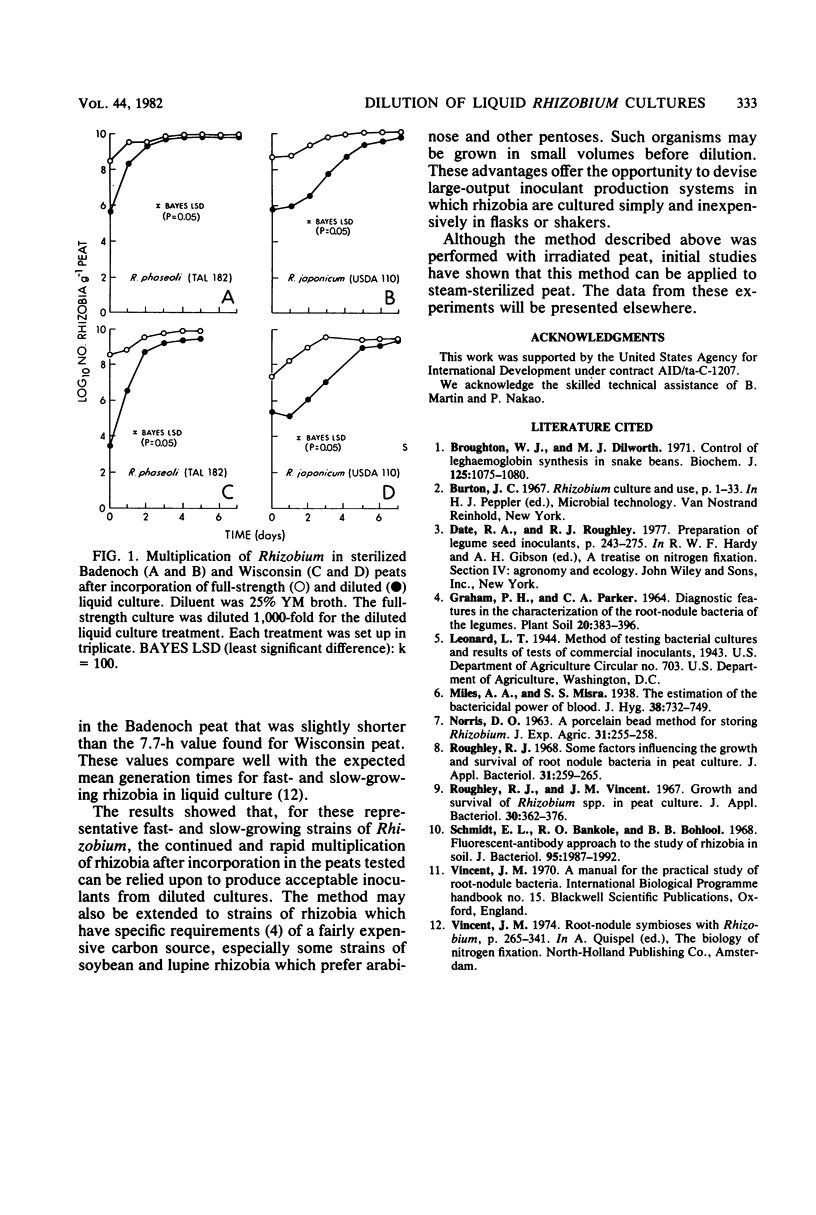
Abstract
Experiments were undertaken to test whether peat-based legume seed inoculants, which are prepared with liquid cultures that have been deliberately diluted, can attain and sustain acceptable numbers of viable rhizobia. Liquid cultures of Rhizobium japonicum and Rhizobium phaseoli were diluted to give 108, 107, or 106 cells per ml, using either deionized water, quarter-strength yeast-mannitol broth, yeast-sucrose broth, or yeast-water. The variously diluted cultures were incorporated into gamma-irradiated peat, and the numbers of viable rhizobia were determined at intervals. In all of the inoculant formulations, the numbers of rhizobia reached similarly high ceiling values by 1 week after incorporation, irrespective not only of the number of cells added initially but also of the nature of the diluent. During week 1 of growth, similar multiplication patterns of the diluted liquid cultures were observed in two different peats. Numbers of rhizobia surviving in the various inoculant formulations were not markedly different after 6 months of storage at 28°C. The method of inoculant preparation did not affect the nitrogen fixation effectiveness of the Rhizobium strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broughton W. J., Dilworth M. J. Control of leghaemoglobin synthesis in snake beans. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1042/bj1251075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Bakole R. O., Bohlool B. B. Fluorescent-antibody approach to study of rhizobia in soil. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1987-1992.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



