Abstract
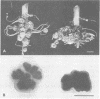
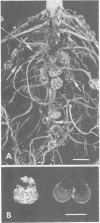
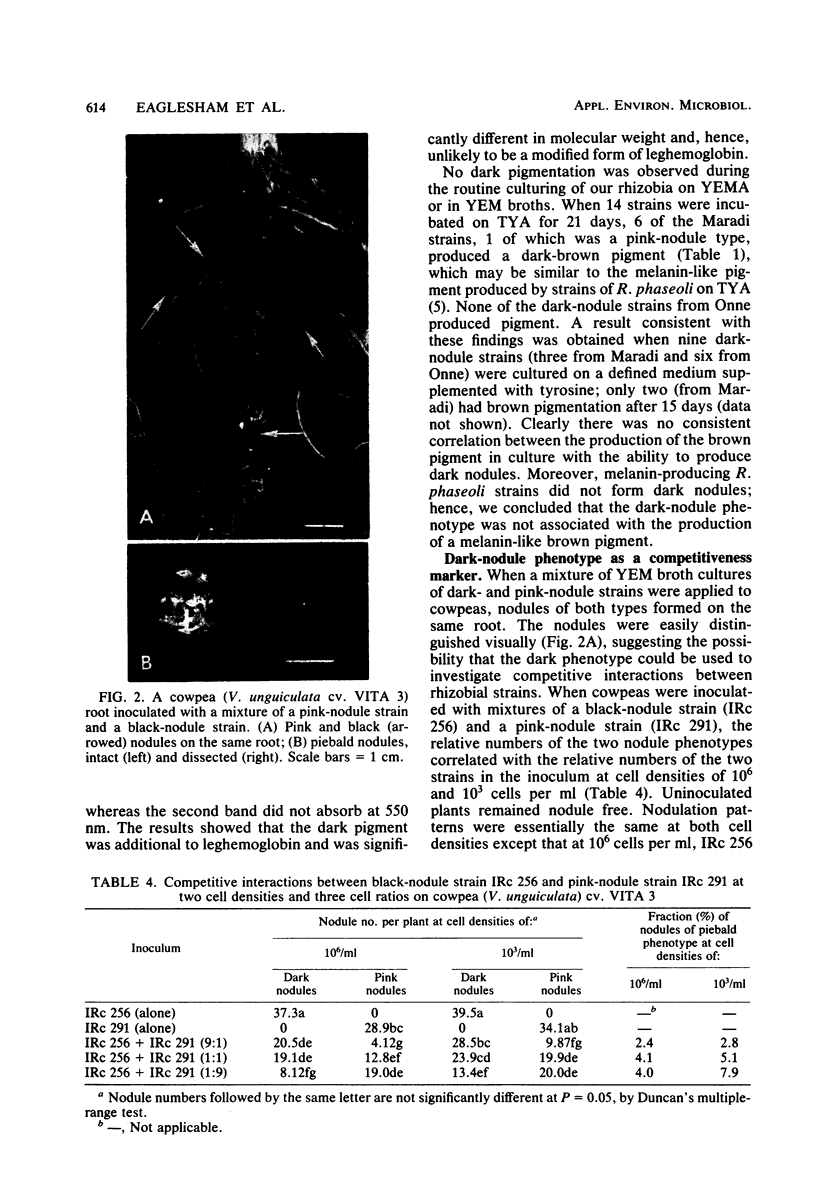
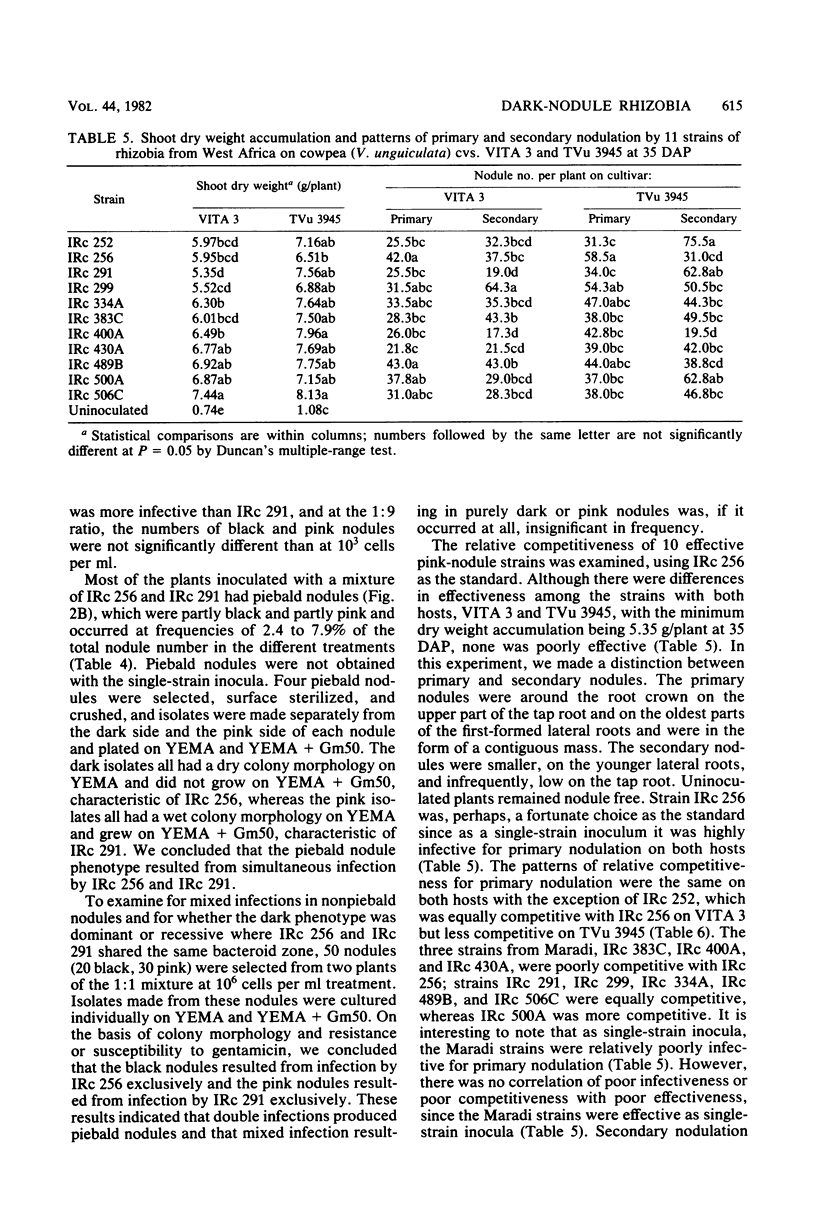
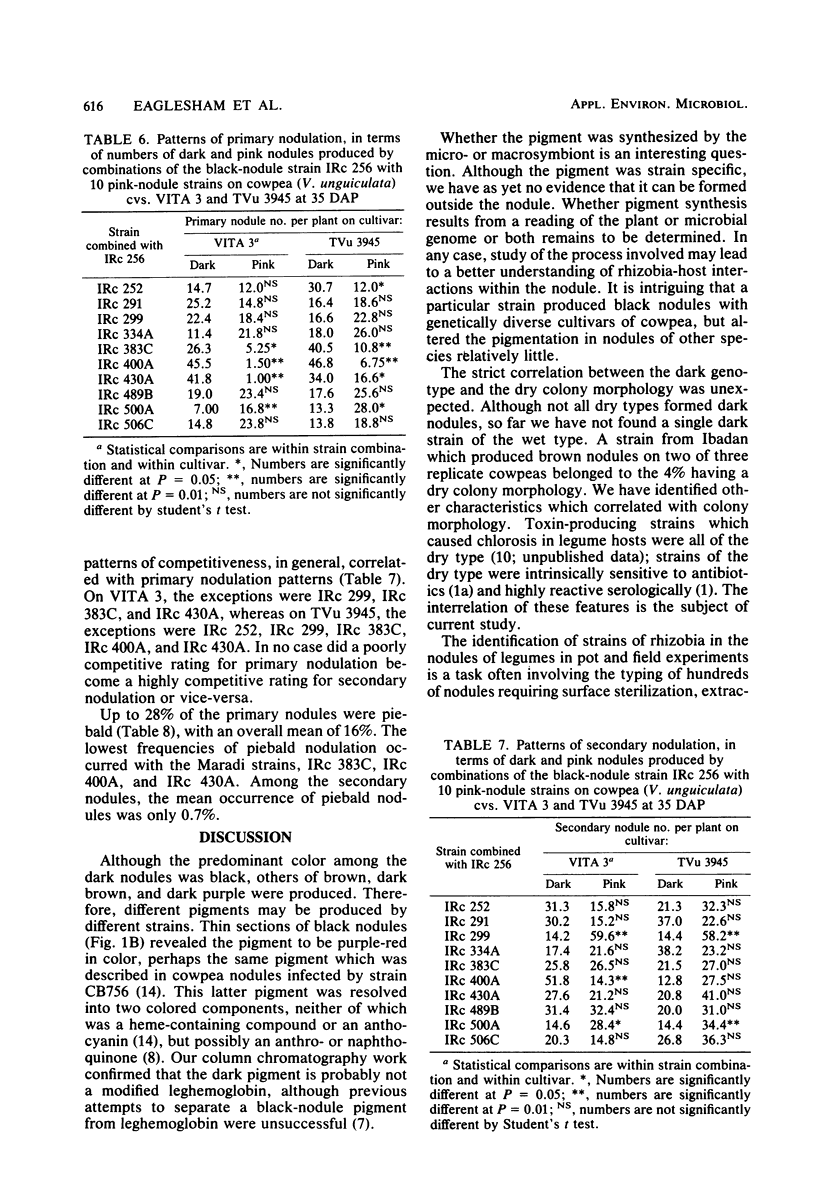
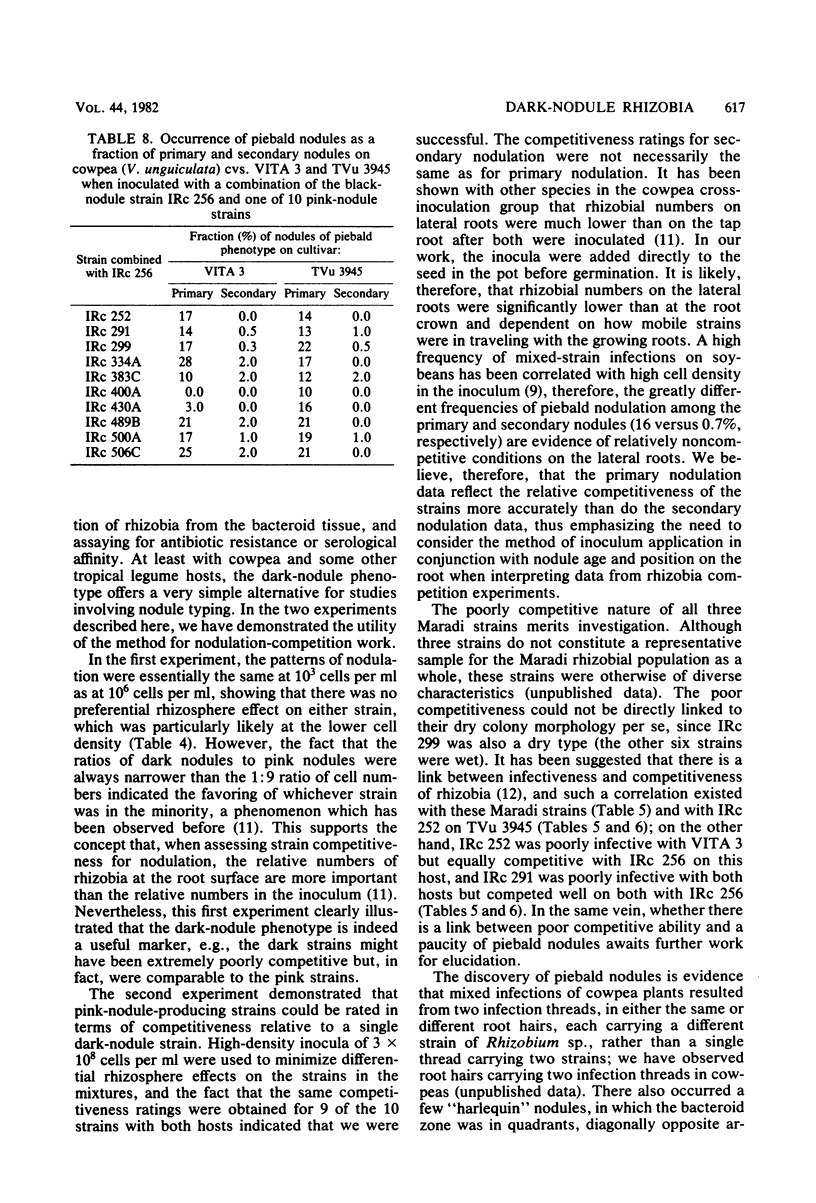
During a program of screening rhizobia from West Africa, it was found that some strains produced nodules of unusually dark appearance on cowpeas, but not on peanuts, soybeans, pigeon peas, or mung beans. The dark pigmentation was in the bacteroid zone, was not correlated with nodule effectiveness, and was additional to the leghemoglobin pigment. Only rhizobial strains with a nongummy (“dry”) colony morphology produced dark nodules. Visually distinguishable pink and dark nodules formed on the same root when a mixture of pink and dark strains was applied as inoculum. The dark-nodule phenotype was therefore appraised as a marker and found to be useful for studying nodulation competition with strains of the orthodox pink-nodule type. The competitiveness of 10 pink-nodule strains was examined relative to a black-nodule strain, IRc 256; a range of competitiveness was obtained of less competitive than, equally competitive to, or more competitive than IRc 256. Patterns of primary (early) nodulation were generally the same as patterns of secondary (later) nodulation. Mixed infections by dark and pink strains produced piebald nodules, the frequency of occurrence of which was much greater among primary than among secondary nodules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine T. E., Kuykendall L. D., Breithaupt B. H. Nodulation of soybeans carrying the nodulation-restrictive gene, rj1, by an incompatible Rhizobium japonicum strain upon mixed inoculation with a compatible strain. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):179–182. doi: 10.1139/m80-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Holsten R. D., Jackson E. K., Burns R. C. The acetylene-ethylene assay for n(2) fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1185–1207. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]