Abstract
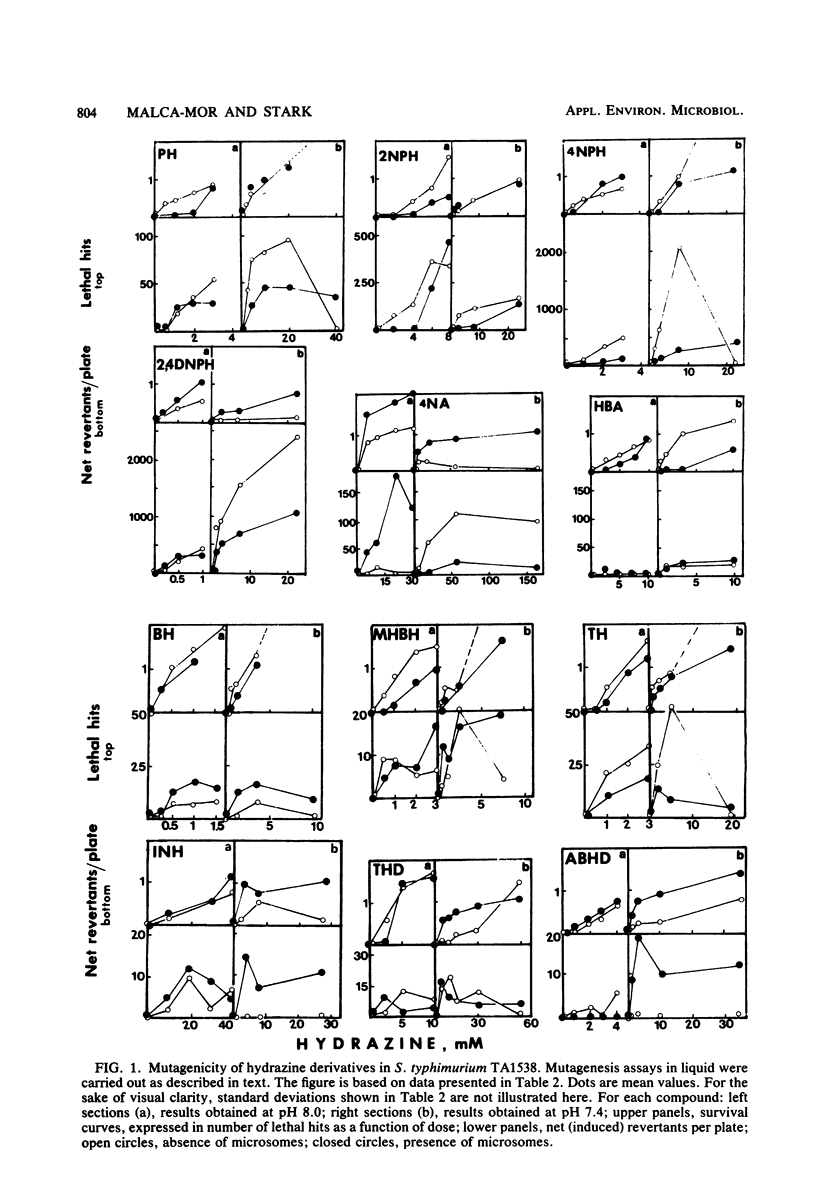
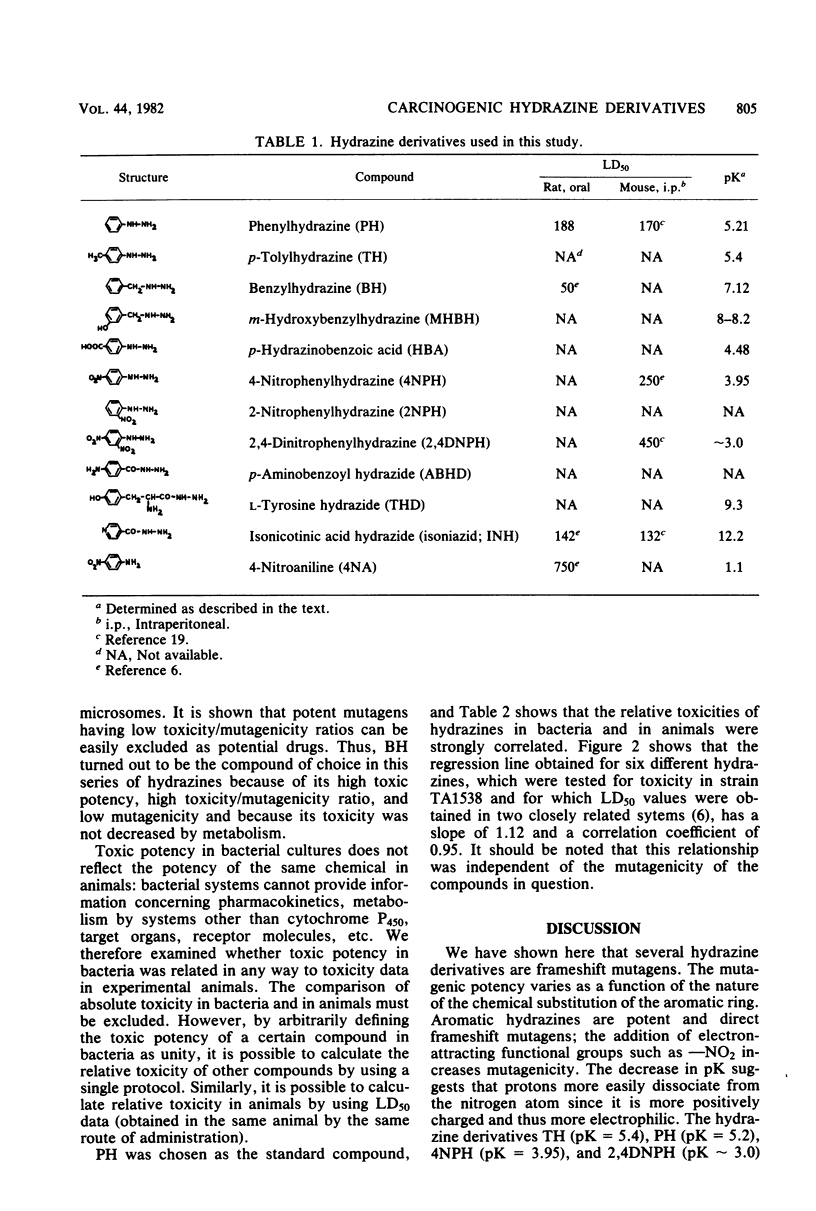
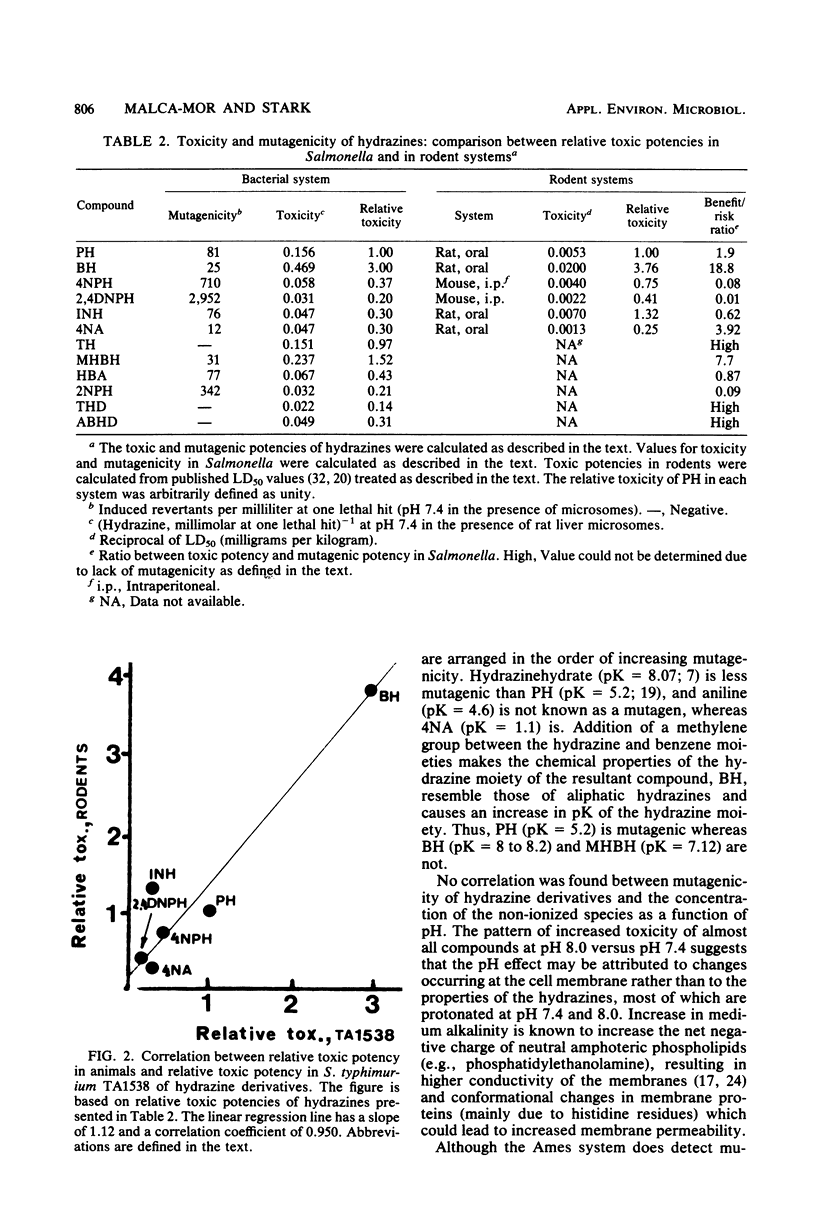
Eleven hydrazine derivatives and an aromatic amine were examined for mutagenicity and toxicity to Salmonella typhimurium. Phenylhydrazine, 2-nitrophenylhydrazine, 4-nitrophenylhydrazine, 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, p-tolylhydrazine, and 4-nitroaniline were found to be frameshift mutagens (strain TA1538). Benzylhydrazine, m-hydroxybenzylhydrazine, p-hydrazinobenzoic acid, L-tyrosine hydrazide, p-aminobenzoyl hydrazide, and isoniazid were not mutagenic. All chemicals were toxic to strain TA1538. A qualitative correlation was found between the pK of the compounds and their mutagenicity. Relative toxicities of hydrazines to bacteria were found to be closely correlated with the relative toxicities of the same compounds in animals. Described herein is a methodology for the rapid prescreening of chemicals which may be used as drugs for those with a high benefit/risk ratio.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Mccann J., Yamasaki E. Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test. Mutat Res. 1975 Dec;31(6):347–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(75)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awerbuch T. E., Samson R., Sinskey A. J. A quantitative model of diffusion bioassays. J Theor Biol. 1979 Aug 7;79(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awerbuch T. E., Stark A. A. Plate diffusion assay as a rapid method for dosimetry of mutagens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1127–1131. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1127-1131.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E., Sklarow S., Freese E. B. DNA damage caused by antidepressant hydrazines and related drugs. Mutat Res. 1968 May-Jun;5(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(68)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram T. E. Separation of hepatic smooth and rough microsomes associated with drug-metabolizing enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:225–237. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLY M. G., O'GARA R. W., GADEKAR K., YANCEY S. T., OLIVERIO V. T. CARCINOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A NEW ANTITUMOR AGENT, N-ISOPROPYL-ALPHA-(2-METHYLHYDRAZINO)-P-TOLUAMIDE, HYDROCHLORIDE (NSC-77213). Cancer Chemother Rep. 1964 Jul;39:77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. G., O'Gara R. W., Yancey S. T., Botkin C. Induction of tumors in rats with procarbazine hydrochloride. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 May;40(5):1027–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHE G., SCHWEISGUTH O., SCHNEIDER M., AMIEL J. L., BERUMEN L., BRULE G., CATTAN A., SCHWARZENBERG L. METHYL-HYDRAZINE IN TREATMENT OF HODGKIN'S DISEASE AND VARIOUS FORMS OF HAEMATOSARCOMA AND LEUKAEMIA. Lancet. 1963 Nov 23;2(7317):1077–1080. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92854-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Szabo G., Eisenman G., Ciani S. M. Surface charge and the conductance of phospholipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1268–1275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriya M., Watanabe K., Ohta T., Shirasu Y. Detection of mutagenicity of procarbazine by the host-mediated assay with polychlorinated biphenyl (aroclor 1254) as enzyme inducer. Mutat Res. 1980 Oct;79(2):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(80)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi S., De Flora S., Cavanna M., Pino A., Robbiano L., Bennicelli C., Brambilla G. DNA-damaging activity in vivo and bacterial mutagenicity of sixteen hydrazine derivatives as related quantitatively to their carcinogenicity. Cancer Res. 1981 Apr;41(4):1469–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Hayashi K., Takemura N. [Relationships between the mutagenic and carcinogenic effects of hydrazine derivatives (author's transl)]. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 1978 Aug;33(3):474–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G., Eisenman G., McLaughlin S. G., Krasne S. Ionic probes of membrane structures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:273–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosk J., Schmeltz I., Hoffmann D. Hydrazines as mutagens in a histidine-requiring auxotroph of Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1979 Mar;66(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(79)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth B. 1-Acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine carcinogenesis in mice. Br J Cancer. 1979 May;39(5):584–587. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth B. Nicotinic acid hydrazide carcinogenesis in mice. Oncology. 1981;38(2):106–109. doi: 10.1159/000225532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth B., Patil K., Jae H. S. Carcinogenesis of 4-(hydroxymethyl)benzenediazonium ion (tetrafluoroborate) of Agaricus bisporus. Cancer Res. 1981 Jun;41(6):2444–2449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth B. The large bowel carcinogenic effects of hydrazines and related compounds occurring in nature and in the environment. Cancer. 1977 Nov;40(5 Suppl):2427–2431. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197711)40:5+<2427::aid-cncr2820400906>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth B., Tompa A., Patil K. Tumorigenic effect of 4-methylphenylhydrazine hydrochloride in Swiss mice. Z Krebsforsch Klin Onkol Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1977 Aug 15;89(3):245–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00283781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger E., Guthrie J. Cyclic hydrazides are mutagenic for Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1981 May;91(3):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wright A., Niskanen A., Pyysalo H. Mutagenic properties of ethylidene gyromitrin and its metabolites in microsomal activation tests and in the host-mediated assay. Mutat Res. 1978 Oct;54(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(78)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


