Abstract
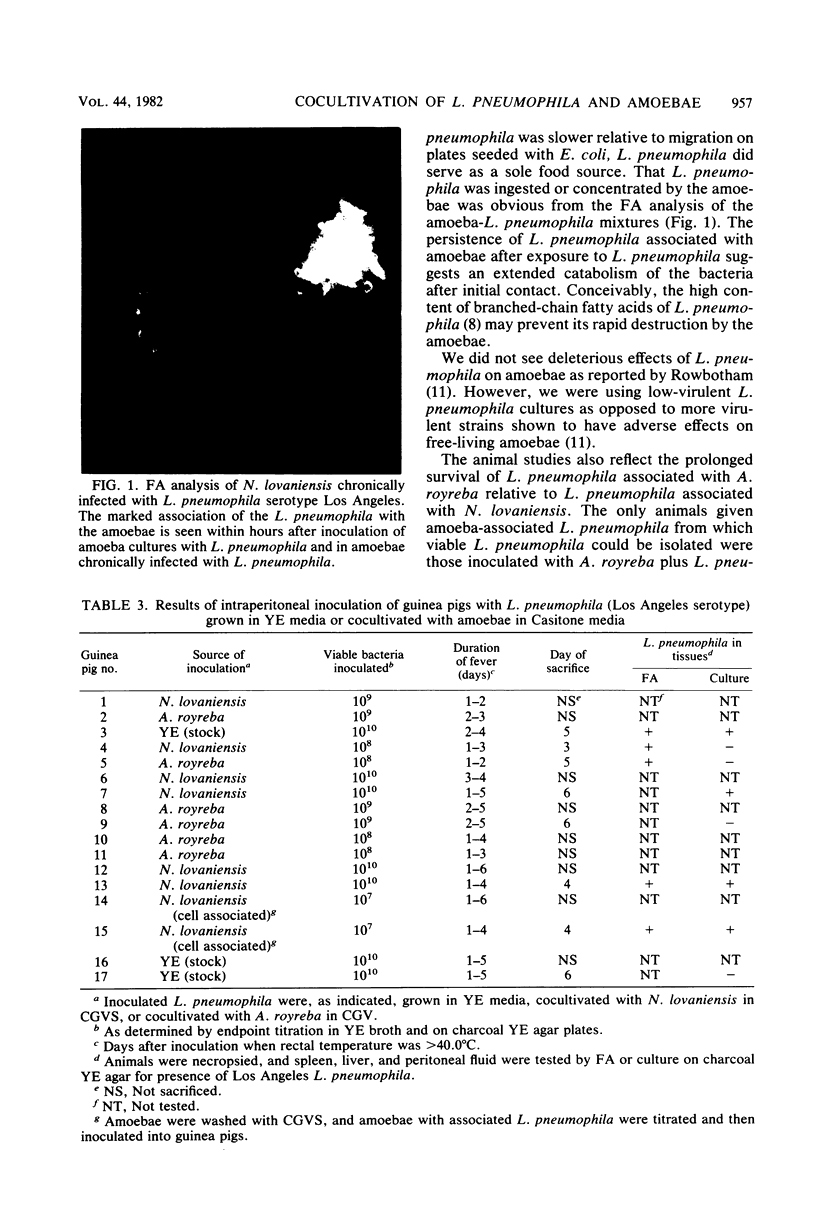
Studies of the interaction of Legionella pneumophila with free-living amoebae showed that Naegleria lovaniensis and Acanthamoeba royreba could use L. pneumophila as a sole food source. However, growth of the amoebae on nonnutrient agar plates seeded with L. pneumophila was slower than growth on nonnutrient agar plates seeded with Escherichia coli. On inoculation of L. pneumophila into axenic cultures of N. lovaniensis and A. royreba, 99.9% of the L. pneumophila was destroyed within 24 h. After several weeks, however, some amoeba cultures became chronically infected and supported the growth of L. pneumophila. Amoebae exposed to L. pneumophila and containing adhered L. pneumophila, L. pneumophila antigens, or both, showed no increased pathogenic potential on intranasal inoculation of weanling mice. Similarly, L. pneumophila propagated in chronically infected amoeba cultures showed no increase in virulence on intraperitoneal inoculation of guinea pigs relative to L. pneumophila grown in yeast extract broth.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cordes L. G., Fraser D. W., Skaliy P., Perlino C. A., Elsea W. R., Mallison G. F., Hayes P. S. Legionnaires' disease outbreak at an Atlanta, Georgia, Country Club: evidence for spread from an evaporative condenser. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Apr;111(4):425–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deubner D. C., Gilliam D. K. Fever of undetermined etiology after cleaning of steam turbine condensers. Arch Environ Health. 1977 May-Jun;32(3):116–119. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1977.10667266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondero T. J., Jr, Rendtorff R. C., Mallison G. F., Weeks R. M., Levy J. S., Wong E. W., Schaffner W. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a contaminated air-conditioning cooling tower. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 14;302(7):365–370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002143020703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Thacker L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from nonepidemic-related aquatic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1239–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1239-1242.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P., Willaert E., Juechter K. B., Stevens A. R. A case of keratitis due to Acanthamoeba in New York, New York, and features of 10 cases. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):662–667. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Weaver R. E., Dees S. B., Cherry W. B. Cellular fatty acid composition of isolates from Legionnaires disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):140–143. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.140-143.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naginton J., Watson P. G., Playfair T. J., McGill J., Jones B. R., Steele A. D. Amoebic infection of the eye. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1537–1540. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert V. B., Rorke L. B. Primary amebic encephalitis, probably from Acanthamoeba. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Aug;79(2):174–179. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-2-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1179–1183. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., De Jonckheere J., Willaert E. Naegleria lovaniensis new species: isolation and identification of six thermophilic strains of a new species found in association with Naegleria fowleri. Int J Parasitol. 1980 Feb;10(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(80)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willaert E., Stevens A. R., Tyndall R. L. Acanthamoeba royreba sp. n. from a human tumor cell culture. J Protozool. 1978 Feb;25(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb03854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. C., Ewing E. P., Jr, Callaway C. S., Peacock W. L., Jr Intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in cultured human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1014–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1014-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]