Abstract
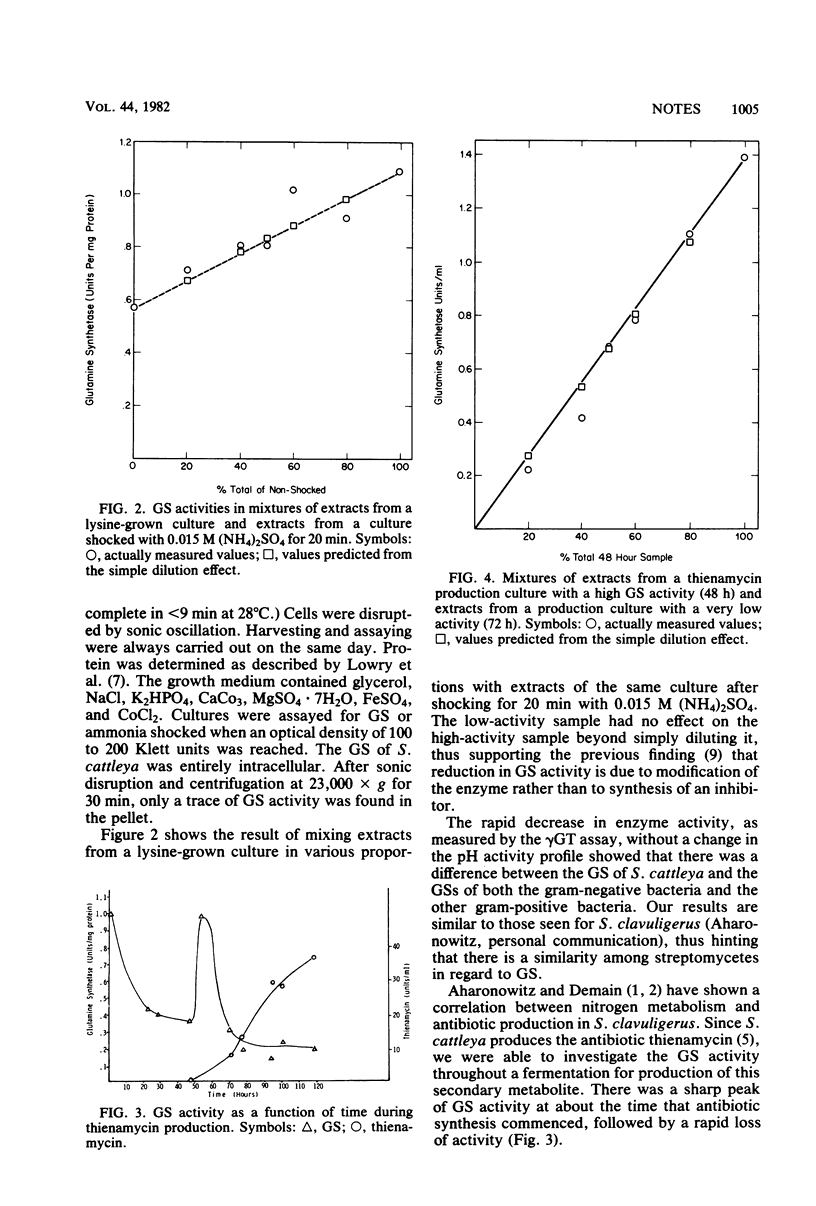
In cultures of the gram-positive bacterium Streptomyces cattleya, a rapid inactivation of glutamine synthetase was seen after ammonia shock. pH activity curves for ammonia-shocked and control cultures are shown. A peak of glutamine synthetase activity was seen during fermentation for production of the antibiotic thienamycin.
Full text
PDF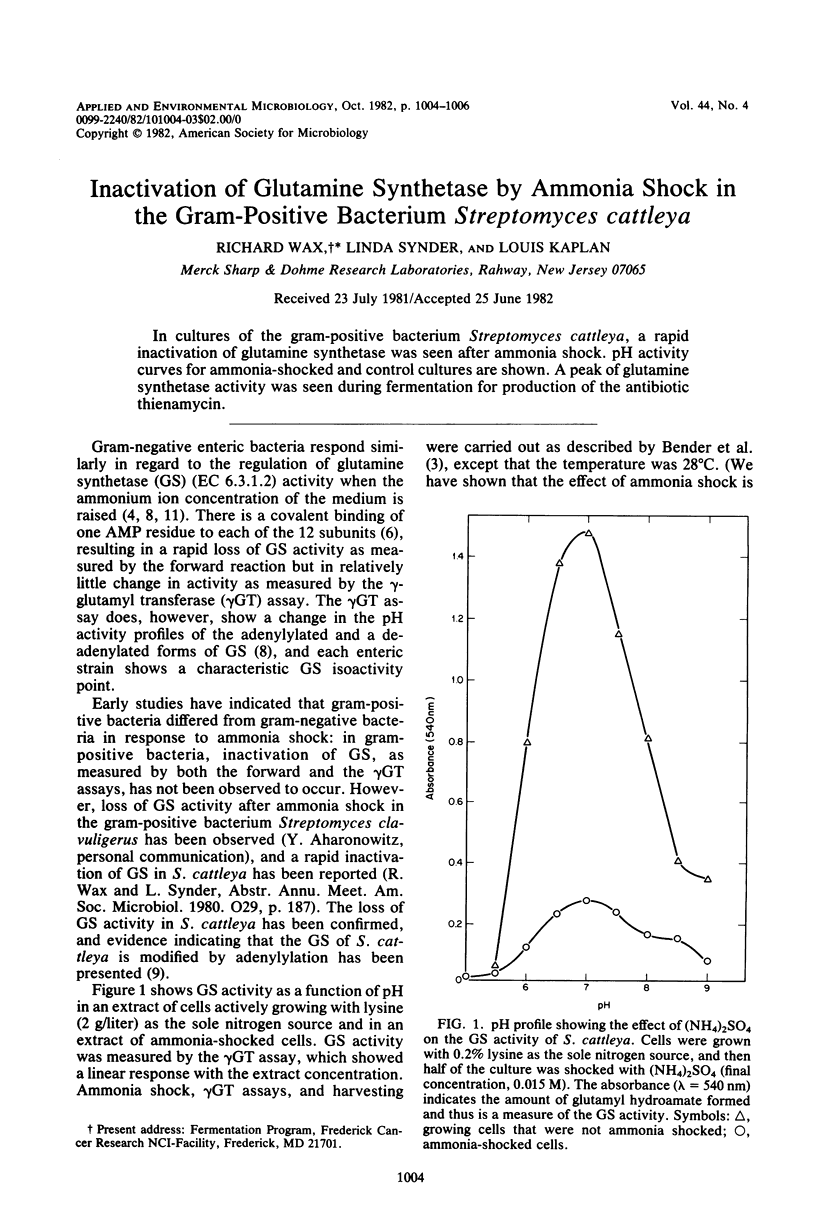

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonowitz Y., Demain A. L. Nitrogen nutrition and regulation of cephalosporin production in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jan;25(1):61–67. doi: 10.1139/m79-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo C., Holzer H. Enzymatic inactivation of glutamine synthetase in Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Apr 3;4(2):190–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan J. S., Kahan F. M., Goegelman R., Currie S. A., Jackson M., Stapley E. O., Miller T. W., Miller A. K., Hendlin D., Mochales S. Thienamycin, a new beta-lactam antibiotic. I. Discovery, taxonomy, isolation and physical properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979 Jan;32(1):1–12. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.32.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon H. S., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. 8. ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase, an enzyme that catalyzes alterations in the regulatory properties of glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1703–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. The regulation of glutamine synthesis in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:501–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streicher S. L., Tyler B. Regulation of glutamine synthetase activity by adenylylation in the Gram-positive bacterium Streptomyces cattleya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):229–233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Ciardi J. E., Stadtman E. R. Comparative biochemical and immunological studies of bacterial glutamine synthetases. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):858–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.858-868.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


