Abstract
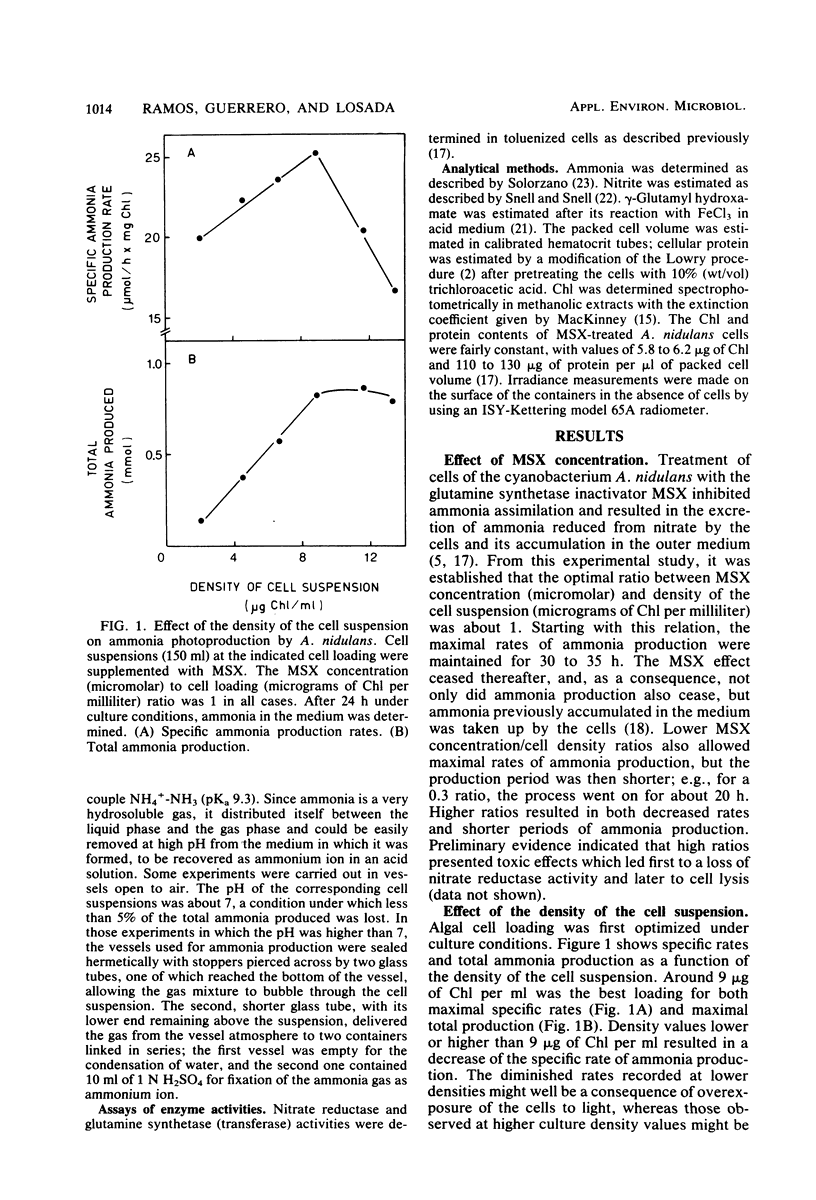
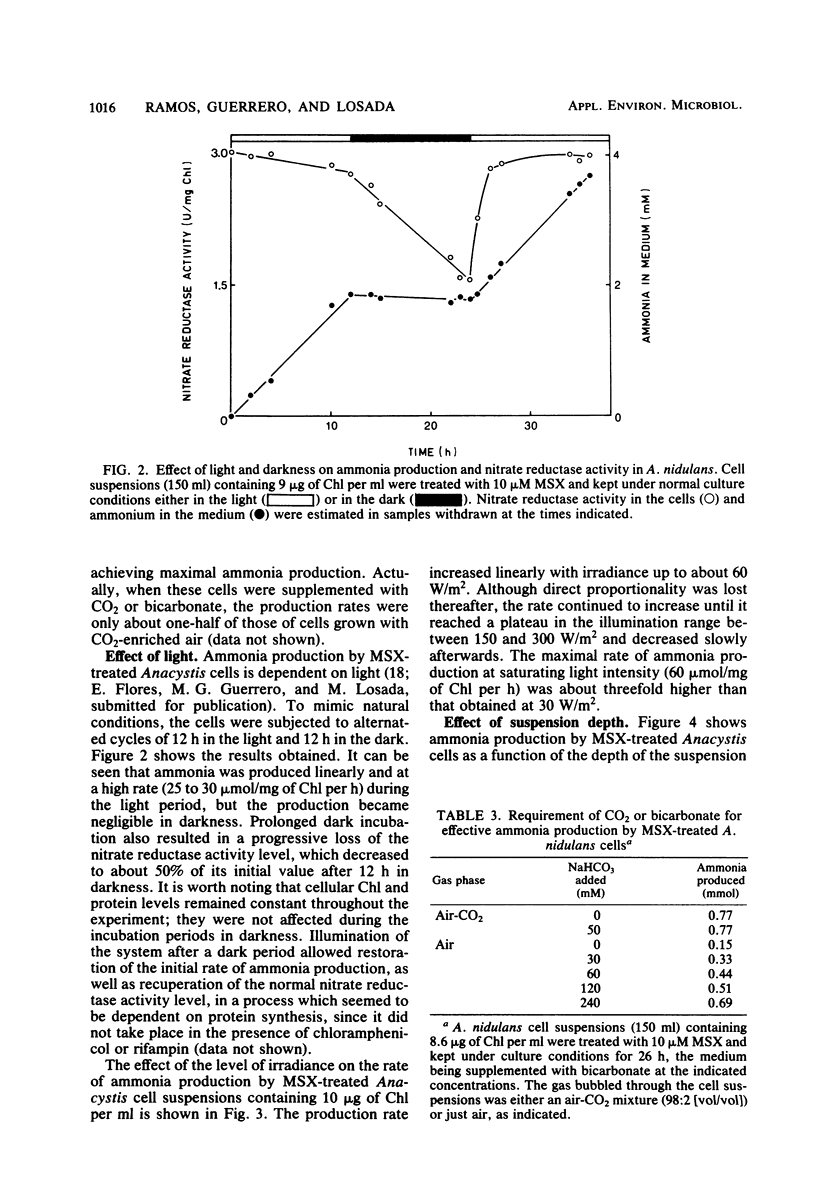
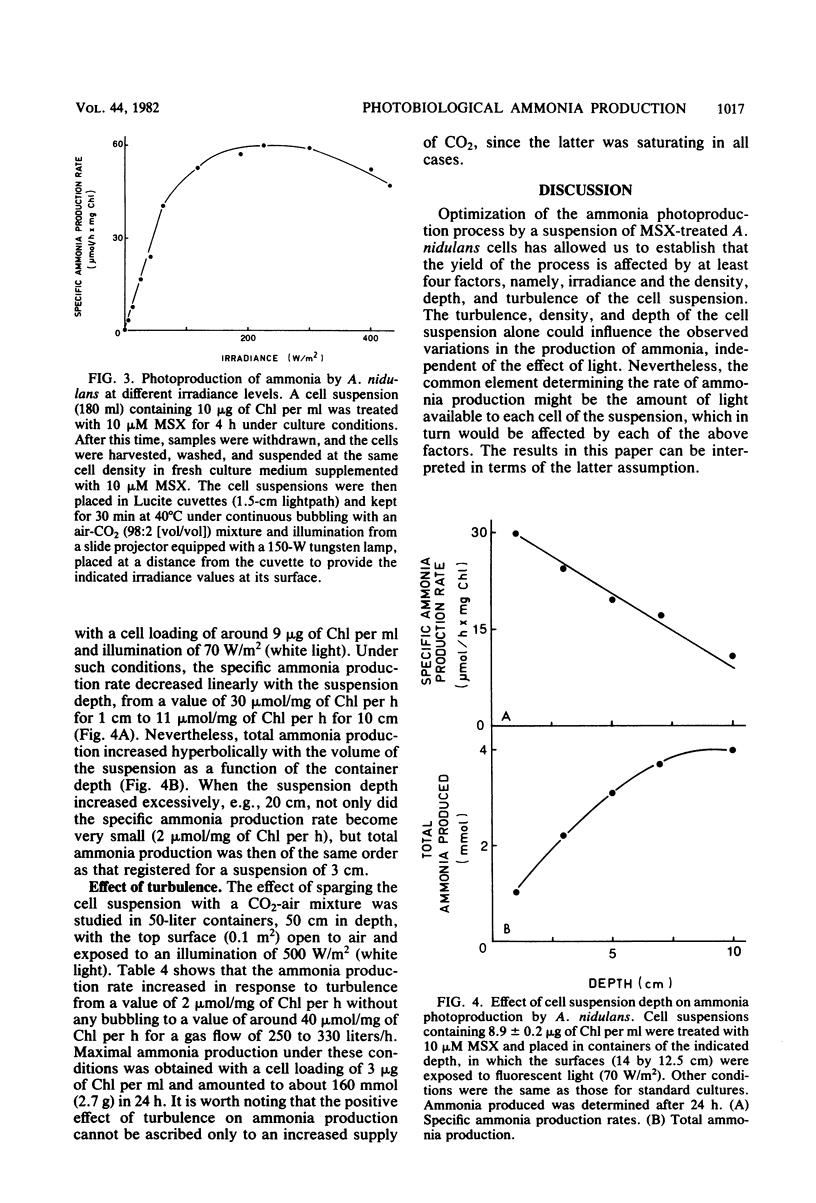
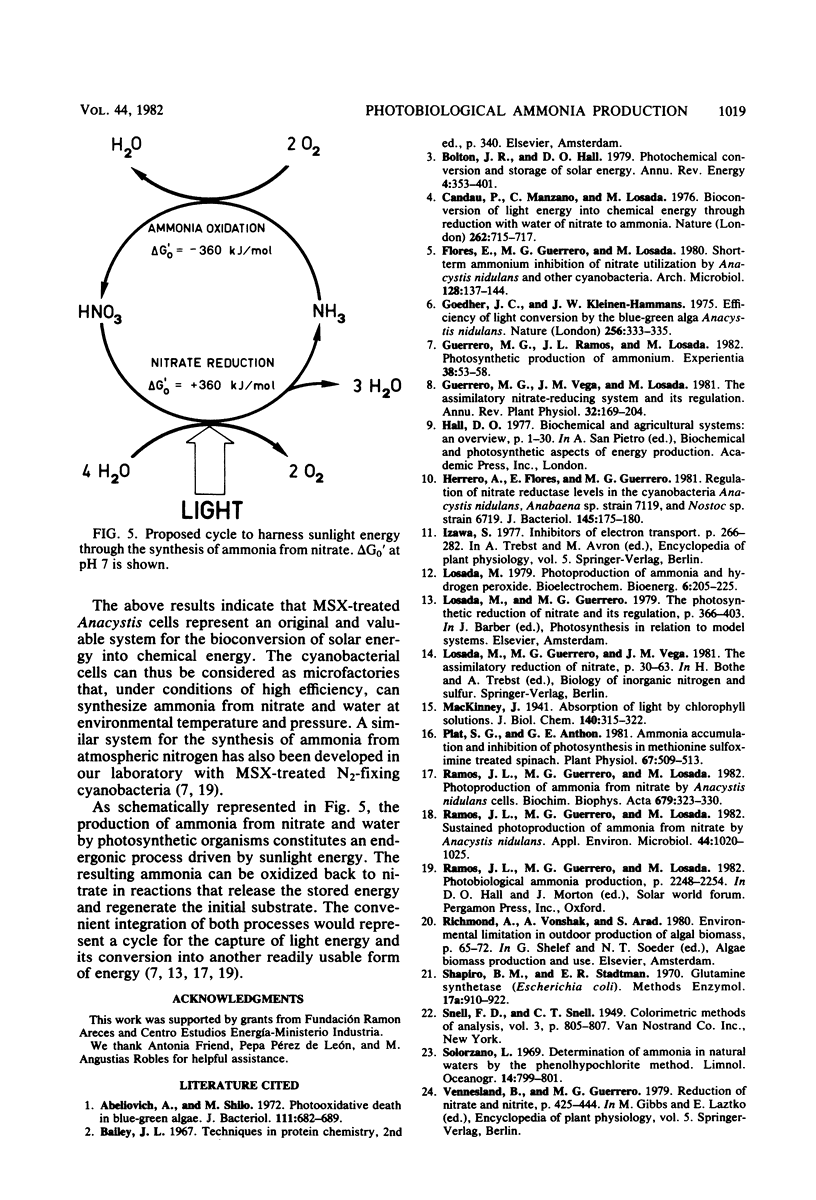
The effect of several relevant environmental factors influencing the photoproduction of ammonia from nitrate by Anacystis nidulans cells treated with the glutamine synthetase inhibitor l-methionine-dl-sulfoximine has been investigated. The optimal ratio between l-methionine-dl-sulfoximine concentration (micro-molar) and cell density (micrograms of chlorophyll per milliliter) was around 1, the process taking place at maximal rate at a temperature of about 40°C, within the pH range of 7 to 10. Ammonia production was stimulated by CO2 or bicarbonate and was not affected by the accumulation of ammonia in the medium up to concentrations of 30 mM. The rate of ammonia production was found to be determined by the interaction of at least four factors, namely, irradiance and the density, depth, and turbulence of the cell suspension. Ammonia photoproduction from nitrate and water represents an interesting process for the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, which can operate at high efficiency, around 30% of its theoretical maximum.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeliovich A., Shilo M. Photooxidative death in blue-green algae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):682–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.682-689.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero A., Flores E., Guerrero M. G. Regulation of nitrate reductase levels in the cyanobacteria Anacystis nidulans, Anabaena sp. strain 7119, and Nostoc sp. strain 6719. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.175-180.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt S. G., Anthon G. E. Ammonia accumulation and inhibition of photosynthesis in methionine sulfoximine treated spinach. Plant Physiol. 1981 Mar;67(3):509–513. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Guerrero M. G., Losada M. Sustained Photoproduction of Ammonia from Nitrate by Anacystis nidulans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1020–1025. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1020-1025.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



