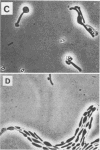
Abstract
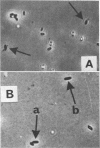
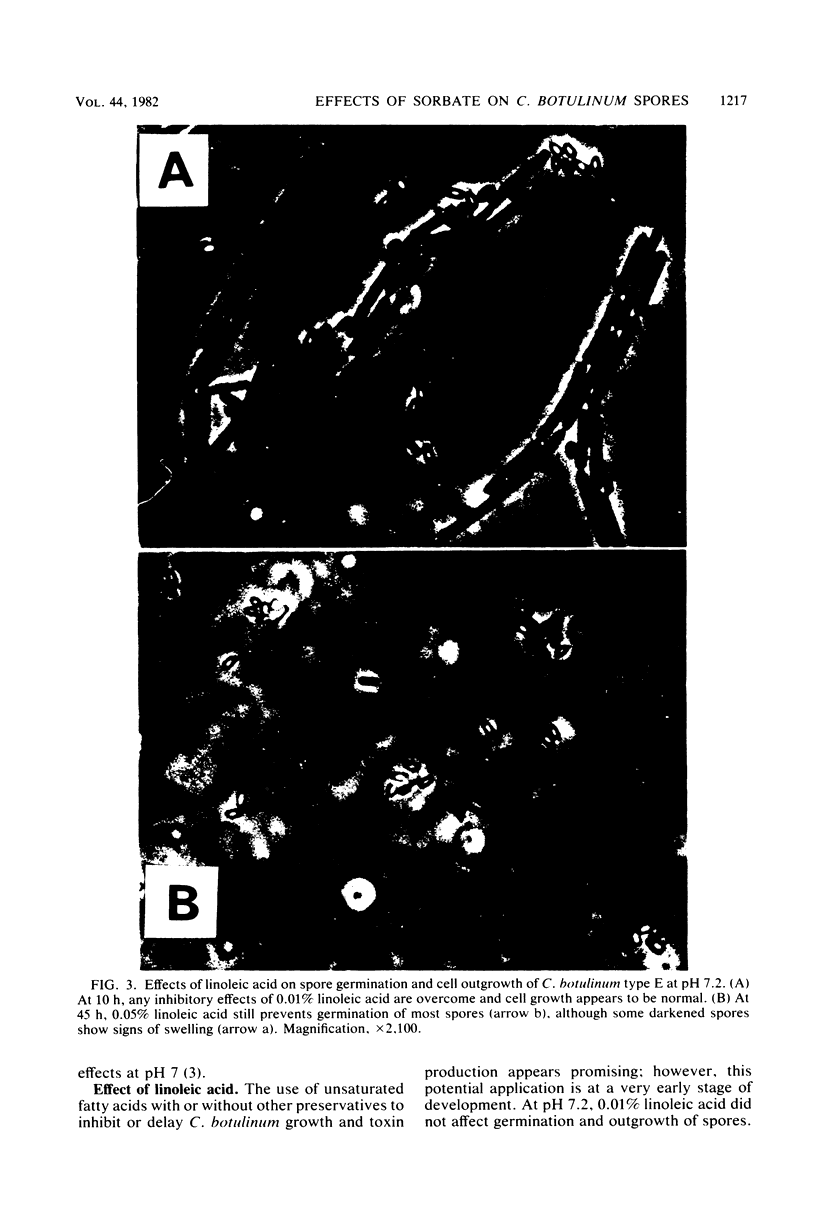
The effects of potassium sorbate, sodium hypophosphite, sodium tripolyphosphate, sodium nitrite, and linoleic acid on the germination and outgrowth of Clostridium botulinum type E spores were studied in microcultures. At pH 5.8 to 6.0 in liver veal agar, the germination rate was decreased to nearly zero with 1.0, 1.5, or 2.0% sorbate. At pH 7.0 t 7.2, these levels of sorbate afforded germination and outgrowth of abnormally shaped cells that were defective in cell division. At the high pH range, 0.5 or 1.0% hypophosphite had effects similar to those of sorbate. The use of 0.05% sodium nitrite with sorbate enhanced the lysis of outgrowing cells at pH 7.2 or lower. Emergence and elongation were inhibited by 0.05% linoleic acid with or without 1.0% sorbate at pH 7.0 to 7.2. The addition of 0.5% tripolyphosphate to media containing 1.5% sorbate at pH 7.1 prevented normal cell growth to an extent greater than with sorbate alone.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncan C. L., Foster E. M. Effect of sodium nitrite, sodium chloride , and sodium nitrate on germination and outgrowth of anaerobic spores. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Feb;16(2):406–411. doi: 10.1128/am.16.2.406-411.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Wynne E. S. Physiological Studies on Spore Germination, with Special Reference to Clostridium botulinum: IV. Inhibition of Germination by Unsaturated C(18) Fatty Acids. J Bacteriol. 1948 Apr;55(4):495–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grecz N., Arvay L. H. Effect of temperature on spore germination and vegetative cell growth of Clostridium botulinum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):331–337. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.331-337.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimble C. E., McCollough M. L., Paterno V. A., Anderson A. W. Comparison of the fatty acids of proteolytic type B and nonproteolytic types E and F of Clostridium botulinum. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):883–888. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.883-888.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu C. W., Salomon D., Simmons J. L., Sreevalsan T., Freese E. Inhibitory effects of lipophilic acids and related compounds on bacteria and mammalian cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):349–363. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoot L. A., Pierson M. D. Mechanisms of sorbate inhibition of Bacillus cereus T and Clostridium botulinum 62A spore germination. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):477–483. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.477-483.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]