Abstract
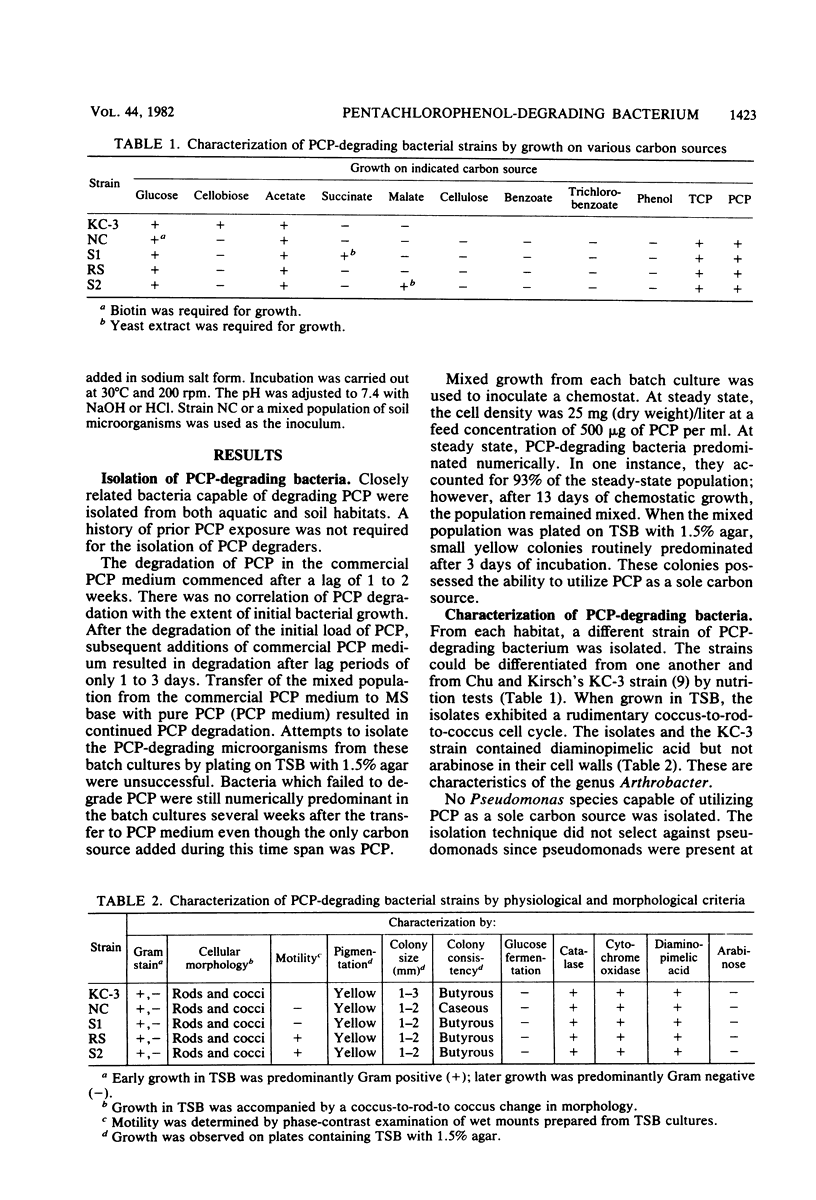
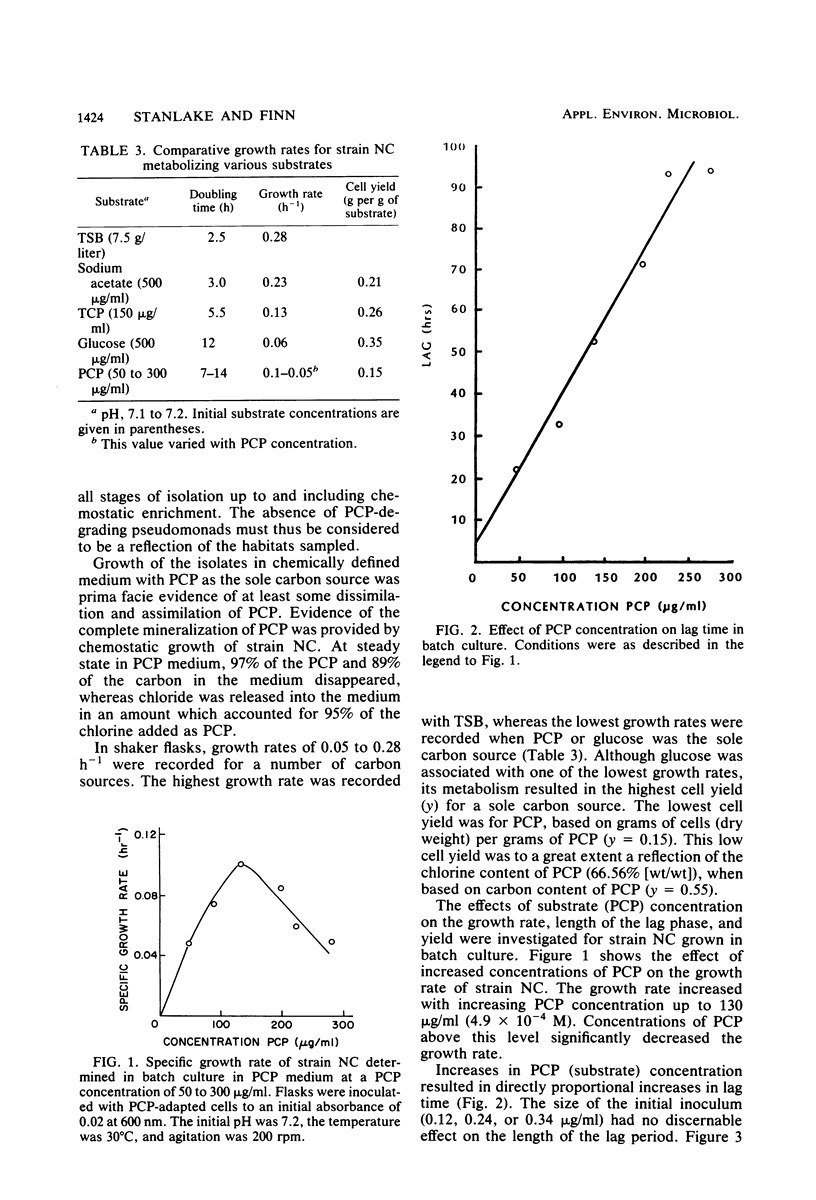
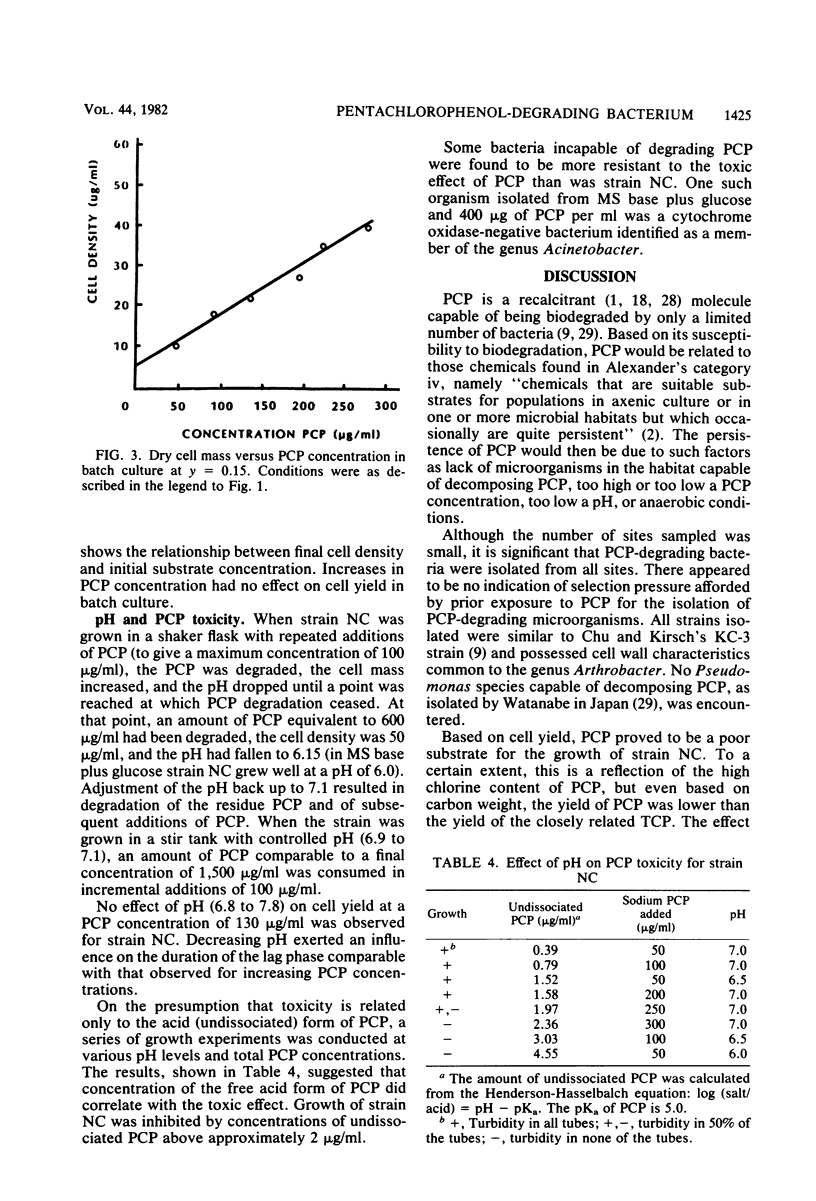
With a new enrichment protocol, pentachlorophenol (PCP)-degrading bacteria were isolated from soil, water, and sewage. When characterized, all isolates were related and shared characteristics of the genus Arthrobacter. Growth rates for strain NC were determined for a number of substrates, including PCP and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. Changes in PCP concentration affected growth rate and length of the lag phase but not cell yield. Increasing the pH from 6.8 to 7.8 decreased the length of the lag phase for growth on PCP. Cessation of growth, upon incremental addition of PCP, was found to be related to a decrease in pH rather than to a buildup of a toxic metabolite. Degradation of PCP by strain NC was shown to be complete.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER B., LECHEVALIER M. P., GORDON R. E., LECHEVALIER H. A. RAPID DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN NOCARDIA AND STREPTOMYCES BY PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF WHOLE-CELL HYDROLYSATES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Sep;12:421–423. doi: 10.1128/am.12.5.421-423.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevenue A., Beckman H. Pentachlorophenol: a discussion of its properties and its occurrence as a residue in human and animal tissues. Residue Rev. 1967;19:83–134. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8425-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone C. J., Pine L. Rapid method for characterization of actinomycetes by cell wall composition. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Feb;16(2):279–284. doi: 10.1128/am.16.2.279-284.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brilon C., Beckmann W., Hellwig M., Knackmuss H. J. Enrichment and isolation of naphthalenesulfonic Acid-utilizing pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.39-43.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu J. P., Kirsch E. J. Metabolism of pentachlorophenol by an axenic bacterial culture. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):1033–1035. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.1033-1035.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABY W. L., HADLEY C. Practical laboratory test for the identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1957 Sep;74(3):356–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.3.356-358.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingols R. S., Gaffney P. E., Stevenson P. C. Biological activity of halophenols. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1966 Apr;38(4):629–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray I. G., Proctor A. G. Paper chromatography as an aid to the identification of Nocardia species. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):163–167. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. E., Finn R. K. Growth rates of a pseudomonad on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4-dichlorophenol. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.181-184.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vela-Múzquiz R., Kasper P. Effecto del pentaclorofenol sobre la flora microbiana de suelos seleccionados. Microbiol Esp. 1973 Jan-Mar;26(1):21–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


