Abstract
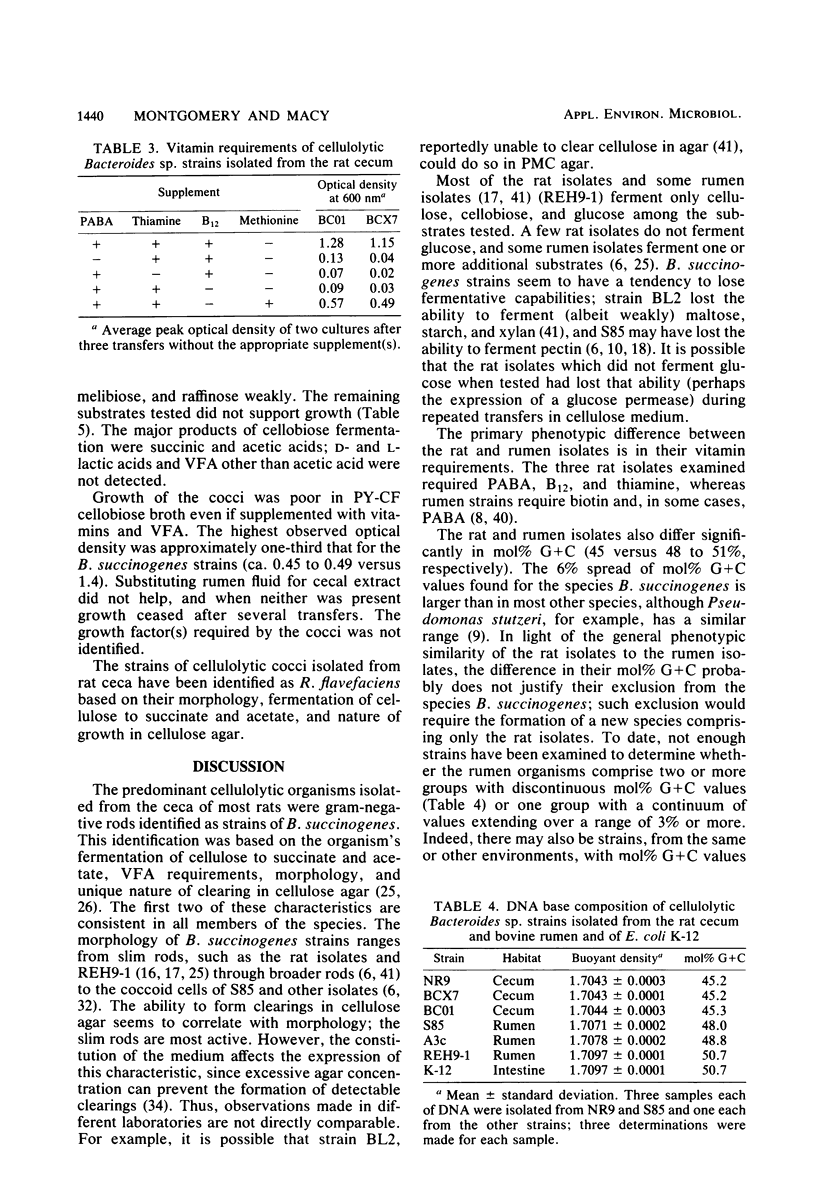
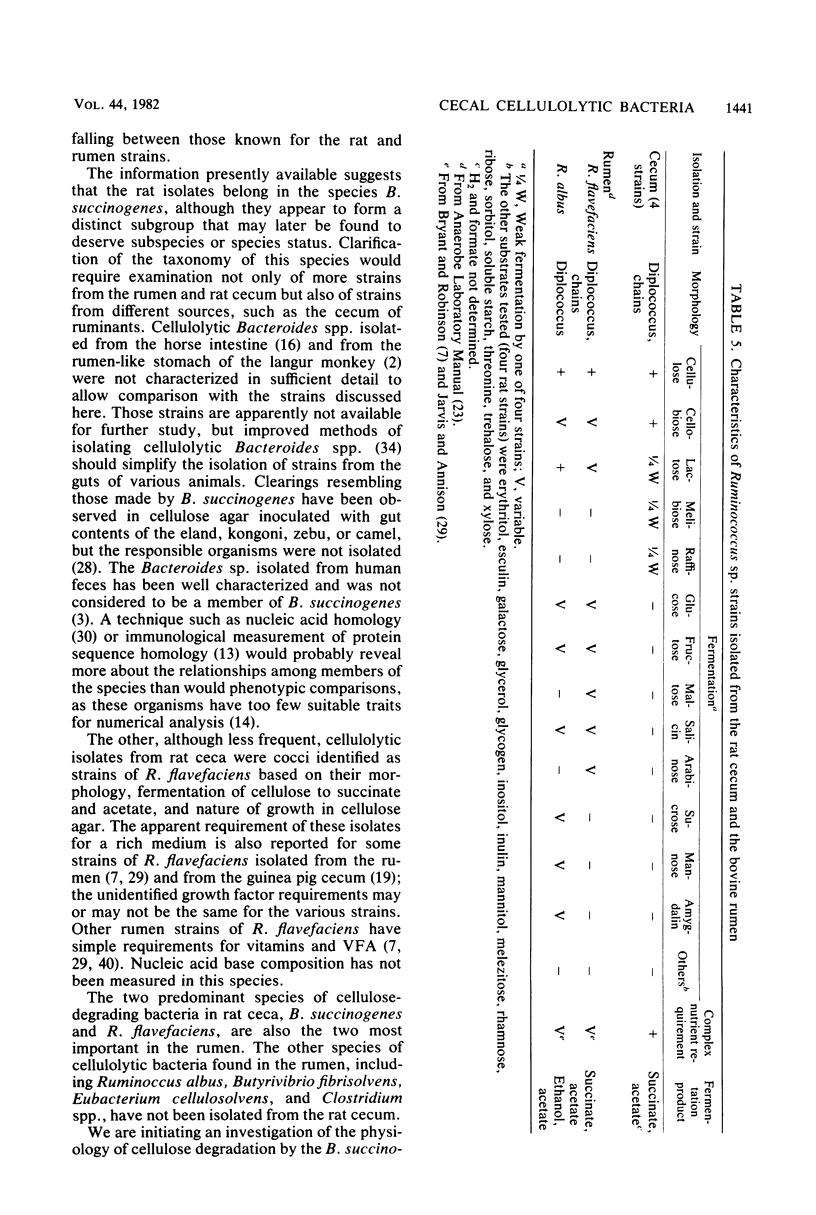
Cellulose-degrading bacteria previously isolated from the ceca of rats have been characterized and identified. The most commonly isolated type was rods identified as Bacteroides succinogenes. These bacteria fermented only cellulose (e.g., pebble-milled Whatman no. 1 filter paper), cellobiose, and in 43 of 47 strains, glucose, with succinic and acetic acids as the major products. The only organic growth factors found to be required by selected strains were p-aminobenzoic acid, cyanocobalamine, thiamine, and a straight-chain and a branched-chain volatile fatty acid. These vitamin requirements differ from those of rumen strains of B. succinogenes, indicating the rat strains may form a distinct subgroup within the species. The mole percent guanine plus cytosine was 45%, a value lower than those (48 to 51%) found for three rumen strains of B. succinogenes included in this study. Cellulolytic cocci were isolated less frequently than the rods and were identified as Rumminococcus flavefaciens. Most strains fermented only cellulose and cellobiose, and their major fermentation products were also succinic and acetic acids. Their required growth factors were not identified but were supplied by rumen fluid.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. E. Microscopic evaluation of forage digestion by rumen microorganisms--a review. J Anim Sci. 1979 Mar;48(3):701–710. doi: 10.2527/jas1979.483701x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauchop T., Martucci R. W. Ruminant-like digestion of the langur monkey. Science. 1968 Aug 16;161(3842):698–700. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3842.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betian H. G., Linehan B. A., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V. Isolation of a cellulotytic Bacteroides sp. from human feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):1009–1010. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.1009-1010.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Nutritional requirements of the predominant rumen cellulolytic bacteria. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Robinson I. M. Some Nutritional Requirements of the Genus Ruminococcus. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Mar;9(2):91–95. doi: 10.1128/am.9.2.91-95.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Localization of alkaline phosphatase in three gram-negative rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):424–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.424-440.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. T., Bailey R. W., Gaillard B. D. Growth of rumen bacteria on plant cell wall polysaccharides. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Apr;56(1):9–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks G. T., Wilson A. C. Enzyme evolution in the Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):793–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.793-802.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Damgaard H. N., Cheng K. J. Cell envelope morphology of rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):1132–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.1132-1143.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Cellulolytic cocci isolated from the cecum of guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jun;33(6):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.6.1278-1283.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Pectin-fermenting bacteria isolated from the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.189-196.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsdale D., Morris E. J., Bacon J. S. Electron microscopy of the microbial populations present and their modes of attack on various cellulosic substrates undergoing digestion in the sheep rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.160-168.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Cellulolytic activity of the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):517–530. doi: 10.1139/m81-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL E. R. Investigations on the microbiology of cellulose utilization in domestic rabbits. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Nov;7(3-4):350–357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-3-4-350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E., PHILLIPS G. D., McGREGOR A., HUNGATE D. P., BUECHNER H. K. Microbial fermentation in certain mammals. Science. 1959 Oct 30;130(3383):1192–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3383.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E. Studies on Cellulose Fermentation: III. The Culture and Isolation for Cellulose-decomposing Bacteria from the Rumen of Cattle. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):631–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.53.5.631-645.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis B. D., Annison E. F. Isolation, classification and nutritional requirements of cellulolytic cocci in the sheep rumen. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 May;47(2):295–307. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Ordal E. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid homology in bacterial taxonomy: effect of incubation temperature on reaction specificity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):893–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.893-900.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham M. J., Brooker B. E., Pettipher G. L., Harris P. J. Adhesion of Bacteroides succinogenes in pure culture and in the presence of Ruminococcus flavefaciens to cell walls in leaves of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1166–1173. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1166-1173.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham M. J., Brooker B. E., Pettipher G. L., Harris P. J. Ruminococcus flavefaciens Cell Coat and Adhesion to Cotton Cellulose and to Cell Walls in Leaves of Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):156–165. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.156-165.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy J. M., Farrand J. R., Montgomery L. Cellulolytic and non-cellulolytic bacteria in rat gastrointestinal tracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1428–1434. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1428-1434.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. W., Fuson G. B., Phaff H. J. Genome comparison in yeast systematics: delimitation of species within the genera Schwanniomyces, Saccharomyces, Debaryomyces, and Pichia. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):161–193. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.161-193.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. A., Bryant M. P. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of certain species of the genus Bacteroides. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1252–1256. doi: 10.1139/m77-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT H. W., DEHORITY B. A. VITAMIN REQUIREMENTS OF SEVERAL CELLULOLYTIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1169–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1169-1175.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. S., Paniagua C., Dinsdale D., Cheng K. J., Garrow S. H. Selective isolation and characteristics of Bacteriodes succinogenes from the rumen of a cow. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):504–510. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.504-510.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. J., McMeekin T. A. Spoilage of chicken skin at 2 degrees C: electron microscopic study. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):492–503. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.492-503.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




