Abstract
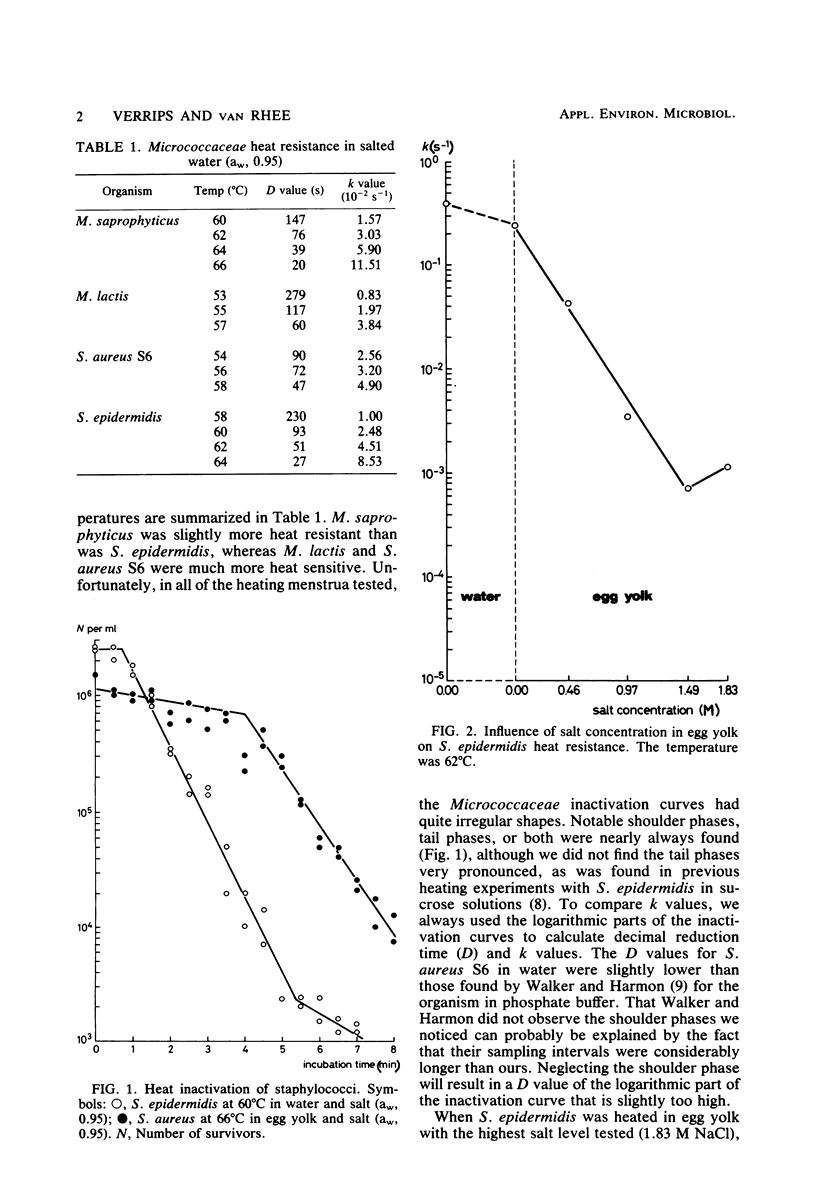
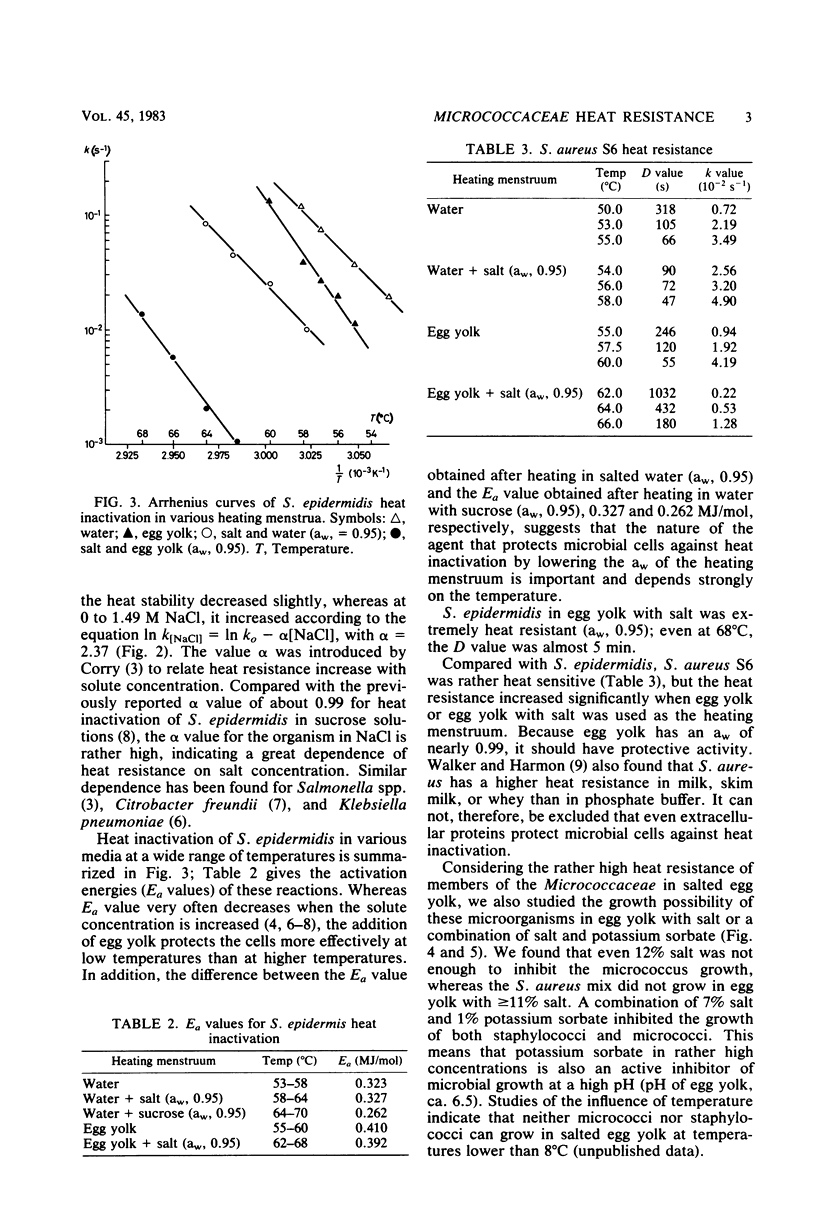
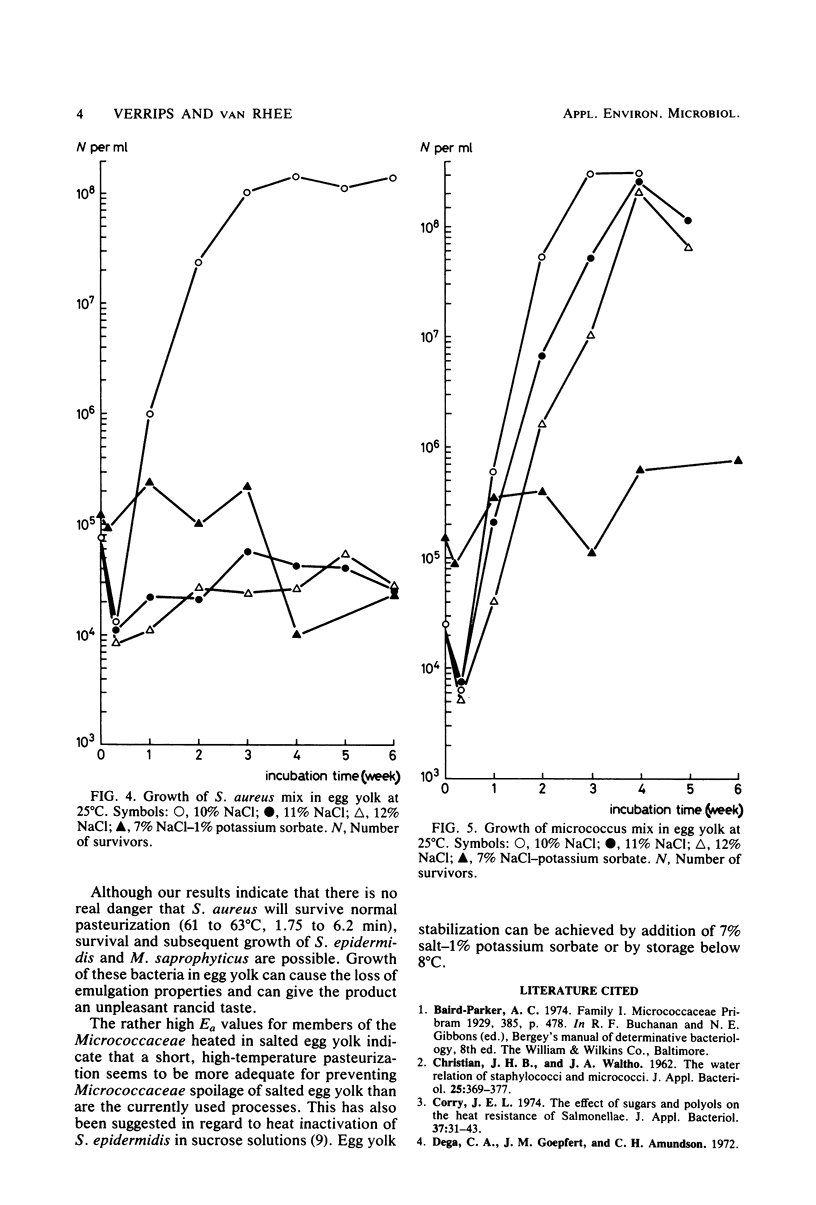
The heat resistance and growth possibilities of various members of the Micrococcaceae in egg yolk and egg yolk with added salt were determined. Egg yolk alone protected members of the Micrococcaceae considerably against heat. Whereas in water Staphylococcus aureus S6 had a decimal reduction time (D) value of 66 s at 55 degrees C, its D value in egg yolk at the same temperature was 246 s. In salted egg yolk (water activity, 0.95), S. aureus S6 had a D value of 180 s at 66 degrees C and was largely inactivated during the pasteurization processes currently applied. Micrococcus saprophyticus and S. epidermidis (D value of each under the same conditions, 390 s) could survive such treatments to a certain extent and can thus spoil commercial egg yolk.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corry J. E. The effect of sugars and polysols on the heat resistance of salmonellae. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;37(1):31–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dega C. A., Goepfert J. M., Amundson C. H. Heat resistance of salmonellae in concentrated milk. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):415–420. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.415-420.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrips C. T., Van Rhee R. Heat inactivation of staphylococcus epidermidis at various water activities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1128–1131. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1128-1131.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C., Harmon L. G. Thermal resistance of Staphylococcus aureus in milk, whey, and phosphate buffer. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):584–590. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.584-590.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


