Abstract
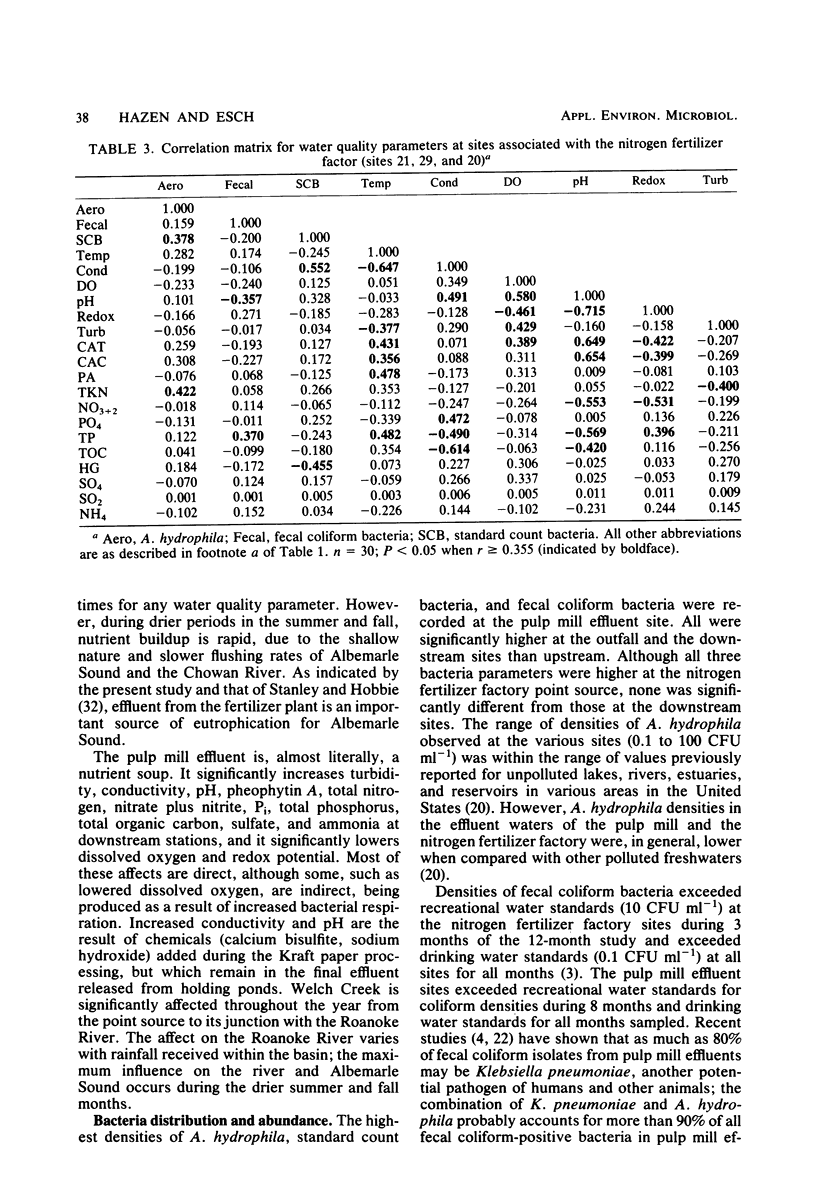
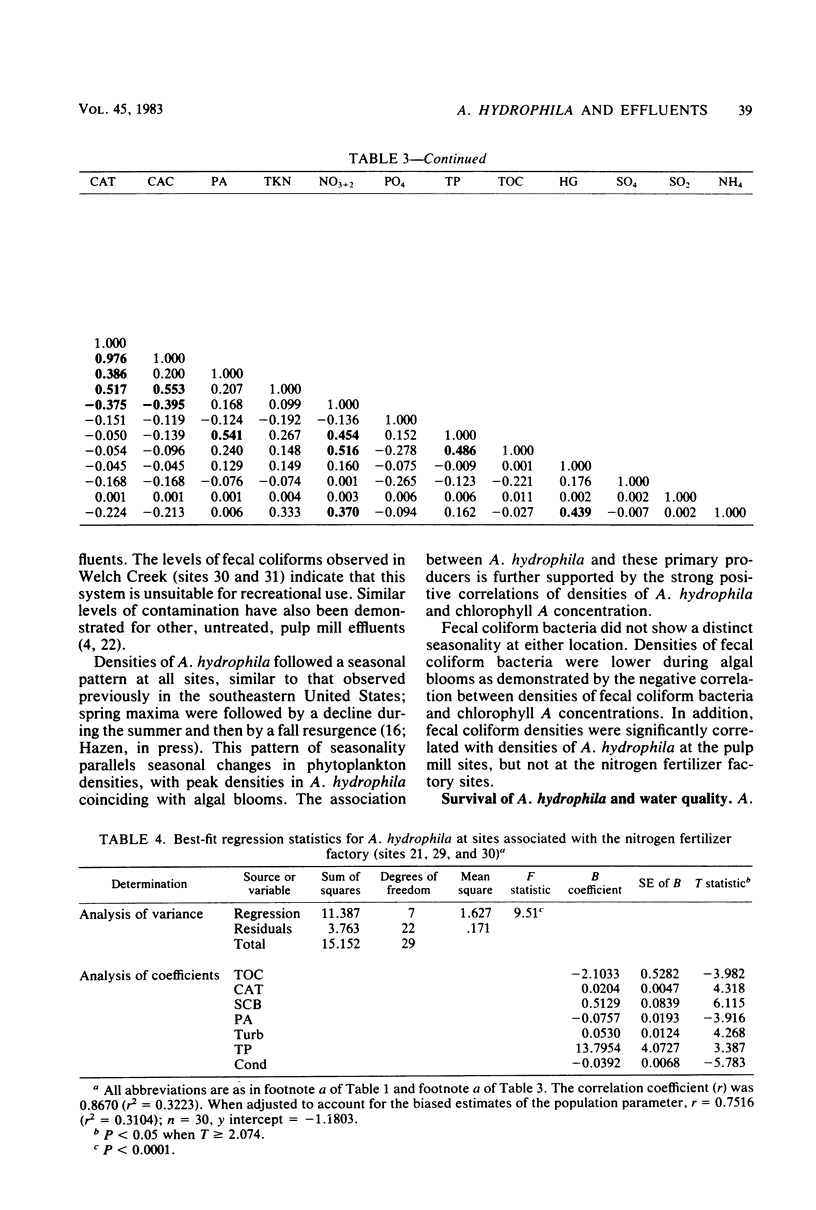
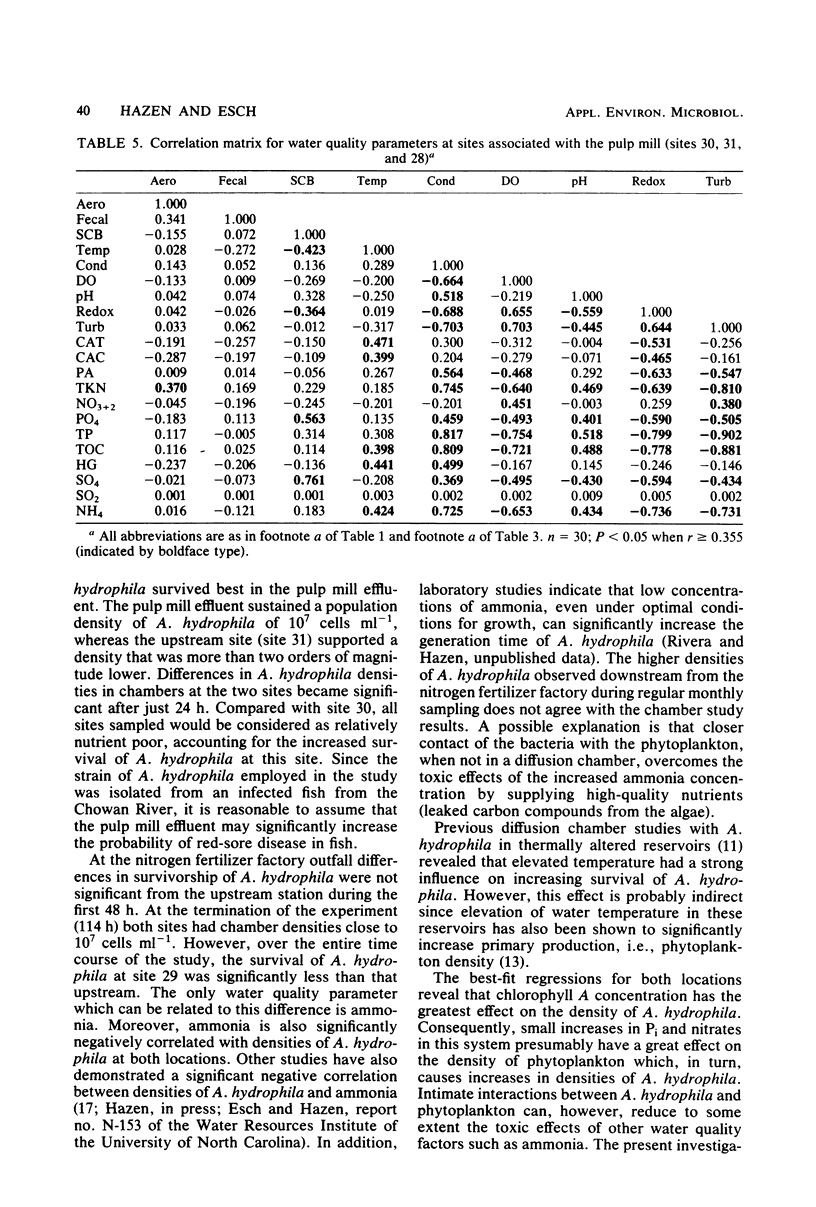
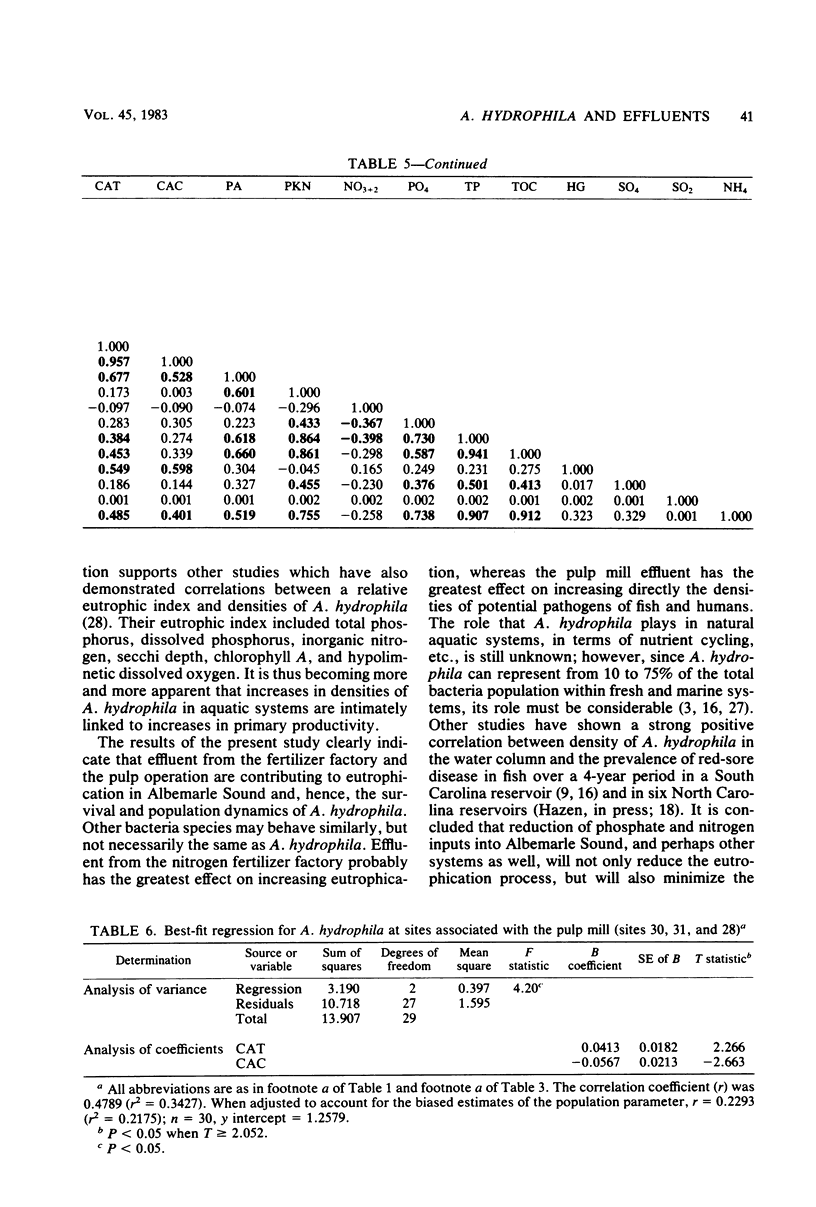
The density of Aeromonas hydrophila, standard count bacteria, fecal coliform bacteria, and 18 physical and chemical parameters were measured simultaneously at six sites for 12 months in Albemarle Sound, N.C. One site was above and two sites were below the discharge plume of a Kraft pulping process paper mill. The fourth site was above and the remaining two sites were below the discharge point of a nitrogen fertilizer factory. The impact of the pulp mill on water quality was acute, whereas that of the nitrogen fertilizer factory was chronic and much more subtle. Diffusion chamber studies indicated that A. hydrophila survival is increased by pulp mill effluent and decreased by nitrogen fertilizer factory effluent. From correlation and regression analysis, A. hydrophila was found to be directly affected by phytoplankton density and, thus, indirectly by concentrations of phosphate, nitrate, and total organic carbon. These two point sources are suspect as indirect causes of red-sore disease epizootics, a disease of fish caused by A. hydrophila.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caplenas N. R., Kanarek M. S., Dufour A. P. Source and extent of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the paper industry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):779–785. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.779-785.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. A., 2nd, Kane J. G., Garagusi V. F. Human aeromonas infections: a review of the literature and a case report of endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 May;57(3):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Gorden R. W., Hazen T. C., Esch G. W. Aeromonas distribution and survival in a thermally altered lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.114-122.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Hazen T. C. Immunofluorescence of Aeromonas hydrophila as measured by fluorescence photometric microscopy. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):161–168. doi: 10.1139/m80-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden R. W., Hazen T. C., Esch G. W., Fliermans C. B. Isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila from the American alligator, Alligator mississippiensis. J Wildl Dis. 1979 Apr;15(2):239–243. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-15.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabow W. O., du Preez M. Comparison of m-Endo LES, MacConkey, and Teepol media for membrane filtration counting of total coliform bacteria in water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Sep;38(3):351–358. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.3.351-358.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B. Distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in natural and man-made thermal effluents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):166–168. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.166-168.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B., Hirsch R. P., Esch G. W. Prevalence and distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):731–738. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.731-738.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Raker M. L., Esch G. W., Fliermans C. B. Ultrastruct of red-sore lesions on largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides): associattion of the ciliate Epistylis sp. and the bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila. J Protozool. 1978 Aug;25(3 Pt 2):351–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb03901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao C. F., Dawson R. N. Microbiology of two-stage kraft waste treatment. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1975 Oct;47(10):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus L. C. Infectious diseases of reptiles. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Dec 1;159(11):1626–1631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Survival of coliform bacteria in natural waters: field and laboratory studies with membrane-filter chambers. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):805–811. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.805-811.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peele E. R., Singleton F. L., Deming J. W., Cavari B., Colwell R. R. Effects of pharmaceutical wastes on microbial populations in surface waters at the puerto rico dump site in the atlantic ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):873–879. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.873-879.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Allen D. A., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W., Daily O. P. Isolation, enumeration, and characterization of Aeromonas from polluted waters encountered in diving operations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):1010–1018. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.1010-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Gaines J. L., Jr, Martin L., Prestwood A. K. Aeromonas-induced deaths among fish and reptiles in an eutrophic inland lake. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Sep 15;161(6):603–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Rimler R. Medium for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):550–553. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.550-553.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Chipman D. C. Clinical involvement of Aeromonas hydrophila. Can Med Assoc J. 1979 Apr 21;120(8):942–946. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlgemuth K., Pierce R. L., Kirkbride C. A. Bovine abortion associated with Aeromonas hydrophila. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Apr 1;160(7):1001–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



