Abstract
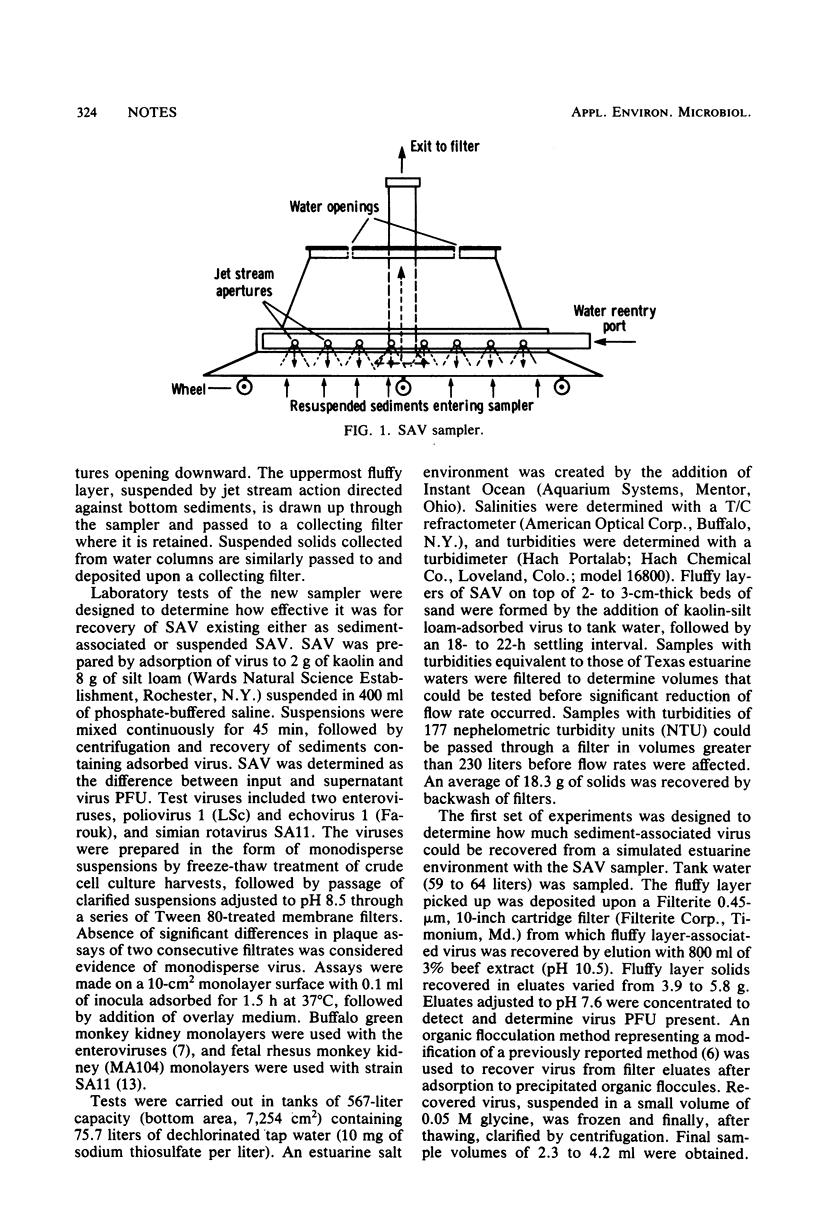
Laboratory trials of a new sampler for collection of estuarine sediment-associated virus resulted in a recovery effectiveness averaging 30% for two enteroviruses and rotavirus SA11. A minimal recovery potential of 54% was calculated when losses caused by virus concentration procedure inadequacies were excluded. Both sediment-associated and suspended solids-associated viruses were collected with the sampler. Recoveries of 61 and 60% poliovirus and rotavirus, respectively, were obtained from salt water-suspended, solids-associated virus. The unique advantage of the sampler for selective collection of virus-associated top layers of sediment, plus collection over extensive areas, resulted in recovery of more virus than was obtained with a commonly used dredge-type sampler.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron R. C., Murphy F. D., Greenberg H. B., Davis C. E., Bregman D. J., Gary G. W., Hughes J. M., Schonberger L. B. Norwalk gastrointestinal illness: an outbreak associated with swimming in a recreational lake and secondary person-to-person transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Feb;115(2):163–172. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. A., Lehmann J. D., Setiady I. F., Hatch M. H. An outbreak of hepatitis-A associated with recreational lake water. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Feb;99(2):145–154. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Flora S., De Renzi G. P., Badolati G. Detection of animal viruses in coastal seawater and sediments. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):472–475. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.472-475.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Smith E. M., Melnick J. L. Development of a quantitative method for detecting enteroviruses in estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):158–163. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.158-163.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. M., Grohmann G. S., Christopher P. J., Lopez W. A., Davey G. R., Millsom R. H. An Australia-wide outbreak of gastroenteritis from oysters caused by Norwalk virus. Med J Aust. 1979 Oct 6;2(7):329–333. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1979.tb104133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy B. L., Mackowiak P. A., Caraway C. T., Walker J. A., McKinley T. W., Klein C. A., Jr Oyster-associated hepatitis. Failure of shellfish certification programs to prevent outbreaks. JAMA. 1975 Sep 8;233(10):1065–1068. doi: 10.1001/jama.233.10.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROOS B. Hepatitepidemi, spridd genom ostron. Sven Lakartidn. 1956 Apr 20;53(16):989–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub S. A., Sagik B. P. Association of enteroviruses with natural and artificially introduced colloidal solids in water and infectivity of solids-associated virions. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):212–222. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.212-222.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Gerba C. P. A plaque assay for the simian rotavirus SAII. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):513–519. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Gerba C. P., Melnick J. L. Role of sediment in the persistence of enteroviruses in the estuarine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Apr;35(4):685–689. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.4.685-689.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Lewis A. L., Mountain C. W. Demonstration of solids-associated virus in wastewater and sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):354–358. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.354-358.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


