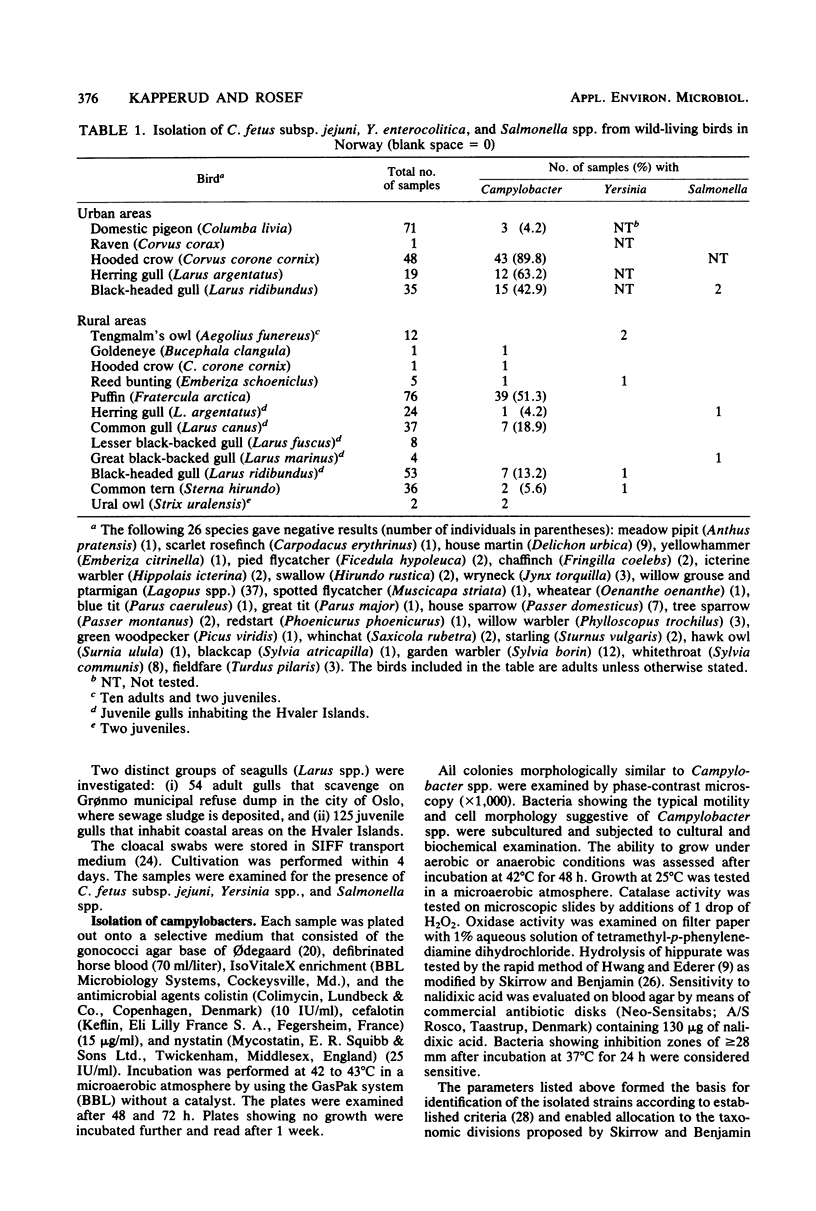
Abstract
Cloacal swabs from 540 wild-living birds were cultured for Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni, Yersinia spp., and Salmonella spp. The carrier rates detected were as follows: C. fetus subsp. jejuni, 28.4%; Yersinia spp., 1.2%; and Salmonella spp., 0.8%. All birds were apparently healthy when captured. C. fetus subsp. jejuni was isolated from 11 of the 40 bird species examined. Among birds inhabiting the city of Oslo, the highest isolation rate was found in crows (Corvus corone cornix) (89.8%), followed by gulls (Larus spp.) (50.0%) and domestic pigeons (Columba livia domesticus) (4.2%). The gulls and crows scavenge on refuse dumps. High carrier rates were also detected among the following birds from nonurban, coastal areas: puffin (Fratercula arctica) (51.3%), common tern (Sterna hirundo) (5.6%), common gull (Larus canus) (18.9%), black-headed gull (Larus ridibundus) (13.2%), and herring gull (Larus argentatus) (4.2%). The list of species harboring C. fetus subsp. jejuni also includes the Ural owl (Strix uralensis), goldeneye (Bucephala clangula), and reed bunting (Emberiza schoeniclus). The following five Yersinia strains were isolated: Y. kristensenii (two strains), Y. intermedia (two strains), and "Yersinia X2" (one strain). Four strains belonging to the genus Salmonella were isolated from three different species of gulls. These isolates were identified as S. typhimurium, S. indiana, and S. djugu. The results indicate that campylobacters are a normal component of the intestinal flora in several bird species, whereas Salmonella and Yersinia carriers are more sporadic.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottone E. J., Robin T. Prevalence of unique Yersinia enterocolitica in the area of the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, N.Y. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Jevring J. Infektion med Salmonella typhi-murium hos vilda småfåglar i Sverige. Nord Vet Med. 1974 Jun;26(6):392–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUHLIN I., ERICSON C. A new medium for the bacteriologic examination of stools (LSU-agar). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1961;52:185–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1961.tb03192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G. Enterotoxin production at 4 degrees, 22 degrees, and 37 degrees C and Y. enterocolitica-like bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Jun;90(3):185–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G. Survey on the reservoirs of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia enterocolitica-like bacteria in Scandinavia. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Feb;89(1):29–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00148_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G. Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia like microbes isolated from mammals and water in Norway and Denmark. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Apr;85(2):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luechtefeld N. A., Blaser M. J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from migratory waterfowl. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):406–408. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.406-408.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzing L. O. Waterborne outbreaks of campylobacter enteritis in central Sweden. Lancet. 1981 Aug 15;2(8242):352–354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90658-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollaret H. H., Bercovier H., Alonso J. M. Summary of the data received at the WHO Reference Center for Yersinia enterocolitica. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:174–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosef O. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from the gallbladder of normal slaughter pigs, using an enrichment procedure. Acta Vet Scand. 1981;22(1):149–151. doi: 10.1186/BF03547219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosef O., Yndestad M. Some characteristics of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni isolated from pigs, birds and man. Acta Vet Scand. 1982;23(1):9–15. doi: 10.1186/BF03546816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandven P., Solberg O., Odegaard K., Myhre G. Improved medium for the transportation of gonococcal specimens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Feb;90(1):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. '1001' Campylobacters: cultural characteristics of intestinal campylobacters from man and animals. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Dec;85(3):427–442. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smibert R. M. The genus Campylobacter. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:673–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smibert R. M. Vibrio fetus var. intestinalis isolated from the intestinal content of birds. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Aug;30(8):1437–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



